College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780134609034
Author: Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 22, Problem 9CQ
- a. Which direction—clockwise or counterclockwise—does an electron travel through the wire in Figure Q22.9? Explain.
Figure Q22.Q
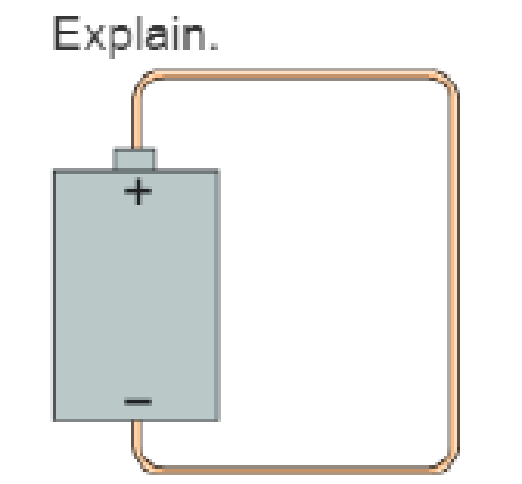
- b. Does an electron's electric potential energy increase, decrease, or stay the same as it moves through the wire? Explain.
- c. If you answered “decrease” in part b, where does the energy go? If you answered “increase” in part b, where does the energy come from?
- d. Which way—up or down—does an electron move through the battery? Explain.
- e. Does an electron's electric potential energy increase, decrease, or stay the same as it moves through the battery? Explain.
- f. If you answered “decrease” in part e, where does the energy go? If you answered “increase” in part e, where does the energy come from?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
a. Which direction—clockwise or counterclockwise—does an electron travelthrough the wire shown?Explain.b. Does an electron’s electric potential energy increase, decrease, or stay the same as it moves through the wire?Explain.c. If you answered “decrease” in part b, where does the energy go? If you answered “increase” in part b, where does the energy come from?d. Which way—up or down—does an electron move throughthe battery? Explain.e. Does an electron’s electric potential energy increase, decrease, or stay the same as it moves through the battery?Explain.f. If you answered “decrease” in part e, where does the energy go? If you answered “increase” in part e, where does the energy come from?
V=J/C. A negatively charged particle (q= - 2 C) moves through a 2000 V loss of electric potential. Will there be a loss or a gain in electric potential and kinetic energy?
A. Electrical potential energy is increased, while Kinetic Energy is decreasedB. Both Electrical potential energy and Kinetic energy are decreasedC. Electrical potential energy is decreased, while Kinetic Energy is increasedD. Both electrical potential energy and kinetic energy are increased
stion 4.
A.
In all electronic camera flashes, there is a capacitor, which is a device that allows large
quantities of charge to be stored. The charge accumulates and is then released very quickly.
The electrical energy stored in a capacitor is given by E=FV².
Which of the following combinations of coulombs, joules, and/or volts is equivalent to
a farad?
ç
B. č
C. č
D. &
Question 5.
where V = the potential difference across the capacitor
and F = the capacitance of the capacitor in farads
131
trd
10
Ch
Ang in de pontos d
sigbeha
Two horizontal plates are separated by a distance of 5.00 cm. A beam of electrons is
directed, horizontally, into the region between the pla
1E1=E/
Chapter 22 Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
Ch. 22 - Prob. 2CQCh. 22 - Prob. 3CQCh. 22 - Prob. 4CQCh. 22 - All wires in Figure Q22.519 are made of the same...Ch. 22 - A wire carries a 4 A current. What is the current...Ch. 22 - Prob. 7CQCh. 22 - Cells in the nervous system have a potential...Ch. 22 - a. Which directionclockwise or...Ch. 22 - Prob. 10CQCh. 22 - Prob. 11CQ
Ch. 22 - The two circuits in Figure Q22.12 use identical...Ch. 22 - The two circuits in Figure Q22.13 use identical...Ch. 22 - Prob. 14CQCh. 22 - Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the...Ch. 22 - The circuit in Figure Q22.16 has three batteries...Ch. 22 - Prob. 17CQCh. 22 - Prob. 18CQCh. 22 - Over time, atoms boil off the hot filament in an...Ch. 22 - Prob. 20CQCh. 22 - A 100 W lightbulb is brighter than a 60 W...Ch. 22 - Lightbulbs are typically rated by their power...Ch. 22 - Lightbulbs are typically rated by their power...Ch. 22 - A copper wire is stretched so that its length...Ch. 22 - The potential difference across a length of wire...Ch. 22 - Prob. 26MCQCh. 22 - A resistor connected to a 3.0 V battery dissipates...Ch. 22 - If a 1.5 V battery stores 5.0 kJ of energy (a...Ch. 22 - Figure Q22.29 shows a side view of a wire of...Ch. 22 - A person gains weight by adding fatand therefore...Ch. 22 - Prob. 31MCQCh. 22 - The current in an electric hair dryer is 10 A. How...Ch. 22 - Prob. 2PCh. 22 - Three wires meet at a junction. Wire 1 has a...Ch. 22 - When a nerve cell depolarizes, charge is...Ch. 22 - A wire carries a 15 A current. How many electrons...Ch. 22 - In a typical lightning strike, 2.5 C flows from...Ch. 22 - Prob. 7PCh. 22 - In an ionic solution, 5.0 1015 positive ions with...Ch. 22 - Prob. 9PCh. 22 - What are the values of currents IB and IC in...Ch. 22 - The currents through several segments of a wire...Ch. 22 - How much electric potential energy does 1.0 C of...Ch. 22 - What is the emf of a battery that increases the...Ch. 22 - A 9.0 V battery supplies a 2.5 mA current to a...Ch. 22 - Prob. 16PCh. 22 - An electric catfish can generate a significant...Ch. 22 - A Wire with resistance R is connected to the...Ch. 22 - Wires 1 and 2 are made of the same metal. Wire 2...Ch. 22 - Prob. 20PCh. 22 - Resistivity measurements on the leaves of corn...Ch. 22 - Prob. 22PCh. 22 - A motorcyclist is making an electric vest that,...Ch. 22 - Prob. 24PCh. 22 - A 3.0 V potential difference is applied between...Ch. 22 - Prob. 26PCh. 22 - Prob. 27PCh. 22 - Prob. 28PCh. 22 - Figure P22.29 shows the...Ch. 22 - Figure P22.30 is a...Ch. 22 - In Example 22.6 the length of a 60 W, 240 ...Ch. 22 - The electric field inside a 30-cm-long copper wire...Ch. 22 - A copper wire is 1.0 mm in diameter and carries a...Ch. 22 - Two identical lightbulbs are connected in series...Ch. 22 - Prob. 35PCh. 22 - a. What is the resistance of a 1500 W (120 V) hair...Ch. 22 - Prob. 37PCh. 22 - A 70 W electric blanket runs at 18 V. a. What is...Ch. 22 - A 60-cm-long heating wire is connected to a 120 V...Ch. 22 - An electric eel develops a potential difference of...Ch. 22 - Prob. 41PCh. 22 - A 3.0 V battery powers a flashlight bulb that has...Ch. 22 - A heating element in a toaster dissipates 900 W...Ch. 22 - Prob. 44GPCh. 22 - Prob. 45GPCh. 22 - The hot dog cooker described in the chapter heats...Ch. 22 - Air isnt a perfect electric insulator, but it has...Ch. 22 - The biochemistry that takes place inside cells...Ch. 22 - High-resolution measurements have shown that an...Ch. 22 - When an ion channel opens in a cell wall (see...Ch. 22 - The total charge a battery can supply is rated in...Ch. 22 - Prob. 52GPCh. 22 - The heating element of a simple heater consists of...Ch. 22 - Variations in the resistivity of blood can give...Ch. 22 - A 40 W (120 V) lightbulb has a tungsten filament...Ch. 22 - Prob. 56GPCh. 22 - When the starter motor on a car is engaged, there...Ch. 22 - Prob. 58GPCh. 22 - The two segments of the wire in Figure P22.59 have...Ch. 22 - Prob. 60GPCh. 22 - Prob. 61GPCh. 22 - Prob. 62GPCh. 22 - Prob. 63GPCh. 22 - Prob. 64GPCh. 22 - An immersion heater used to boil water for a...Ch. 22 - The graph in Figure P22.66 shows the current...Ch. 22 - Its possible to estimate the percentage of fat in...Ch. 22 - If you touch the two terminals of a power supply...Ch. 22 - The average resistivity of the human body (apart...Ch. 22 - MCAT-Style Passage Problems Lightbulb Failure...Ch. 22 - MCAT-Style Passage Problems Lightbulb Failure...Ch. 22 - MCAT-Style Passage Problems Lightbulb Failure...Ch. 22 - MCAT-Style Passage Problems Lightbulb Failure...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
TEST YOUR UNDERSTANDING OF SECTION 23.5 In a certain region of space the potential is given by V = A + Bx + Cy3...
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
Write each number in scientific notation.
2. 798
Applied Physics (11th Edition)
A drinking straw 20 cm long and 3.0 mm in diameter stands vertically in a cup of juice 8.0 cm in diameter. A se...
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
A gas follows on an isothermal curve, where p is the pressure, V is the volume, b is a constant, and c is a fun...
University Physics Volume 2
28.74 Long, straight conductors with square cross section, each carrying current I, are laid side by side to fo...
University Physics (14th Edition)
11. The foot of a 55 kg sprinter is on the ground for 0.25 s while her body accelerates from rest to 2.0 m/s.
a...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics (4th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- FIGURE P26.8 A Find an expression for the electric potential energy associated with each system in Figure P26.8 in terms of the quantities provided on the figure.arrow_forwardIn nuclear fission, a nucleus splits roughly in half, (a) What is the potential 2.001014 in from a fragment that has 46 protons in it? (b) What is the potential energy in MeV of a similarly charged fragment at this distance?arrow_forwardUnreasonable Results (a) What is the final speed of an electron accelerated from rest through a voltage of 25.0 MV by a negatively charged Van de Graaff terminal? (b) What is unreasonable about this result? (C) Which assumptions are responsible?arrow_forward
- (a) Calculate the potential difference between points a and b in Figure P27.37 and (b) identify which point is at the higher potential. Figure P27.37arrow_forwardA charged particle is moved in a uniform electric field between two points, A and B, as depicted in Figure P26.65. Does the change in the electric potential or the change in the electric potential energy of the particle depend on the sign of the charged particle? Consider the movement of the particle from A to B, and vice versa, and determine the signs of the electric potential and the electric potential energy in each possible scenario.arrow_forwardA bare helium nucleus has two positive charges and a mass of 6.641027kg . (a) Calculate its kinetic energy in joules at 2.00% of the speed of light, (b) What is this in electron-volts? (c) What voltage would be needed to obtain this energy?arrow_forward
- (a) Find the electric potential difference Ve required to stop an electron (called a stopping potential) moving with an initial speed of 2.85 107 m/s. (b) Would a proton traveling at the same speed require a greater or lesser magnitude of electric potential difference? Explain. (c) Find a symbolic expression for the ratio of the proton stopping potential and the electron stopping potential. Vp/Ve.arrow_forward(a) How much charge is on each plate of a 4.00-F capacitor when it is connected to a 12.0-V battery? (b) If this same capacitor is connected to a 1.50-V battery, what charge is stored?arrow_forwardThree capacitors having capacitances of 8.40, 8.40, and 4.20F , respectively, are connected in series across a 36.0-V potential difference. (a) What is the charge on the 4.20F capacitor? (b) The capacitors are disconnected from the potential difference without allowing them to discharge. They are then reconnected in parallel with each other with the positively charged plates connected together. What is the voltage across each capacitor in the parallel combination?arrow_forward
- In three regions of space, the electric potential is given by V(r)=0forrRV(r)=V04R2r2forRr2RV(r)=V0forr2R a. Plot V as a function of r. b. Find expressions for the electric field in all three regions. c. Plot E versus r in all three regions.arrow_forwardTo form a helium atom, an alpha particle that contains two protons and two neutrons is fixed at one location, and two electrons are brought in from far away, one at a time. The first electron is placed at 0.6001010 m from the alpha particle and held there while the second electron is brought to 0.6001010 m from the alpha particle on the other side from the first electron. See die final configuration below, (a) How much work is done in each step? (b) What is the electrostatic energy of die alpha particle and two electrons in the final configuration?arrow_forwardAt a certain distance from a charged particle, the magnitude of the electric field is 500 V/m and the electric potential is 3.00 kV. (a) What is the distance to the particle? (b) What is the magnitude of the charge?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY