
College Physics (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780321902788
Author: Hugh D. Young, Philip W. Adams, Raymond Joseph Chastain
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
thumb_up100%
Chapter 23, Problem 25P
Two plane mirrors intersect at right angles. A laser beam strikes the first of them at a point 11.5 cm from their point of intersection, as shown in Figure 23.47. For what angle of incidence at the first mirror will this ray strike the midpoint of the second mirror (which is 28.0 cm long) after reflecting from the first mirror?
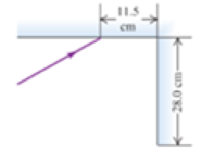
Figure 23.47
Problem 25.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A light ray travels from air (n=1.00) into a crown glass (n=1.52) with an angle of incidence of 49 degrees. The light ray continues to travel through the crown glass material into the diamond (n=2.42). At what angle does the light ray make with the normal line as it enters the diamond?
Two plane mirrors are facing each other. They are parallel, 3.00
cm apart, and 17.0 cm in length, as the drawing indicates. A
laser beam is directed at the top mirror from the left edge of
the bottom mirror. What is the smallest angle of incidence with
respect to the top mirror, such that the laser beam (a) hits only
one of the mirrors and (b) hits each mirror only once?
Laser
(a) Number
(b) Number
i
17.0 cm
Units
Units
마음이
3.00 cm
>
A ray of light hits the surface between air and an unknown material at an angle A of 46.8°. The index of refraction of the material is 1.287. What is the angle of refraction?
Chapter 23 Solutions
College Physics (10th Edition)
Ch. 23 - Prob. 1CQCh. 23 - Why is the average radiation pressure on a...Ch. 23 - Prob. 3CQCh. 23 - How does the refraction of light account for the...Ch. 23 - Light requires about 8 min to travel from the sun...Ch. 23 - Prob. 6CQCh. 23 - A student claimed that, because of atmospheric...Ch. 23 - If you look at your pet fish through the corner of...Ch. 23 - How could you determine the direction of the...Ch. 23 - In three-dimensional movies, two images are...
Ch. 23 - Prob. 11CQCh. 23 - When light is incident on an interface between two...Ch. 23 - A ray is traveling in material a when it reaches...Ch. 23 - Unpolarized light with an original intensity I0...Ch. 23 - Prob. 3MCPCh. 23 - If a sinusoidal electromagnetic wave with...Ch. 23 - A plane electromagnetic wave is traveling...Ch. 23 - A ray of light going from one material into...Ch. 23 - Which of the following statements about radio...Ch. 23 - Two lasers each produce 2 mW beams. The beam of...Ch. 23 - A ray of light follows the path shown in Figure...Ch. 23 - A light beam has a wavelength of 300 nm in a...Ch. 23 - Prob. 11MCPCh. 23 - Prob. 12MCPCh. 23 - When a solar flare erupts on the surface of the...Ch. 23 - The microprocessor in a modern laptop computer...Ch. 23 - (a) How much time does it take light to travel...Ch. 23 - A geostationary communications satellite orbits...Ch. 23 - Prob. 5PCh. 23 - Prob. 6PCh. 23 - Prob. 7PCh. 23 - Prob. 8PCh. 23 - Visible light. The wavelength of visible light...Ch. 23 - Prob. 10PCh. 23 - Medical x rays. Medical x rays are taken with...Ch. 23 - Prob. 12PCh. 23 - Prob. 13PCh. 23 - Prob. 14PCh. 23 - Prob. 15PCh. 23 - Laboratory lasers. HeNe lasers are often used in...Ch. 23 - Prob. 17PCh. 23 - High-energy cancer treatment. Scientists are...Ch. 23 - Prob. 19PCh. 23 - The intensity at a certain distance from a bright...Ch. 23 - A sinusoidal electromagnetic wave from a radio...Ch. 23 - Prob. 22PCh. 23 - Prob. 23PCh. 23 - A sinusoidal electromagnetic wave emitted by a...Ch. 23 - Two plane mirrors intersect at right angles. A...Ch. 23 - Two plane mirrors A and 8 intersect at a 45 angle....Ch. 23 - Prove that when a ray of light travels at any...Ch. 23 - A light beam travels at 1.94 108 m/s in quartz....Ch. 23 - Prob. 29PCh. 23 - Light with a frequency of 5.80 1014 Hz travels in...Ch. 23 - Prob. 31PCh. 23 - Light inside the eye. The vitreous humor, a...Ch. 23 - Prob. 33PCh. 23 - A 1 55-m-tall fisherman stands at the edge of a...Ch. 23 - A light ray passes through a rectangular slab of...Ch. 23 - A glass plate having parallel faces and a...Ch. 23 - A beam of light in air makes an angle of 47.5 with...Ch. 23 - Reversibility of rays. Ray 1 of light in medium a...Ch. 23 - You (height of your eyes above the water. 1.75 m)...Ch. 23 - A parallel-sided plate of glass having a...Ch. 23 - As shown in Figure 23.53, a layer of water covers...Ch. 23 - A ray of light in diamond (index of refraction...Ch. 23 - The critical angle for total internal reflection...Ch. 23 - A ray of light is traveling in a glass cube that...Ch. 23 - Light is incident along the normal to face AB of a...Ch. 23 - Light pipe. Light enters a solid tube made of...Ch. 23 - Prob. 47PCh. 23 - A beam of light strikes a sheet of glass at an...Ch. 23 - The table gives the index of refraction of fused...Ch. 23 - Use the graph in Figure 23.29 for silicate flint...Ch. 23 - The indices of refraction for violet light ( = 400...Ch. 23 - Unpolarized light with intensity I0 is incident on...Ch. 23 - Unpolarized light is incident on two ideal...Ch. 23 - A beam of unpolarized light of intensity I0 passes...Ch. 23 - Three ideal polarizing filters are stacked, with...Ch. 23 - Light of original intensity I0 passes through two...Ch. 23 - The polarizing angle for light in air incident on...Ch. 23 - A beam of polarized light passes through a...Ch. 23 - A beam of unpolarized light in air is incident at...Ch. 23 - Plane-polarized light passes through two...Ch. 23 - The energy flow to the earth from sunlight is...Ch. 23 - Prob. 62GPCh. 23 - A powerful searchlight shines on a man. The mans...Ch. 23 - Prob. 64GPCh. 23 - Prob. 65GPCh. 23 - Prob. 66GPCh. 23 - Solar sail. NASA is doing research on the concept...Ch. 23 - A thick layer of oil is floating on the surface of...Ch. 23 - Prob. 69GPCh. 23 - A light ray in air strikes the right-angle prism...Ch. 23 - A ray of light is incident in air on a block of a...Ch. 23 - A light beam is directed parallel to the axis of a...Ch. 23 - Heart sonogram. Physicians use high-frequency (f =...Ch. 23 - A light ray refracts through a glass block having...Ch. 23 - A beaker with a mirrored bottom is filled with a...Ch. 23 - A ray of light traveling in a block of glass (n =...Ch. 23 - In a physics lab, light with wavelength 490 nm...Ch. 23 - The refractive index of a certain glass is 1.66....Ch. 23 - A thin layer of ice (n = 1.309) floats on the...Ch. 23 - Optical activity of biological molecules. Many...Ch. 23 - Passage Problems Safe exposure to electromagnetic...Ch. 23 - Doubling the frequency of a wave in the range of...Ch. 23 - The ICNIRP also has guidelines for magnetic-field...Ch. 23 - First, light with a plane of polarization at 45 to...Ch. 23 - Prob. 85PPCh. 23 - To vary the angle as well as the intensity of...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. Which describes our understanding of f...
The Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals (2nd Edition)
For motion 1, draw vector in region II of the enlargement that represent the momentum of the ball at the top of...
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
3. What is free-fall, and why does it make you weightless? Briefly describe why astronauts are weightless in th...
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
7.11 •• You are testing a new amusement park roller coaster with an empty car of mass 120 kg. One part of the t...
University Physics (14th Edition)
36. The basic unit of mass is _______.
Applied Physics (11th Edition)
13. The hand in FIGURE Q7.13 is pushing on the back of block A. Blocks A and B, with mB > mA, are connected by ...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics (4th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The disk of the Sun subtends an angle of 0.533 at the Earth. What are (a) the position and (b) the diameter of the solar image formed by a concave spherical mirror with a radius of curvature of magnitude 3.00 m?arrow_forwardThe index of refraction for water is about 43. What happens as a beam of light travels from air into water? (a) Its speed increases to 43c, and its frequency decreases. (b) Its speed decreases to 34c, and its wavelength decreases by a factor of 34. (c) Its speed decreases to 34c, and its wavelength increases by a factor of 43. (d) Its speed and frequency remain the same. (e) Its speed decreases to 34c, and its frequency increases.arrow_forwardA layer of oil (n=1.45) floats on an unknown liquid. A ray of light originates in the oil and passes into the unknown liquid. The angle of incidence is 64∘, and the angle of refraction is 53∘. What is the index of refraction of the unknown liquid?arrow_forward
- A mirror hangs 1.60 m above the floor on a vertical wall. A ray of sunlight, reflected off the mirror, forms a spot on the floor 1.14 m from the wall. Later in the day, the spot has moved to a point 2.50 m from the wall. (a) What is the change in the angle of elevation of the Sun, between the two observations? °(b) What time of day were these observations made? morning or afternoonarrow_forwardIn an experiment designed to measure the speed of light, a laser is aimed at a mirror that is 50.0 km due north. A detector is placed 117 m due east of the laser. The mirror is to be aligned so that light from the laser reflects into the detector. (a) When properly aligned, what angle should the normal to the surface of the mirror make with due south? (b) Suppose the mirror is misaligned, so that the actual angle between the normal to the surface and due south is too large by 0.0048. By how many meters (due east) will the reflected ray miss the detector?arrow_forwardTwo plane mirrors are facing each other. They are parallel, 3.00 cm apart, and 17.0 cm in length, as the drawing indicates. A laser beam is directed at the top mirror from the left edge of the bottom mirror. What is the smallest angle of incidence with respect to the top mirror, such that the laser beam (a) hits only one of the mirrors and (b) hits each mirror only once? (a) Number (b) Number i Laser Units Units 17.0 cm 3.00 cmarrow_forward
- Walking by a lake, you notice that a light ray from the sun reflects from the lake surface back to you. If the angle of incidence is 24°, what is the angle between the reflected ray and the incident ray at the water surface?arrow_forwardThe following figure shows a ray of light entering one end of an optical fiber at an angle of incidence θi = 49.5°. The index of refraction of the fiber is 2.04. Find the angle θ the ray makes with the normal when it reaches the curved surface of the fiber.arrow_forwardThe drawing shows a laser beam shining on a plane mirror that is perpendicular to the floor. The angle of incidence is 33.0°. The beam emerges from the laser at a point that is 1.10 m from the mirror and 1.80 m above the floor. After reflection, how far from the base of the mirror does the beam strike the floor?arrow_forward
- Why is the following situation impossible? The perpendicular distance of a lightbulb from a large plane mirror is twice the perpendicular distance of a person from the mirror. Light from the lightbulb reaches the person by two paths: (1) it travels to the mirror and reflects from the mirror to the person,and (2) it travels directly to the person without reflecting off the mirror. The total distance traveled by the light in the first case is 3.10 times the distance traveled by the light in the second case.arrow_forwardTwo light rays, originating from the same point, have an angle of 35.0° between them and reflect off a plane mirror. Determine the angle between the reflected rays.arrow_forwardAs shown in the figure, a ray of light strikes a plane mirror with some incident angle. The mirror is now rotated by an angle of ? = 19.0° about an axis through the point where N1 contacts the mirror, without altering the incident ray. The new position is shown by the line M2. (a) Determine the angle through which the reflected ray rotates if the incident angle is 40.0°.° (b) Determine the angle through which the reflected ray rotates if the incident angle is 50.0°.°arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
What Are Electromagnetic Wave Properties? | Physics in Motion; Author: GPB Education;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ftyxZBxBexI;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY