
Chemistry
12th Edition
ISBN: 9780078021510
Author: Raymond Chang Dr., Kenneth Goldsby Professor
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 23.1, Problem 1RC
Identify the following
Table 7.3 The Ground-State Electron Configurations of the Elements*
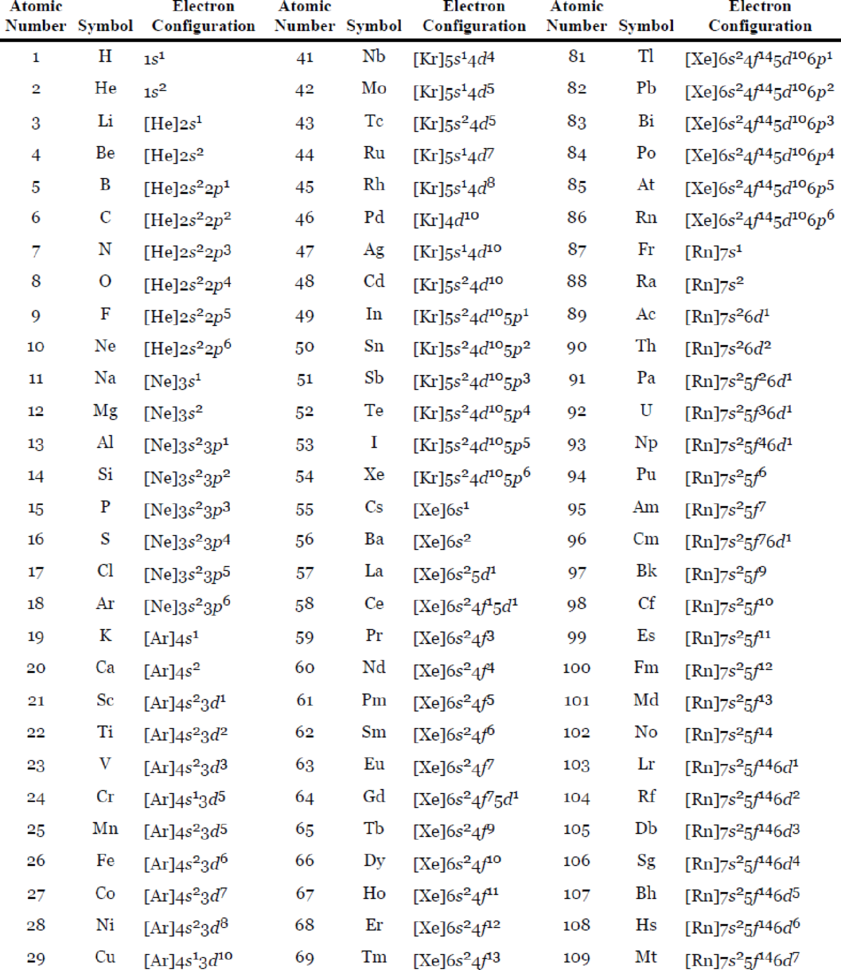
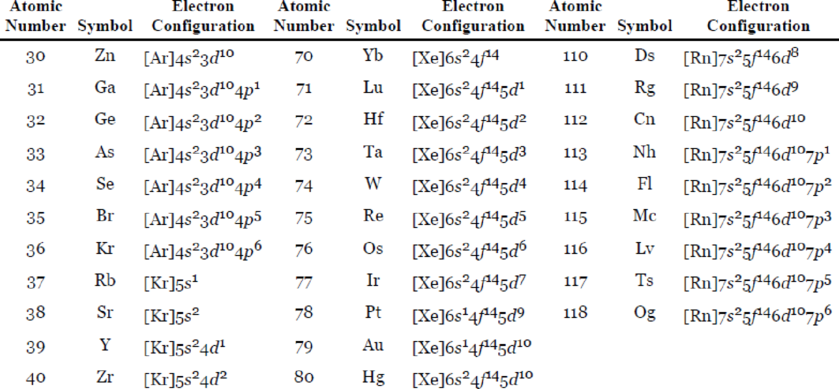
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
The Concept of Aromaticity
21.15 State the number of 2p orbital electrons in each molecule or ion.
(a)
(b)
(e)
(f)
(c)
(d)
(h)
(i)
DA
(k)
21.16 Which of the molecules and ions given in Problem 21.15 are aromatic according to the
Hückel criteria? Which, if planar, would be antiaromatic?
21.17 Which of the following structures are considered aromatic according to the Hückel
criteria?
---0-0
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
(h)
H
-H
.8.0-
21.18 Which of the molecules and ions from Problem 21.17 have electrons donated by a
heteroatom?
1. Show the steps necessary to make 2-methyl-4-nonene using a
Wittig reaction. Start with triphenylphosphine and an alkyl
halide. After that you may use any other organic or inorganic
reagents.
2. Write in the product of this reaction:
CH3
CH₂
(C6H5)₂CuLi
H₂O+
3. Name this compound properly, including stereochemistry.
H₂C
H3C
CH3
OH
4. Show the step(s) necessary to transform the compound on the
left into the acid on the right.
Bri
CH2
5. Write in the product of this
LiAlH4
Br
H₂C
OH
Chapter 23 Solutions
Chemistry
Ch. 23.1 - Identify the following transition metal atoms and...Ch. 23.3 - What is the difference between these two...Ch. 23.3 - Write the oxidation numbers of the metals in the...Ch. 23.3 - Prob. 2PECh. 23.3 - Prob. 3PECh. 23.3 - Prob. 2RCCh. 23.4 - Prob. 1RCCh. 23.5 - Prob. 4PECh. 23.5 - Prob. 1RCCh. 23 - What distinguishes a transition metal from a...
Ch. 23 - Why is zinc not considered a transition metal?Ch. 23 - Explain why atomic radii decrease very gradually...Ch. 23 - Without referring to the text, write the...Ch. 23 - Write the electron configurations of the following...Ch. 23 - Why do transition metals have more oxidation...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.7QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.8QPCh. 23 - Define the following terms: coordination compound,...Ch. 23 - Describe the interaction between a donor atom and...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.11QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.12QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.13QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.14QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.15QPCh. 23 - What are the systematic names for the following...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.17QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.18QPCh. 23 - Define the following terms: stereoisomers,...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.20QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.21QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.22QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.23QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.24QPCh. 23 - Draw structures of all the geometric and optical...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.26QPCh. 23 - Briefly describe crystal field theory.Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.28QPCh. 23 - What is the origin of color in a coordination...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.30QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.31QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.32QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.33QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.34QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.35QPCh. 23 - The absorption maximum for the complex ion...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.37QPCh. 23 - A solution made by dissolving 0.875 g of...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.39QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.40QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.41QPCh. 23 - The [Fe(CN)6]3 complex is more labile than the...Ch. 23 - Aqueous copper(II) sulfate solution is blue in...Ch. 23 - When aqueous potassium cyanide is added to a...Ch. 23 - A concentrated aqueous copper(II) chloride...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.46QPCh. 23 - As we read across the first-row transition metals...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.48QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.49QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.50QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.51QPCh. 23 - Chemical analysis shows that hemoglobin contains...Ch. 23 - Explain the following facts: (a) Copper and iron...Ch. 23 - A student in 1895 prepared three coordination...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.55QPCh. 23 - From the standard reduction potentials listed in...Ch. 23 - Using the standard reduction potentials listed in...Ch. 23 - The Co2+-porphyrin complex is more stable than the...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.59QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.60QPCh. 23 - Hydrated Mn2+ ions are practically colorless (see...Ch. 23 - Which of the following hydrated cations are...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.63QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.64QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.65QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.66QPCh. 23 - The compound 1,1,1-trifluoroacetylacetone (tfa) is...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.68QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.69QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.70QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.71QPCh. 23 - Commercial silver-plating operations frequently...Ch. 23 - Draw qualitative diagrams for the crystal field...Ch. 23 - (a) The free Cu(I) ion is unstable in solution and...Ch. 23 - Prob. 23.75QPCh. 23 - Prob. 23.76QP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What are the major products of the following reaction? Please provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the reaction proceeds.arrow_forwardWhat are the major products of the following enolate alkylation reaction? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing as to how the reaction proceeds.arrow_forwardA block of zinc has an initial temperature of 94.2 degrees celcius and is immererd in 105 g of water at 21.90 degrees celcius. At thermal equilibrium, the final temperature is 25.20 degrees celcius. What is the mass of the zinc block? Cs(Zn) = 0.390 J/gxdegrees celcius Cs(H2O) = 4.18 J/gx degrees celcusarrow_forward
- Potential Energy (kJ) 1. Consider these three reactions as the elementary steps in the mechanism for a chemical reaction. AH = -950 kJ AH = 575 kJ (i) Cl₂ (g) + Pt (s) 2C1 (g) + Pt (s) Ea = 1550 kJ (ii) Cl (g)+ CO (g) + Pt (s) → CICO (g) + Pt (s) (iii) Cl (g) + CICO (g) → Cl₂CO (g) Ea = 2240 kJ Ea = 2350 kJ AH = -825 kJ 2600 2400 2200 2000 1800 1600 1400 1200 1000 a. Draw the potential energy diagram for the reaction. Label the data points for clarity. The potential energy of the reactants is 600 kJ 800 600 400 200 0 -200- -400 -600- -800- Reaction Progressarrow_forwardCan u help me figure out the reaction mechanisms for these, idk where to even startarrow_forwardHi, I need your help with the drawing, please. I have attached the question along with my lab instructions. Please use the reaction from the lab only, as we are not allowed to use outside sources. Thank you!arrow_forward
- Hi, I need your help i dont know which one to draw please. I’ve attached the question along with my lab instructions. Please use the reaction from the lab only, as we are not allowed to use outside sources. Thank you!arrow_forward5. Write the formation reaction of the following complex compounds from the following reactants: 6. AgNO₃ + K₂CrO₂ + NH₄OH → 7. HgNO₃ + excess KI → 8. Al(NO₃)₃ + excess NaOH →arrow_forwardIndicate whether the product formed in the reaction exhibits tautomerism. If so, draw the structure of the tautomers. CO₂C2H5 + CH3-NH-NH,arrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this reaction N-(cyclohex-1-en-1-yl)-1-(pyrrolidino) reacts with CH2=CHCHO, heat, H3O+arrow_forwardDraw the starting material that would be needed to make this product through an intramolecular Dieckmann reactionarrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Nitropropane reacts + pent-3-en-2-one reacts with NaOCH2CH3, CH3CHOHarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to Coordination ComplexesWave Function for Hydrogen atom # All Vital Topics # Quantum Mechanics part -21; Author: Priyanka Jain;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GKgNV9dmUHo;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry || The d & f Block Elements Part 1 || Full Chapter || By Shiksha House; Author: Best for NEET;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LzZWHSdYaxw;License: Standard Youtube License