
Concept explainers
The budget director of Gold Medal Athletic Co., with the assistance of the controller, treasurer, production manager, and sales manager, has gathered the following data for use in developing the budgeted income statement for March:
Estimated sales for March:

Estimated inventories at March 1:

Desired inventories at March 31:

Direct materials used in production:

Anticipated cost of purchases and beginning and ending inventory of direct materials:

Direct labor requirements:

Estimated factory
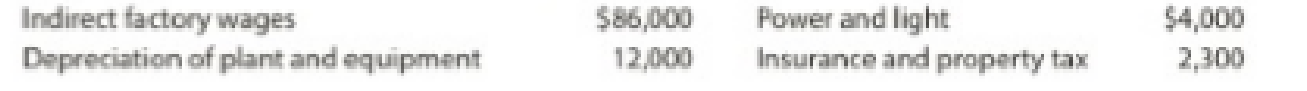
Estimated operating expenses for March:
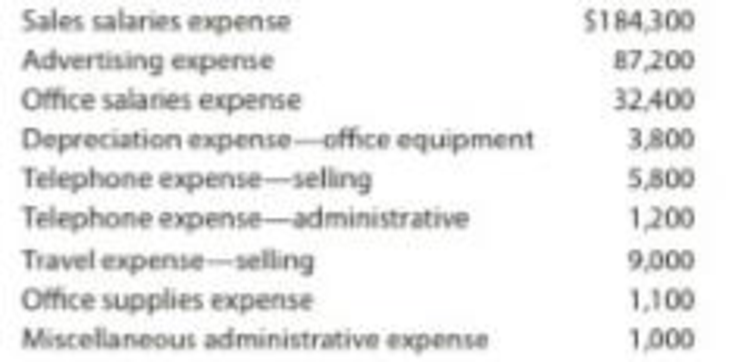
Estimated other revenue and expense for March:

Estimated tax rate: 30%
Instructions
Prepare a sales budget for March.
Prepare a production budget for March.
Prepare a direct materials purchases budget for March.
Prepare a direct labor cost budget for March.
Prepare a
Prepare a cost of goods sold budget for March. Work in process at the beginning of March is estimated to be $15,300, and work in process at the end of March is desired to be $14,800.
Prepare a selling and administrative expenses budget for March.
Prepare a budgeted income statement for March.
1.
Prepare the sales budget for the month ending March 31.
Explanation of Solution
Budgeting:
Budgeting is a process to prepare the financial statement by the manager to estimate the organization’s future actions. It is also helpful to satisfy the everyday activities.
The following table shows the sales budget.
|
Company G Sales Budget For the Month Ending March 31 | |||
| Product and Area | Unit Sales Volume | Unit Selling Price ($) | Total Sales ($) |
| (A) | (B) | (A) × (B) | |
| Birdhouse | 1,200 | 40 | 48,000 |
| Bird feeder | 6,500 | 160 | 1,040,000 |
| Total Revenue from Sales | 1,088,000 | ||
Table (1)
2.
Prepare the production budget for the month ending March 31.
Explanation of Solution
The following table shows the production budget.
|
Company G Production Budget For the Month Ending March 31 | ||
| Details | Units | |
| Batting Helmet | Football Helmet | |
| Expected Units to be Sold | 1,200 | 6,500 |
| Add: Desired Inventory, March 31 | 50 | 220 |
| Total Units Required | 1,250 | 6,720 |
| Less: Estimated Inventory, March 1 | (40) | (240) |
| Total Units to be Produced | 1,210 | 6,480 |
Table (2)
3.
Prepare the direct materials purchase budget for the month ending March 31.
Explanation of Solution
The following table shows the direct materials purchase budget.
|
Company G Direct Materials Purchase Budget For the Month Ending March 31 | ||
| Details | Units | |
| Plastic | Foam Lining | |
| Required units for production: | ||
| Batting Helmet | 1,452 (1) | 605 (2) |
| Football Helmet | 22,680 (3) | 9,720 (4) |
| Add: Desired inventory, March 31 | 50 | 65 |
| Total units required | 24,182 | 10,390 |
| Less: Estimated inventory, March 1 | (90) | (80) |
| Total units to be purchased (A) | 24,092 | 10,310 |
| Unit price (B) | $6 | $4 |
| Total (A) × (B) | $144,552 | $41,240 |
| Total direct materials to be purchased | 185,792 | |
Table (3)
Working note (1):
Calculate the direct material (plastic) for batting helmet.
Working note (2):
Calculate the direct material (foam lining) for batting helmet.
Working note (3):
Calculate the direct material (plastic) for football helmet.
Working note (4):
Calculate the direct material (foam lining) for football helmet.
4.
Prepare the direct labor cost budget of Company B.
Explanation of Solution
The following table shows the direct labor cost budget for molding and assembly department.
| Company B | ||
| Direct Labor Cost Budget | ||
| For the Month Ending March 31 | ||
| Particulars |
Molding Department |
Assembly Department |
| Hours Required for Production: | ||
| Batting helmet | 242 (5) | 605 (6) |
| Football helmet | 3,240 (7) | 11,664 (8) |
| Total Hours Required (A) | 3,482 | 12,269 |
| Hourly Rate (B) | $20 | $14 |
| Total Cost (A) × (B) | $69,640 | $171,766 |
| Total Direct Labor Cost | 241,406 | |
Table (4)
Working note (5):
Calculate the hours required for the production of batting helmet in molding department.
Working note (6):
Calculate the hours required for the production of batting helmet in assembly department.
Working note (7):
Calculate the hours required for the production of football helmet in molding department.
Working note (8):
Calculate the hours required for the production of football helmet in assembly department.
5.
Prepare the factory overhead cost budget of Company G.
Explanation of Solution
The following table shows the factory overhead cost budget.
| Company G | |
| Factory Overhead Cost Budget | |
| For the Month Ending March 31 | |
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Indirect factory wages | 86,000 |
| Depreciation of plant and equipment | 12,000 |
| Power and light | 4,000 |
| Insurance and property tax | 2,300 |
| Total | 104,300 |
Table (5)
6.
Prepare the cost of goods sold budget of Company G.
Explanation of Solution
The following table shows the cost of goods sold budget.
| G Company | |||
| Cost of Goods Sold Budget | |||
| For the month ending March 31 | |||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Finished goods inventory, March 1 | 19,480 (9) | ||
| Work-in-process inventory, March 1 | 15,300 | ||
| Direct material: | |||
| Direct materials inventory, March 1 | 860 (10) | ||
| Direct materials purchases | 185,792 | ||
| Cost of direct materials available for use | 186,652 | ||
| Less: Direct materials inventory, March 31 |
(560) (11) | ||
| Cost of direct materials placed in production | 186,092 | ||
| Direct labor | 241,406 | ||
| Factory overhead | 104,300 | ||
| Total manufacturing cost | 531,798 | ||
| Total work-in-process during the period | 547,098 | ||
| Less: Work-in-process inventory, March 31 | (14,800) | ||
| Cost of goods manufactures | 532,298 | ||
| Cost of finished goods available for sale | 551,778 | ||
| Less: Finished goods inventory, March 31 |
(18,410) (12) | ||
| Cost of Goods Sold | 533,368 | ||
Table (6)
Working note (9):
Calculate the beginning finished goods inventory.
Working note (10):
Calculate the beginning direct material.
Working note (11):
Calculate the ending direct material.
Working note (12):
Calculate the ending finished goods inventory.
7.
Prepare the selling and administrative expenses budget of Company G.
Explanation of Solution
The following table shows the selling and administrative expenses budget.
| Company G | ||
| Selling and Administrative Budget | ||
| For the Month Ending March 31 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Selling expense: | ||
| Sales salaries expense | 184,300 | |
| Advertising expense | 87,200 | |
| Telephone expense | 5,800 | |
| Travel expense | 9,000 | |
| Total selling expense | 286,300 | |
| Administrative expense: | ||
| Office salaries expense | 32,400 | |
| Depreciation expense – office equipment | 3,800 | |
| Telephone expense – Administrative | 1,200 | |
| Office supplies expense | 1,100 | |
| Miscellaneous administrative expense | 1,000 | |
| Total administrative expenses | 39,500 | |
| Total Operating Expenses | 325,800 | |
Table (7)
8.
Prepare the budgeted income statement of Company G.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the budgeted income statement of Company G.
| Company G | ||
| Budgeted Income Statement | ||
| For the Month Ending March 31 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Revenue from sales | 1,088,000 | |
| Less: Cost of goods sold | (533,368) | |
| Gross profit | 554,632 | |
| Operating expenses: | ||
| Selling expenses | 286,300 | |
| Administrative expenses | 39,500 | |
| Total operating expenses | (325,800) | |
| Income from operations | 228,832 | |
| Other revenue and expenses: | ||
| Interest revenue | 940 | |
| Interest expense | (872) | 68 |
| Income before income tax | 228,900 | |
| Income tax expense | (68,670) | |
| Net Income | 160,230 | |
Table (8)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
FINANCIAL&MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING(LL)W/AC
- Please explain the solution to this general accounting problem with accurate principles.arrow_forwardKindly help me with this General accounting questions not use chart gpt please fast given solutionarrow_forwardI am searching for the correct answer to this Financial accounting problem with proper accounting rules.arrow_forward
- I am looking for the correct answer to this Financial accounting question with appropriate explanations.arrow_forwardEcho Tone Technologies reports annual sales of $90,000, and it expects sales to increase to $135,000 next year. The company has a degree of operating leverage (DOL) of 4.2. By what percentage should net income increase? A. 70% B. 189% C. 150% D. 210%arrow_forwardPlease provide the solution to this general accounting question using proper accounting principles.arrow_forward
- No chatgpt Which account will appear in the post-closing trial balance?A. Rent ExpenseB. Sales RevenueC. DividendsD. Capitalarrow_forwardI need help with this financial accounting question using the proper accounting approach.arrow_forwardI need help Which account will appear in the post-closing trial balance?A. Rent ExpenseB. Sales RevenueC. DividendsD. Capitalarrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning





