
Concept explainers
Estimate ΔH for the following reactions using bond energies given in Table 8.5.
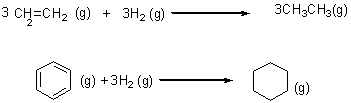
3CH2=CH2(g) + 3H2(g) → 3CH2–CH3(g)
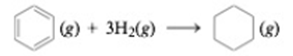
The enthalpies of formation for C6H6(g) and C6H12 (g) are 82.9 and −90.3 kJ/mol. respectively. Calculate ΔH° for the two reactions using standard enthalpies of formation from Appendix 4. Account for any differences between the results obtained from the two methods.
Interpretation:
The estimation has to be done using bond energy values and standard enthalpy of formation values.
Concept Introduction:
Enthalpy is heat content of the system. The value of enthalpy does not depend on the path of a reaction but depend on state of the system. It has a unique value for each state of the system. Thus, enthalpy is a state function. Enthalpy is represented as,
Enthalpy change, denoted by
Where
Energy required to break the existing bonds carries positive sign as energy is supplied to the system and the energy released in formation of new bonds carries negative as energy is removed from the system.
Answer to Problem 158CP
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is,
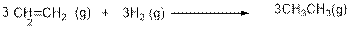
In the above reaction, Hydrogen atoms are added to the
Energy required to break the existing bonds carries positive sign as energy is supplied to the system and the energy released in formation of new bonds carries negative as energy is removed from the system.
Accordingly, the enthalpy change for the above reaction is calculated as –
Enthalpy of formation of ethylene, hydrogen and ethane are
The term “bond energy” and “enthalpy of formation” are not similar. Bond energy refers to energy released or absorbed when isolated elements combine to form a bond. Enthalpy of formation refers to the energy released or absorbed during formation of a compound from other compounds.
Thus, enthalpy of formation of each of the compound on the reactant and product side is widely different from bond energy of the same compounds. Hence enthalpy of reaction calculated using these two different parameters is not same.
The another reaction is,
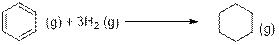
In the above reaction, Hydrogen atoms are added to the
Accordingly, the enthalpy change for the above reaction is calculated as –
Enthalpy of formation of benzene, hydrogen and cyclohexane are
As we discussed earlier, enthalpy of formation of each of the compound on the reactant and product side is widely different from bond energy of the same compounds. Hence enthalpy of reaction calculated using these two different parameters is not same.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Bundle: Chemistry, Loose-Leaf Version, 10th + OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- Li+ is a hard acid. With this in mind, which if the following compounds should be most soluble in water? Group of answer choices LiBr LiI LiF LiClarrow_forwardQ4: Write organic product(s) of the following reactions and show the curved-arrow mechanism of the reactions. Br MeOH OSO2CH3 MeOHarrow_forwardProvide the correct IUPAC name for the compound shown here. Reset cis- 5- trans- ☑ 4-6- 2- 1- 3- di iso tert- tri cyclo sec- oct but hept prop hex pent yl yne ene anearrow_forward
- Q6: Predict the major product(s) for the following reactions. Note the mechanism (SN1, SN2, E1 or E2) the reaction proceeds through. If no reaction takes place, indicate why. Pay attention to stereochemistry. NaCN DMF Br σ Ilm... Br H Br H H NaCN CH3OH KOtBu tBuOH NaBr H₂O LDA Et2O (CH3)2CHOH KCN DMSO NaOH H₂O, A LDA LDA Systemarrow_forwardQ7: For the following reactions, indicate the reaction conditions that would provide the indicated product in a high yield. Note the major reaction pathway that would take place (SN1, SN2, E1, or E2) Note: There may be other products that are not shown. There maybe more than one plausible pathway. Br H3C OH H3C CI ... H3C SCH2CH3 CI i SCH2CH3 ཨ་ Br System Settarrow_forwardQ2: Rank the compounds in each of the following groups in order of decreasing rate of solvolysis in aqueous acetone. OSO2CF3 OSO2CH3 OH a. b. CI Brarrow_forward
- ох 4-tert-butyl oxy cyclohex-1-ene Incorrect, 1 attempt remaining The systematic name of this compound classifies the -OR group as a substituent of the hydrocarbon, which is considered the principal functional group. The ether substituent is named with the suffix 'oxy'. The general format for the systematic name of a hydrocarbon is: [prefix/substituent] + [parent] + [functional group suffix] Substituents are listed in alphabetical order. Molecules with a chiral center will indicate the absolute configuration at the beginning of its name with the R and S notation.arrow_forward5. Compressibility (6 points total). The isothermal compressibility is a measure of how hard/easy it is to compress an object (how squishy is it?) at constant temperature. It is др defined as Br=-()=-(200²)T' (a) You might wonder why there is a negative sign in this formula. What does it mean when this quantity is positive and what does it mean when this quantity is negative? (b) Derive the formula for the isothermal compressibility of an ideal gas (it is very simple!) (c) Explain under what conditions for the ideal gas the compressibility is higher or lower, and why that makes sense.arrow_forward19. (3 pts) in Chapter 7 we will see a reaction of halocyclohexanes that requires that the halogen occupy an axial position with this in mind, would you expect cis-1-bromo-3-methylcyclohexane or trans-1-bromo-3-methylcyclohexane to be more reactive in this reaction? Briefly explain your choice using structures to support your answer. Mere-eries-cecleone) The tran-i-browse-3-methylcyclohexionearrow_forward
- Please help me calculate the undiluted samples ppm concentration. My calculations were 280.11 ppm. Please see if I did my math correctly using the following standard curve. Link: https://mnscu-my.sharepoint.com/:x:/g/personal/vi2163ss_go_minnstate_edu/EVSJL_W0qrxMkUjK2J3xMUEBHDu0UM1vPKQ-bc9HTcYXDQ?e=hVuPC4arrow_forwardProvide an IUPAC name for each of the compounds shown. (Specify (E)/(Z) stereochemistry, if relevant, for straight chain alkenes only. Pay attention to commas, dashes, etc.) H₁₂C C(CH3)3 C=C H3C CH3 CH3CH2CH CI CH3 Submit Answer Retry Entire Group 2 more group attempts remaining Previous Nextarrow_forwardArrange the following compounds / ions in increasing nucleophilicity (least to most nucleophilic) CH3NH2 CH3C=C: CH3COO 1 2 3 5 Multiple Choice 1 point 1, 2, 3 2, 1, 3 3, 1, 2 2, 3, 1 The other answers are not correct 0000arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





