
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The empirical formula of fumaric acid in which the elemental composition is 41.4% C, 3.5 % H and 55.1 % O needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Empirical formula is the simplest formula of any organic or inorganic compound that represents the simple ratio of all atoms present in the molecule. It can be calculated with the help of elemental composition of molecule. Certain steps must be used to get the empirical formula:
- Consider mass % as mass in grams and calculate moles of element with the help of molar mass
- Calculate the moles of each element in least whole number
- Write the number of each atom as subscript to write the empirical formula.
(b)
Interpretation:
The molecular weightof fumaric acidneeds to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Osmotic pressure is a colligative property that depends on the number of solute particles in the solution. It is mainly used to calculate the molecular weight of substance dissolve in certain volume of solvent. The relation between osmotic pressure and concentration can be shown as:
(c)
Interpretation:
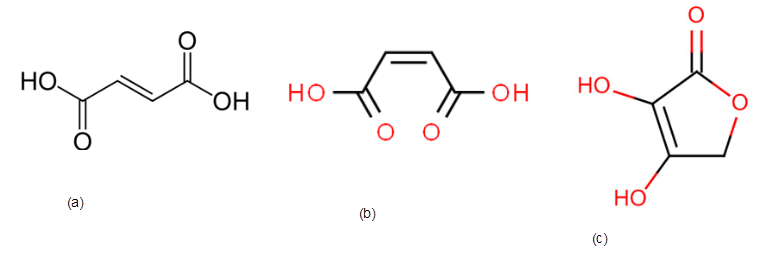
Thethree possible structures of fumaric acid if the empirical formula is CHO and molar mass is 116 g/mol needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Empirical formula is the simplest formula of any organic or inorganic compound that represents the simple ratio of all atoms present in the molecule. It can be calculated with the help of elemental composition of molecule. Certain steps must be used to get the empirical formula:
- Consider mass % as mass in grams and calculate moles of element with the help of molar mass
- Calculate the moles of each element in least whole number
- Write the number of each atom as subscript to write the empirical formula.
(d)
Interpretation:
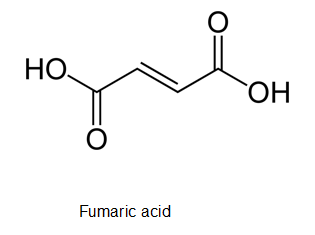
The correct structure of fumaric acid if it contains a trans double bond needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Empirical formula is the simplest formula of any organic or inorganic compound that represents the simple ratio of all atoms present in the molecule. It can be calculated with the help of elemental composition of molecule. Certain steps must be used to get the empirical formula:
- Consider mass % as mass in grams and calculate moles of element with the help of molar mass
- Calculate the moles of each element in least whole number
- Write the number of each atom as subscript to write the empirical formula.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 23 Solutions
EBK CHEMISTRY
- Can I please get help with this.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning





