
Subpart (a):
Long run equilibrium in AD-AS model.
Subpart (a):
Explanation of Solution
The supply depends upon the
The
The equilibrium is a condition where the aggregate demand curve of the economy intersects with the aggregate supply curve of the economy. Then there will be an equilibrium point derived where the economy will be in its equilibrium without any excess demand or supply. The quantity on the X axis will represent the
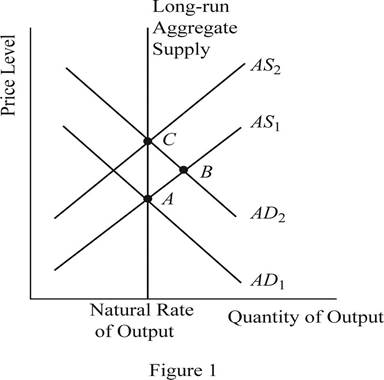
Concept introduction:
Aggregate demand curve: It is the curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the quantity of real GDP demanded by the economic agents such as the households, firms as well as the government.
Equilibrium: The equilibrium in the economy is the point where the economy's aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersects with each other. There will be no excess demand or
Subpart (b):
Long run equilibrium in AD-AS model.
Subpart (b):
Explanation of Solution
When the money supply of the economy increases with the intervention of the Central Bank of the economy, the money with the public will increase. When the money with the public increases, they will feel wealthier and as a result they will demand more consumer goods and services. As a result, the aggregate demand of the economy increases and it will shift the AD curve towards the right. This can be identified as the change to the equilibrium point B as shown in Figure 1. Thus, in short, the increase in the money supply leads to the increase in the output and price level of the economy.
Concept introduction:
Aggregate demand curve: It is the curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the quantity of real GDP demanded by the economic agents such as the households, firms as well as the government.
Aggregate supply curve: In the short run, it is a curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the supply in the economy by the firms. In the long run, it shows the relationship between the price level and the level of quantity supplied by the firms.
Equilibrium: The equilibrium in the economy is the point where the economy's aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersects with each other. There will be no excess demand or excess supply in the economy at the equilibrium.
Subpart (c):
Long run equilibrium in AD-AS model.
Subpart (c):
Explanation of Solution
When the AD curve shifts towards the right and increases the output and the price level in the short run, over time, the nominal wages, prices as well as the perceptions and expectations of the economy would adjust to the new equilibrium level. As a result of this gradual adjustment, the cost of production will increase and the result will be a leftward shift in the aggregate supply curve of the economy. Then the economy will return to its natural level of output at a higher price level of the economy. This can be identified as the movement from point B to point C in the graph shown above.
Concept introduction:
Aggregate demand curve: It is the curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the quantity of real GDP demanded by the economic agents such as the households, firms as well as the government.
Aggregate supply curve: In the short run, it is a curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the supply in the economy by the firms. In the long run, it shows the relationship between the price level and the level of quantity supplied by the firms.
Equilibrium: The equilibrium in the economy is the point where the economy's aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersects with each other. There will be no excess demand or excess supply in the economy at the equilibrium.
Subpart (d):
Long run equilibrium in AD-AS model.
Subpart (d):
Explanation of Solution
The sticky wages theory suggests that when there is inflation in the economy, the wage rate will adjust very slowly to the inflation. More or less the wage rates will be sticky and the main reason will be the long term contracts between the employer and the employees. Thus, in the short run equilibriums such as point A and point B, the wages of the economy would be more or less equal to each other. Whereas the point C represents the long run equilibrium and thus, the wages at the point C will be higher than that in point A and B.
Concept introduction:
Aggregate demand curve: It is the curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the quantity of real GDP demanded by the economic agents such as the households, firms as well as the government.
Aggregate supply curve: In the short run, it is a curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the supply in the economy by the firms. In the long run, it shows the relationship between the price level and the level of quantity supplied by the firms.
Equilibrium: The equilibrium in the economy is the point where the economy's aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersects with each other. There will be no excess demand or excess supply in the economy at the equilibrium.
Subpart (e):
Long run equilibrium in AD-AS model.
Subpart (e):
Explanation of Solution
The sticky wages theory suggests that when there is inflation in the economy, the wage rate will adjust very slowly to the inflation. More or less, the wage rates will be sticky and the main reason will be the long term contracts between the employer and the employees. So, the nominal wages at equilibrium point A and B will be same. But the increase in the general price level in the economy would reduce the real wages of the workers because, the real wage is the nominal wage divided by the price level. When the denominator increases, it will reduce the value of the real wages in the economy.
Concept introduction:
Aggregate demand curve: It is the curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the quantity of real GDP demanded by the economic agents such as the households, firms as well as the government.
Aggregate supply curve: In the short run, it is a curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the supply in the economy by the firms. In the long run, it shows the relationship between the price level and the level of quantity supplied by the firms.
Equilibrium: The equilibrium in the economy is the point where the economy's aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersects with each other. There will be no excess demand or excess supply in the economy at the equilibrium.
Sub part (f):
Long run equilibrium in AD-AS model.
Sub part (f):
Explanation of Solution
When the increase in the money supply happens in the economy, it will lead to the increase in the nominal wages as well as the price level in the economy in the long run. As a result of the increase in the nominal wage rate along with the price level in the economy, the real wage rate of the economy would remain unchanged. Thus, the neutrality of money applies in the long run equilibrium.
Concept introduction:
Aggregate demand curve: It is the curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the quantity of real GDP demanded by the economic agents such as the households, firms as well as the government.
Aggregate supply curve: In the short run, it is a curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the supply in the economy by the firms. In the long run, it shows the relationship between the price level and the level of quantity supplied by the firms.
Equilibrium: The equilibrium in the economy is the point where the economy's aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersects with each other. There will be no excess demand or excess supply in the economy at the equilibrium.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Bundle: Essentials Of Economics, Loose-leaf Version, 8th + Lms Integrated Mindtap Economics, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
- 1. The current price for a barrel of oil is $28. Assume the marginal extraction cost per barrel is $8 and the interest rate is 4 percent per year. a. According to the standard Hotelling model for a nonrenewable resource, what is the forecasted price for next year? b. How would your forecast change (qualitatively) if the demand for oil increased before next year?arrow_forward• What are the 5 positive and 5 negative attitudes a salesperson has? What are the best way to improve those negative attitudes? • What is the another concise definition of Salesmanship? • As a Watson's salesperson in the Philippines what are they're: - earning opportunities? - chances of promotion and career growth? - rewards and awards? - incentives and fringe benefits? - employment requirements?arrow_forwardWhere in the Victoria, BC is the most logging occurring? Include relative and absolute locationsarrow_forward
- In Foresty , What do most clear cut locations have in common with each other? Do they occur along the shorelines of lakes and rivers? Near major highways? Are they near cities or far from people?arrow_forwardHow sustainable is the forestry industry in BC in your opinion? Not at all, somewhat, very and explain your reasoning.arrow_forwardIn a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. 6.Draw a standard Commercial Bank Balance Sheet and briefly explain each of the main components.arrow_forward
- C1 The following model can be used to study whether campaign expenditures affect election outcomes: voteA = 0 + B₁ log(expendA) + ẞ₂ log(expendB) + ẞ3 prtystrA + u, where voteA is the percentage of the vote received by Candidate A, expendA and expend are campaign expenditures by Candidates A and B, and prtystrA is a measure of party strength for Candidate A (the percentage of the most recent presidential vote that went to A's party). == (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) What is the interpretation of B₁? In terms of the parameters, state the null hypothesis that a 1% increase in A's expenditures is offset by a 1% increase in B's expenditures. Estimate the given model using the data in VOTE1.DTA and report the results in usual form. Do A's expenditures affect the outcome? What about B's expenditures? Can you use these results to test the hypothesis in part (ii)? Estimate a model that directly gives the t statistic for testing the hypothesis in part (ii). What do you conclude? (Use a two-sided…arrow_forwardIn a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. 10. What is Tinbergen’s constraint? Explain its importance in regard to US monetary policy.arrow_forwardIn a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. 8. How does monetary policy supposedly translate into changes in AD?arrow_forward
- In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. 2. Carefully explain either Keynes’ “cookie jar” motive for holding money or the “saw-toothed model’s” motive for holding a safety stock.arrow_forwardIn a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. 7.Carefully explain the Fisher equation for interest rates. What insight does it provide?arrow_forwardIn a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. 3. Describe the general architecture of the Federal Reserve System.arrow_forward
 Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781285165912Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781285165912Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305971509Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305971509Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning





