
(a)
Interpretation:
The number of signals of
Concept introduction:
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is applied for the identification of the structure of molecules. The energy in the radiofrequency region is suitable for NMR. Nuclear magnetic resonance results from the spin of the nucleus of an atom. The value of I is obtained using the
Any nucleus with both an even atomic number and the mass number has 0 nuclear spins. There are a total of
However, energy levels become non-degenerate in the presence of a magnetic field.
Deuterated chloroform
The total signal intensity of each set of proton is given by the height of each set of steps. The integration value defines the relative number of each kind of proton in the molecule.
In NMR spectrum, the intensity of signals is plotted against the magnetic field or frequency. Nuclei that are non-equivalent show only one peak in the NMR spectrum. However, protons absorb at different frequencies that are non-equivalent.
An increase in the electron density that surrounds the nucleus shields it from the applied field. This results in a net decrease in the field experienced by the nucleus. The value of the observed chemical shift of the signal therefore decreases, and, on a typical NMR spectrum, the signal moves to the right, which is called an upfield shift because, at a constant frequency, a slightly higher applied magnetic field is required for resonance to occur. De-shielding is the effect of a decline in the electron density around a nucleus which leads to shifting in the peaks of a chemical shift towards left in the NMR spectrum that results in an increase in delta values, hence downshift.
Explanation of Solution
The decoupled
Isopropyl acetate has 4 different types of carbon as here also 2 methyl groups in the isopropyl group that have equivalent chemical environment. So they show 4 signals.
(b)
Interpretation:
The number of signals of
Concept introduction:
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is applied for the identification of the structure of molecules. The energy in the radiofrequency region is suitable for NMR. Nuclear magnetic resonance results from the spin of the nucleus of an atom. The value of I is obtained using the atomic number and the mass number of an atom. The non-zero magnetic moment of an isotopic nucleus is detectable by the NMR technique.
Any nucleus with both an even atomic number and the mass number has 0 nuclear spins. There are a total of
However, energy levels become non-degenerate in the presence of a magnetic field.
Deuterated chloroform
The total signal intensity of each set of proton is given by the height of each set of steps. The integration value defines the relative number of each kind of proton in the molecule.
In NMR spectrum, the intensity of signals is plotted against the magnetic field or frequency. Nuclei that are non-equivalent show only one peak in the NMR spectrum. However, protons absorb at different frequencies that are non-equivalent.
An increase in the electron density that surrounds the nucleus shields it from the applied field. This results in a net decrease in the field experienced by the nucleus. The value of the observed chemical shift of the signal therefore decreases, and, on a typical NMR spectrum, the signal moves to the right, which is called an upfield shift because, at a constant frequency, a slightly higher applied magnetic field is required for resonance to occur. De-shielding is the effect of a decline in the electron density around a nucleus which leads to shifting in the peaks of a chemical shift towards left in the NMR spectrum that results in an increase in delta values, hence downshift.
Explanation of Solution
The decoupled
(c)
Interpretation:
The number of signals for cyclohexane,
Concept introduction:
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is applied for the identification of the structure of molecules. The energy in the radiofrequency region is suitable for NMR. Nuclear magnetic resonance results from the spin of the nucleus of an atom. The value of I is obtained using the atomic number and the mass number of an atom. The non-zero magnetic moment of an isotopic nucleus is detectable by the NMR technique.
Any nucleus with both an even atomic number and the mass number has 0 nuclear spins. There are a total of
However, energy levels become non-degenerate in the presence of a magnetic field.
Deuterated chloroform
The total signal intensity of each set of proton is given by the height of each set of steps. The integration value defines the relative number of each kind of proton in the molecule.
In NMR spectrum, the intensity of signals is plotted against the magnetic field or frequency. Nuclei that are non-equivalent show only one peak in the NMR spectrum. However, protons absorb at different frequencies that are non-equivalent.
An increase in the electron density that surrounds the nucleus shields it from the applied field. This results in a net decrease in the field experienced by the nucleus. The value of the observed chemical shift of the signal therefore decreases, and, on a typical NMR spectrum, the signal moves to the right, which is called an upfield shift because, at a constant frequency, a slightly higher applied magnetic field is required for resonance to occur. De-shielding is the effect of a decline in the electron density around a nucleus which leads to shifting in the peaks of a chemical shift towards left in the NMR spectrum that results in an increase in delta values, hence downshift.
Explanation of Solution
The decoupled
Cyclohexane has 1 type of carbon atom as it is symmetrical molecule with 6 planes of symmetry in it so 1 signal is obtained for it.
(d)
Interpretation:
The number of signals in the following structures in decoupled
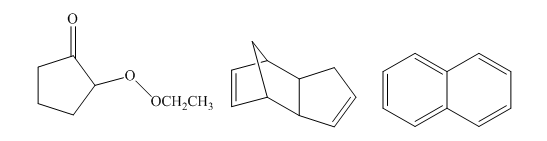
Concept introduction:
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is applied for the identification of the structure of molecules. The energy in the radiofrequency region is suitable for NMR. Nuclear magnetic resonance results from the spin of the nucleus of an atom. The value of I is obtained using the atomic number and the mass number of an atom. The non-zero magnetic moment of an isotopic nucleus is detectable by the NMR technique.
Any nucleus with both an even atomic number and the mass number has 0 nuclear spins. There are a total of
However, energy levels become non-degenerate in the presence of a magnetic field.
Deuterated chloroform
The total signal intensity of each set of proton is given by the height of each set of steps. The integration value defines the relative number of each kind of proton in the molecule.
In NMR spectrum, the intensity of signals is plotted against the magnetic field or frequency. Nuclei that are non-equivalent show only one peak in the NMR spectrum. However, protons absorb at different frequencies that are non-equivalent.
An increase in the electron density that surrounds the nucleus shields it from the applied field. This results in a net decrease in the field experienced by the nucleus. The value of the observed chemical shift of the signal therefore decreases, and, on a typical NMR spectrum, the signal moves to the right, which is called an upfield shift because, at a constant frequency, a slightly higher applied magnetic field is required for resonance to occur. De-shielding is the effect of a decline in the electron density around a nucleus which leads to shifting in the peaks of a chemical shift towards left in the NMR spectrum that results in an increase in delta values, hence downshift.
Explanation of Solution
The decoupled
The number of signals in the structures is indicated as follows:
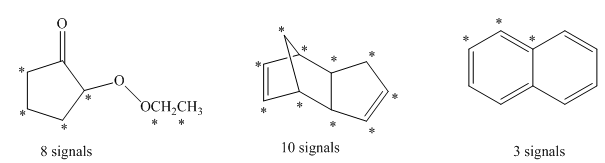
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
LABORATORY TECHNIQUES IN ORGANIC CHEMIS
- PQ-10. What is the major product of this reaction? (A) (C) 930 Me HO O=S=O O-8-CF, C 어 Me H+ OH 270 O 0-5-0 O=S=O O-S-CF CF3 2arrow_forwardPredict the major organic product(s) of the following reactions. Include stereochemistry when necessary. Write NR if no reaction, try to explain.arrow_forwardQ2: Explain why epoxides that react in an SN1 manner will not show any stereochemical inversion in the product. Q3: Rationalize why Alcohol B will react under the indicated reaction conditions, but Alcohol A will not. A ☑ OH B OH PBr3 R-Brarrow_forward
- Q1: Predict the major organic product(s) of the following reactions. Include stereochemistry when necessary. Write NR if no reaction, try to explain. 1.) LDA, THF 2.) СОН CI OH H2SO4, heat OH m...... OH 1.) PCC, CH2Cl2 2.) CH3CH2MgBr, THF 3.) H3O+ 4.) TsCl, pyr 5.) tBuOK, tBuOH 1.) SOCI 2, CHCI 3 2.) CH3CH2ONA, DMF OH 1.) HBr 2.) Mg, THF 3.) H₂CO, THE 4.) H3O+ OH NaH, THFarrow_forwardWhat is the stepwise mechanism for this reaction?arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reactionarrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning


