
Equity as an Option and
a. What is the value of the firm’s equity and debt if Project A is undertaken? If Project B is undertaken?
b. Which project would the stockholders prefer? Can you reconcile your answer with the NPV rule?
c. Suppose the stockholders and bondholders are, in fact, the same group of investors. Would this affect your answer to (b)?
d. What does this problem suggest to you about stockholder incentives?
a.
To compute: Value of the firm’s equity and debt under project A and project B.
Option Pricing:
Option pricing helps in determining correct or fair price in the market. It is the value of one share on the basis of which option is traded. Black-Scholes is one of the pricing methods. Further, equity is also used as an option.
Explanation of Solution
Project A
Given,
Stock price is $21,700+$1,200=$22,900
Exercise price is 20,000.
Risk free rate is 0.05.
Time to expire is 1 year.
Formula to calculate the value of equity by using Black Scholes model is,
Value of equity=SN(d1)−Ee-RtN(d2)
Where,
- S is stock price.
- E is exercise price.
- R is risk free rate.
- T is time to expire.
Substitute $22,900 for S, $20,000 for E, 0.05 for R, and 1 for T.
Value of equity=($22,900(0.8291))−($20,000e−0.05×1(0.5239))=$18,986.39−($20,000×0.9512294(0.5239))=$18,986.76−$9,966.98=$9,019.78
Formula to calculate the value of debt is,
Value of debt=Value of firm−Value of equity
Substitute $22,900 as value of firm and $9,019.78 as value of equity.
Value of debt=$22,900−$9,019.78=$13,880.22
Project B
Given,
Stock price is $21,700.
Exercise price is 20,000.
Risk free rate is 0.05.
Time to expire is 1 year.
Formula to calculate the value of equity by using Black Scholes model is,
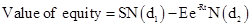
Where,
- S is stock price.
- E is exercise price.
- R is risk free rate.
- T is time to expire.
Substitute $21,700 for S, $20,000 for E, 0.05 for R, and 1 for T.
Value of equity=($21,700(0.7088))−($20,000e−0.05×1(0.5832))=$15,380.96−($20,000×0.9512294(0.5832))=$4,285.82
Formula to calculate the value of debt is,
Value of debt=Value of firm−Value of equity
Substitute $21,700 as value of firm and $4,285.82 as value of equity.
Value of debt=$21,700−$4,285.82=$17,414.18
Working Note:
Formula to calculate d1 is,
d1=In(SE)+(R+σ22)t√σ2t
Calculation of d1 for Project A,
d1=In($22,900$20,000)+(0.05+0.5522)×1√0.552×1=0.1354+0.201250.55=0.6121
From normal distribution table N(d1)=0.8291
Calculation of d1 for Project B,
d1=In($21,700$20,000)+(0.05+0.3422)×1√0.342×1=0.08158+0.10780.34=0.557
From normal distribution table N(d1)=0.7088
Formula to calculate d2 is,
d2=d1−√σ2t
Calculation of d2 for Project A,
d2=0.6121−√0.552×1=0.6121−0.55=0.0621
From normal distribution table N(d2)=0.5239
Calculation of d2 for Project B,
d2=0.557−√0.342×1=0.557−0.34=0.217
From normal distribution table N(d2)=0.5832
Hence, for Project A the value of firm’s equity is $9,019.78, value of firm’s debt is$13,880.22 and for Project B the value of firm’s equity is $4,285.82 and value of firm’s debt is $17,414.18.
b.
To identify: Project that would be preferred by stockholders.
Answer to Problem 22QP
- Here, equity’s value is higher in Project A than Project B.
- Project A does not create more bondholders.
Explanation of Solution
- If Project A is considered, it has increased the firm’s assets to$1,200.
- If Project B is considered, it has increased the firm’s assets to$1,600.
- NPV rules say Project B should be accepted, but value of equity is more in the case of Project A rather than Project B, which shows that Project A has less of bondholders.
- Thus, Project A is more attractive.
Hence, the stockholders prefer Project A.
c.
To identify: Project that would be preferred by stockholders if both stockholders and bondholders are same.
Answer to Problem 22QP
As Project B adds more value to the firm, this would be a good option.
Explanation of Solution
- If stockholders and bondholder would be the same, in that case their interest would also be the same and they can get benefits equally.
- Since Project A increases the firm’s assets to$1,200 and Project B increases the firm’s assets to$1,600.
- Thus, Project B is more attractive.
Hence, the stockholders prefer Project B.
d.
To explain: The effect on stockholders incentives.
Answer to Problem 22QP
In case of leveraged firm, stockholders would definitely prefer those projects, which would increase value of equity.
Explanation of Solution
- Reason for opting equity source is that in the case of debt source, risk is borne by the bondholders and benefits are limited to their debt value, which is not happening in the case of equity sources.
- All benefits after paying the debt, goes to the stockholders pocket.
- Thus, the stockholders incentive would relate to the project that adds more value to the equity.
Hence, stockholder’s incentives are more related with the project that contains equity.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
EBK CORPORATE FINANCE
- [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] The Albertville City Council decided to pool the investments of its General Fund with Albertville Schools and Richwood Township in an investment pool to be managed by the city. Each of the pool participants had reported its investments at fair value as of the end of 2022. At the date of the creation of the pool, February 15, 2023, the fair value of the investments of each pool participant was as follows: Investments 12/31/22 2/15/23 City of Albertville General Fund $ 897,000 $ 935,000 Albertville Schools 4,214,000 4,394,500 Richwood Township 4,030,000 4,020,500 Total $ 9,141,000 $ 9,350,000 On June 15, Richwood Township decided to withdraw $3,080,000 for a capital projects payment. At the date of the withdrawal, the fair value of the Treasury notes had increased by $37,000. Assume that the trust fund was able to redeem the CDs necessary to complete…arrow_forwardStevens Textile Corporation's 2019 financial statements are shown below Balance Sheet as of December 31, 2019 (Thousands of Dollars) Cash $ 1,080 Accounts payable $ 4,320 Receivables 6,480 Accruals 2,880 Inventories 9,000 Line of credit 0 Total current assets $16,560 Notes payable 2,100 Net fixed assets 12,600 Total current liabilities $ 9,300 Mortgage bonds 3,500 Common stock 3,500 Retained earnings 12,860 Total assets $29,160 Total liabilities and equity $29,160 Income Statement for December 31, 2019 (Thousands of Dollars) Sales $36,000 Operating costs 34,000 Earnings before interest and taxes $ 2,000 Interest 160 Pre-tax earnings $ 1,840 Taxes (25%) 460 Net income $ 1,380 Dividends (40%) $ 552 Addition to retained earnings $ 828 Stevens grew rapidly in 2019 and financed the growth with notes payable and long-term bonds. Stevens expects sales to grow by 20% in the next year but will finance…arrow_forwardAt year-end 2019, Wallace Landscaping’s total assets were $2.30 million, and its accounts payable were $430,000. Sales, which in 2019 were $2.9 million, are expected to increase by 20% in 2020. Total assets and accounts payable are proportional to sales, and that relationship will be maintained. Wallace typically uses no current liabilities other than accounts payable. Common stock amounted to $630,000 in 2019, and retained earnings were $330,000. Wallace has arranged to sell $180,000 of new common stock in 2020 to meet some of its financing needs. The remainder of its financing needs will be met by issuing new long-term debt at the end of 2020. (Because the debt is added at the end of the year, there will be no additional interest expense due to the new debt.) Its net profit margin on sales is 5%, and 50% of earnings will be paid out as dividends. What was Wallace's total long-term debt in 2019? Round your answer to the nearest dollar. $ What were Wallace's total liabilities in…arrow_forward
- Solve quicklyarrow_forwardSmiley Corporation's current sales and partial balance sheet are shown below. This year Sales $ 10,000 Balance Sheet: Liabilities Accounts payable $ 2,000 Notes payable $ 2,000 Accruals $ 1,400 Total current liabilities $ 5,400 Long-term bonds $ 2,000 Total liabilities $ 7,400 Common stock $ 1,000 Retained earnings $ 2,500 Total common equity $ 3,500 Total liabilities & equity $ 10,900 Sales are expected to grow by 8% next year. Assuming no change in operations from this year to next year, what are the projected spontaneous liabilities? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to the nearest dollar.arrow_forwardDiscuss in detail the similarities and differences between Preferred Stock and Common Stock. As an investor, which would you rather invest in if you goal is long term wealth maximization?arrow_forward
- Answer itarrow_forwardQUESTION #1: A) What is the Net Operating Profit After Tax (NOPAT) for 2024?B) What is the Operating Cash Flow for 2024? C) What is the Free Cash Flow for 2024? Note: Marketable securities are non-operating current assets, and short-term debt (bank loan) is a non-operating current liability. Both of these items are excluded from the calculation of net operating working capital. D) If the stock trades for $85 per share at the end of 2024, and there are 315,000 shares outstanding, what is the MVA in 2024? E) Given that the firm’s WACC is 14%, what is the EVA during 2024? F) Create common size income statement and balance sheet for 2024, 2023 and 2022. G) Using 2022 as the base year, create income statement and balance sheet percentage change analysis for 2024 and 2023. QUESTION #2: In addition to the AAA Ltd. financial statements in Problem One, you are given more information as follows. Sales are forecast to increase by 80% in 2025. Short-term Debt, Long-term Debt, and Common…arrow_forwardBrightwoodę Furniture provides the following financial data for a given enod: Sales Less Variable E Contribwaon Margin Less Fixed Expenses et Income - Aount ($) Per Unit ($) 150,000 3 L96,000 13 10 35,000 25,000 a. What is the company's CM ratio? b. If quarterly sales increase by $5,200 and there is no change in fixed expenses, by how much would you expect quarterly net operating income to increase?arrow_forward
- If image is blurr then comment i will write values in comment . dont amswer with unclear data i will give unhelarrow_forwardQUESTION #1: ABC Inc. is debating the purchase of a new digital printer that will replace an older printer. The printer they acquired 2 years ago for $500,000 is worth $220,000 today and will have a salvage value of $80,000 after 5 more years. The printer generates revenues of $750,000 per year. The costs of operating the printer are $480,000 per year. The company currently has $110,000 invested in net operating working capital. The investment in net operating working capital will remain at this level for the remaining 5 years of the project. The new printer will cost $830,000. It will cost $60,000 to install the new printer. The new printer will generate revenues of $1,120,000 per year. In addition, the costs of operating the new printer will be $550,000 per year. The company will have to increase its investment in net operating working capital to $175,000 at time zero. The investment in operating new working capital will remain at this level for the remaining 5 years of the…arrow_forwardQUESTION #1: ABC Inc. is debating the purchase of a new digital printer that will replace an older printer. The printer they acquired 2 years ago for $500,000 is worth $220,000 today and will have a salvage value of $80,000 after 5 more years. The printer generates revenues of $750,000 per year. The costs of operating the printer are $480,000 per year. The company currently has $110,000 invested in net operating working capital. The investment in net operating working capital will remain at this level for the remaining 5 years of the project. The new printer will cost $830,000. It will cost $60,000 to install the new printer. The new printer will generate revenues of $1,120,000 per year. In addition, the costs of operating the new printer will be $550,000 per year. The company will have to increase its investment in net operating working capital to $175,000 at time zero. The investment in operating new working capital will remain at this level for the remaining 5 years of the…arrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





