
Concept explainers
(a)
To describe: The chemical transformation which is required to convert glutamate to (2S)-4-amino-2-hydroxybutyrate (AHBA).
Introduction:
Glutamate comes under the category of non-essential amino acid and it contains two carboxyl groups. It is an acidic amino acid which is important part of the neurotransmission process. AHBA (4-amino-2-bydoxy butyrate) it is main component of many antibiotics.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 shows formation of AHBA from glutamate.
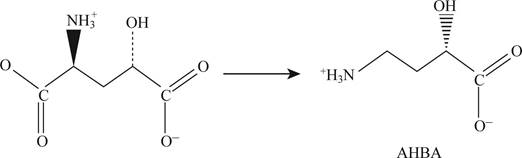
Fig.1: Formation of AHBA from glutamate.
Explanation:
AHBA (4-amino-2-bydoxy butyrate) is formed from the glutamate by the process of decarboxylation. When there is a removal of α-carboxyl group from the glutamate and addition of one –OH group to the γ-carbon then AHBA is formed which is given in Fig. 1.
(b)
To determine: How Btrl can act as an acyl carrier protein with a Coenzyme A prosthetic group.
Introduction:
Coenzyme A is important in the synthesis and oxidation of the fatty acids and it also help in the citric acid cycle during the oxidation of the pyruvate.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
Btrl and acyl carrier proteins have similarities in terms of their sequences. When this compound incubated in CoA conditions it increases its molecular weight. It is because CoA molecule can bind to Btrl molecule when CoA is added to the serine residue (any one) with the replacement of the hydroxyl group with a 4’-phosphopantertheine group
The molecular weight of the CoA is 17;
And the molecular weight of 4’phosphopantetheine is 356;
Molecular mass of purified Btrl protein is 11,812.
So, the overall molecular weight of the Btrl which could act as an acyl carrier protein with a Coenzyme A would be as follows:
This calculated molecular weight is very much close to the observed molecular weight 12,153.
Conclusion:
Btrl can act as an acyl carrier protein with a Coenzyme A because the expected molecular weight is very close to the calculated value of molecular weight which is 12,153.
(c)
To determine: The structures which are consistent with the proposed structure of γ-glutamyl-S-Btrl.
Introduction:
Alpha carboxyl group is any organic molecule group that contains basic amino group and acidic carboxyl group which is very unique to each amino acid.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: Fig. 2 shows glutamyl-S-Btrl.
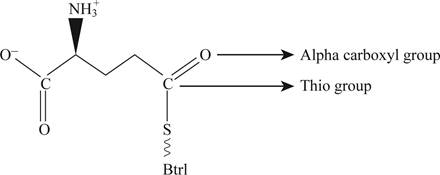
Fig.2: Glutamyl-S-Btrl
Explanation:
One more structure which is consistent is that a thio-ester could formed with the α-carboxyl group which is represented in the Fig. 2. Thio-ester is the compound which has
(d)
To determine: The chemical basis of the γ-glutamyl-S-Btrl can be correct because the alpha carboxyl group might be removed at some stage in the process.
Introduction:
Organic molecule group such as alpha carboxyl group that contains basic amino group and acidic carboxyl group and it is very unique to each amino acid.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
The process of removal of a carboxyl group from a compound is termed as decarboxylation. In many reactions, carboxyl group should be in a free state for an amino acid to be removed. It is very difficult to imagine that decarboxylation process can occur with a carboxyl group in its thio-ester form.
(e)
To determine: The most likely structure of the BtrK species
Introduction:
Decarboxylation is a
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: Fig 3 shows most likely structure of the BtrK
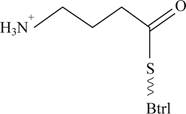
Fig 3: Most likely structure of the BtrK
Explanation:
The molecular species of Mr is 12,240 when the γ-glutymyl-S-Btrl is incubated with purified Btrl.
The molecular species of Mr is 12,281 of γ-glutymyl-S-Btrl.
Therefore,
Due to decarboxylation of the BtrK, carboxyl group would be deleted from the structure and only
(f)
To determine: The molecular structure of the species whose molecular mass is 12,370.
Introduction:
A pure substance is made from molecules with the average geometrical structure. The chemical formula and the structure of a molecule are the two important factors that determine.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representations: Fig 4 shows expected molecular structure of the species whose molecular mass is 12,370.
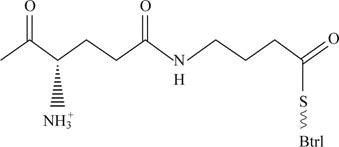
Fig 4: Expected molecular structure of the species whose molecular mass is 12,370.
Explanation:
The Molecular structure of the species whose molecular mass is 12,370 is represented in the figure 4. The molecular species of Mr is 12,240 when the γ-glutymyl-S-Btrl is incubated with purified Btrl. The Molecular structure of the species whose molecular mass is 12,370.
Therefore,
This molecular structure would have free amino group and alpha carboxyl group and thio group will remain in the new species.
(g)
To propose: The plausible pathway for the synthesis of AHBA with the help of enzymes that catalyze each step and any kind of cofactors and substrate required during the pathway.
Introduction:
In the plausible pathways different kind of enzyme and cofactor and substrate are used with the help of these factors a useful product can be synthesized.
(g)
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: Fig.5 shows the plausible pathway for t.he synthesis of AHBA
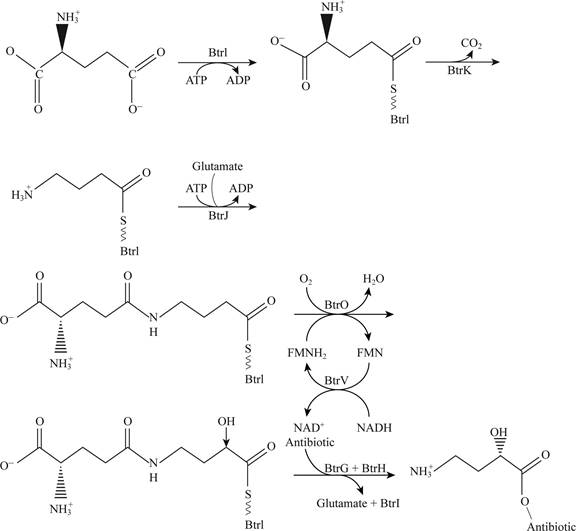
Fig.5: The plausible pathway for the synthesis of AHBA
Explanation:
The plausible pathway for the synthesis of AHBA and respective addition of antibiotics is represented in the Fig. 5. This pathway includes the involvement of co-factor such as ATP, NAD and glutamate amino acid.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
EBK LEHNINGER PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTR
- The reduced coenzymes generated by the citric acid cycle donate electrons in a series of reactions called the electron-transport chain. The energy from the electron-transport chain is used for oxidative phosphorylation. Which compounds donate electrons to the electron- transport chain? H₂O NADH பப NAD+ ATP ADP FADH₂ FAD Which compounds are the final products of the electron-transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation? H₂O NADH NAD+ ΠΑΤΡ Π ADP FADH₂ FAD Which compound is the final electron acceptor in the electron-transport chain? Оно NADH NAD+ ATP ADP FADH₂ FADarrow_forwardHexokinase in red blood cells has a Michaelis constant (KM) of approximately 50 μM. Because life is hard enough as it is, let's assume that hexokinase displays Michaelis-Menten kinetics. What concentration of blood glucose yields an initial velocity (V) equal to 90% of the maximal velocity (Vmax)? [glucose] = What does the calculated substrate concentration at 90% Vmax tell you if normal blood glucose levels range between approximately 3.6 and 6.1 mM? Hexokinase operates near Vmax only when glucose levels are low. Hexokinase normally operates far below Vmax. Hexokinase operates near Vmax only when glucose levels are high. Hexokinase normally operates near Vmax mMarrow_forwardClassify each coenzyme or distinguishing characteristic based on whether it corresponds to catalytic or stoichiometric coenzymes. Catalytic coenzymes Answer Bank Stoichiometric coenzymes lipoic acid FAD used once coenzyme A regenerated thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) NAD+arrow_forward
- The oxidation of malate by NAD+ to form oxaloacetate is a highly endergonic reaction under standard conditions. AG +29 kJ mol¹ (+7 kcal mol-¹) Malate + NAD+ oxaloacetate + NADH + H+ The reaction proceeds readily under physiological conditions. = Why does the reaction proceed readily as written under physiological conditions? The NADH produced during glycolysis drives the reaction in the direction of malate oxidation. The steady-state concentrations of the products are low compared with those of the substrates. The reaction is pushed forward by the energetically favorable oxidation of fumarate to malate. Endergonic reactions such as this occur spontaneously without the input of free energy. Assuming an [NAD+ ]/[NADH] ratio of 8, a temperature of 25°C, and a pH of 7, what is the lowest [malate]/[oxaloacetate] ratio at which oxaloacetate can be formed from malate? [malate] [oxaloacetate]arrow_forwardCalculate and compare the AG values for the oxidation of succinate by NAD+ and FAD. Use the data given in the table to find the E of the NAD+: NADH and fumarate:succinate couples, and assume that E for the enzyme-bound FAD: FADH2 redox couple is nearly +0.05 V. Oxidant Reductant " E' (V) NAD+ NADH + H+ 2 -0.32 Fumarate Succinate AG°' for the oxidation of succinate by NAD+: AG°' for the oxidation of succinate by FAD: 2 -0.03 Why is FAD rather than NAD+ the electron acceptor in the reaction catalyzed by succinate dehydrogenase? The electron-transport chain can regenerate FAD, but not NAD+. FAD is an oxidant, whereas NAD+ is a reductant. The oxidation of succinate requires two NAD+ molecules but only one FAD molecule. The oxidation of succinate by NAD+ is not thermodynamically feasible. kJ mol-1 kJ mol-1arrow_forwardUse the cellular respiration interactive to help you complete the passage. 2,4-dinitrophenol (DNP) was a popular ingredient in diet pills in the 1930s before it was discovered that moderate doses of the compound cause exceptionally high body temperature and even death. Complete the passage detailing how DNP's mechanism of action explains why it causes both high body temperature and weight loss. 2,4-dinitrophenol (DNP) causes of returning to the mitochondrial matrix through to pass directly across the inner mitochondrial membrane instead proteins. Because of DNP's effect on the mitochondrion, less energy is captured in the form of energy is instead wasted as heat. and more protons electrons ATP NADH sugars cytochrome ATP synthase heatarrow_forward
- To answer this question, you may reference the Metabolic Map. Select the reactions of glycolysis in which ATP is produced. 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate 3-phosphoglycerate Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate Fructose 6-phosphate fructose 1,6-bisphosphate Phosphoenolpyruvate pyruvate Glucose glucose 6-phosphate Suppose 17 glucose molecules enter glycolysis. Calculate the total number of inorganic phosphate (P) molecules required as well as the total number of pyruvate molecules produced. P required: pyruvate produced: molecules moleculesarrow_forwardSuppose a marathon runner depletes carbohydrate stores after a four-hour run. The runner's nutritionist suggests replenishing carbohydrate stores by eating carbohydrates. However, the runner is also concerned about weight loss and wants to know if fats can be directly converted into carbohydrates. How should the nutritionist respond to the runner? Yes, the glyoxylate cycle can be used to convert acetyl CoA into succinate, which can then be converted into carbohydrates. No, the two decarboxylation reactions of the citric acid cycle preclude the net conversion of acetyl CoA into carbohydrates. No, the citric acid cycle converts acetyl CoA into oxaloacetate, but there is no pathway to form glucose from oxaloacetate. Yes, pyruvate carboxylase can convert acetyl CoA into pyruvate, which can be used to form glucose through gluconeogenesis.arrow_forwardThe crossover technique can reveal the precise site of action of a respiratory-chain inhibitor. Britton Chance devised elegant spectroscopic methods for determining the proportions of the oxidized and reduced form of each carrier. This determination is feasible because the forms have distinctive absorption spectra, as illustrated in the graph for cytochrome c. Upon the addition of a new inhibitor to respiring mitochondria, the carriers between NADH and ubiquinol (QH2) become more reduced, and those between cytochrome c and O₂ become more oxidized. Where does your inhibitor act? Complex I Complex II Complex III Complex IV Absorbance coefficient (M-1 cm x 10-5) 10 1.0 0.5 400 Reduced Oxidized 500 Wavelength (nm) 600arrow_forward
- Why are the electrons carried by FADH2 not as energy rich as those carried by NADH? FADH2 carries fewer high-energy electrons than NADH. OFADH2 is less negatively charged than NADH. OFADH2 has a lower phosphoryl-transfer potential than NADH. FADH₂ has a lower reduction potential than NADH. What is the consequence of this difference? Electrons flow from NADH to FADH2 before they are transferred to O₂. Electron flow FADH₂ to O, results in the production of more ATP than does electron flow from NADH. Electron flow from FADH₂ to O, pumps fewer protons than does electron flow from NADH. Electron flow from FADH, to O, consumes more free energy than does electron flow from NADH. A simple equation relates the standard free-energy change, AG", to the change in reduction potential, AE. AG=-FAE Then represents the number of transferred electrons, and F is the Faraday constant with a value of 96.48 kJ mol¹ V-¹. Use the standard reduction potentials provided to determine the standard free energy…arrow_forwardMatch each enzyme with its description. catalyzes the formation of isocitrate synthesizes succinyl CoA generates malate generates ATP converts pyruvate into acetyl CoA converts pyruvate into oxaloacetate condenses oxaloacetate and acetyl CoA catalyzes the formation of oxaloacetate synthesizes fumarate catalyzes the formation of a-ketoglutarate Answer Bank succinate dehydrogenase a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase aconitase fumarase citrate synthase malate dehydrogenase pyruvate carboxylase pyruvate dehydrogenase complex isocitrate dehydrogenase succinyl CoA synthetasearrow_forwardcoo ☐ CH2 coo Malonate Determine how the concentration of each citric acid cycle intermediate will change immediately after the addition of malonate. The concentration of citrate will The concentration of isocitrate will The concentration of α-ketoglutarate will The concentration of succinyl CoA will The concentration of succinate will The concentration of fumarate will The concentration of malate will The concentration of oxaloacetate will Why is malonate not a substrate for succinate dehydrogenase? Malonate lacks a thioester bond that has high transfer potential. Malonate has two carboxylic acid groups. Malonate is not large enough to bind to the enzyme. Malonate only has one methylene group.arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON





