
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
For the given complex the orbital splitting diagram has to be drawn using spectrochemial series.
Concept introduction:
The element in the periodic table and count its position in the respective transition series. These elements are in Periods 5 and 6, so the general configuration is
The spectrochemical series is
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Electron configuration of
Charge on
Electron configuration of
Six ligands indicate an octahedral arrangement. Using Hund’s rule, fill the lower energy
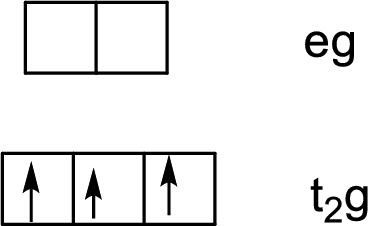
(b)
Interpretation:
For the given complex the orbital splitting diagram has to be drawn using spectrochemial series.
Concept introduction:
The element in the periodic table and count its position in the respective transition series. These elements are in Periods 5 and 6, so the general configuration is
The spectrochemical series is
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Electron configuration of
Charge on
Electron configuration of
Four ligands and a
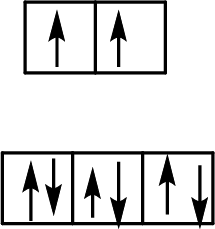
(c)
Interpretation:
For the given complex the orbital splitting diagram has to be drawn using spectrochemial series.
Concept introduction:
The element in the periodic table and count its position in the respective transition series. These elements are in Periods 5 and 6, so the general configuration is
The spectrochemical series is
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Electron configuration of
Charge on
Electron configuration of
Six ligands indicate an octahedral arrangement. Use Hund’s rule to fill the orbitals.
F– is a weak-field ligand, so the splitting energy, Δ, is not large enough to overcome the resistance to electron pairing. The electrons remain unpaired, and the complex is called high-spin.
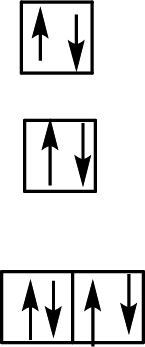
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
CHEM 212:STUDENT SOLUTION MANUAL
- Can I get helpp drawing my arrowsarrow_forwardWhich of the m/z values corresponds to the base peak in the mass spectrum shown? 100 80 A. 45 B. 44 C. 29 D. 15 Intensity 20 0 10 20 30 40 B- m/z -8 50 E. 30 Which of the m/z values correspond to the molecular ion for the compound shown? A. 18 B. 82 OH C. 100 D. 102 E. 103arrow_forwardCan someone help me with drawing my arrows.arrow_forward
- I'm having trouble with converting lewis diagrams into VSEPR diagrams. I currently have this example of C2BrCl3 which I want to turn into a lewis structure, but I'm not sure what steps I need to do in order to do so. I have the table written down, however, there's two central atoms so what would I do? There seems to be 4 electron domains on the carbon atom and no lone pairs so it would seem like this shape would be tetrahedral. Here's what I have now. Thanks!arrow_forwardWe discussed the solid phase resin using in peptide synthesis. Provide a mechanism, for its formation. DRAW THE MECHANISM.arrow_forwardPlease help. Every time I've asked an expert in the past, it's been wrong :(arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





