
Concept explainers
Subpart (a):
The budget constraint and trade-off.
Subpart (a):
Explanation of Solution
When the wants and needs of a human are unlimited and the budget of an individual is limited, it will lead to a constraint of needs and this constraint raised is due to the limited budget is known as the budget constraint of an individual. Thus, the budget constraint is defined as the possible combination of goods and services that is purchased at a given price level with the entire income.
Here, the income of the person is given as $60, the price of one meal at dining hall is $6, and the price of cup 'o soup is $1.5. Thus, when the consumer spends her entire income on the meal in dining hall, the quantity that she receives can be calculated by dividing the income by the per meal price as follows:
Thus, when she spends all her income on meal from dining hall, she can buy 10 meals. When she spends all her income on the cup 'o soup meal, the quantity can be calculated by replacing the price of dining hall meal with that of cup 'o soup as follows:
Thus, when she spends all her income on the cup 'o soup meals, she can receive 40 cup 'o soup meals.
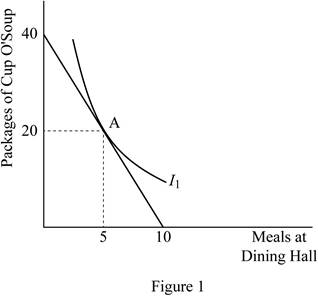
The budget constraint represents all the combinations of these two goods ranging between 10 dining hall meals and no cup 'o soup meal to no dining hall meals and 40 cup 'o soup meals. However in this case, the consumer spends her income equally on both of the commodities. Thus, she spends $30 each on dining hall meals and cup 'o soup meals. Thus, when the consumer spends $30 on the meal in dining hall, the quantity that she receives can be calculated by dividing the income by per meal price as follows:
Thus, when she spends $30 of her income on meal from dining hall, she can buy 5 meals. When she spends $30 of her income on the cup 'o soup meal, the quantity can be calculated by replacing the price of dining hall meal with that of cup 'o soup as follows:
Thus, when she spends $30 of her income on the cup 'o soup meals, she can receive 20 cup 'o soup meals. This will be the point of her consumption, when the income is equally spent on both commodities. The graphical representation shows this combination at point A and it is represented as follows:
Concept introduction:
Budget constraint: Budget constraint is defined as the possible combination of goods and services that is purchased at a given price level with the entire income.
Normal good: The goods whose quantity demanded increases, when the income of the consumer increases and vice versa.
Inferior good: The goods whose quantity demanded falls, when the income of the consumer increases and vice versa.
Giffen goods: They are the special cases of inferior goods in which an income effect overweighs the substitution effect.
Subpart (b):
The budget constraint and trade-off.
Subpart (b):
Explanation of Solution
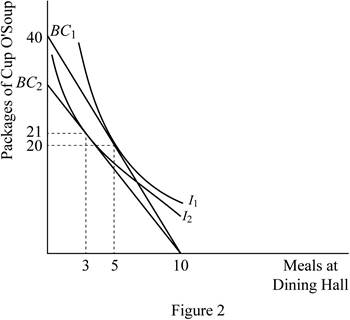
When the price of the cup o' soup increases to $2 from $1.5, the vertical intercept of the student's budget constraint will shift downwards; this will flatten the budget constraint curve. When she spends all her income on the cup 'o soup meal, the quantity can be calculated by replacing the price of dining hall meal with that of cup 'o soup as follows:
Thus, when she spends all her income on the cup 'o soup meals, she can only receive 30 cup 'o soup meals. This flattens the budget constraint curve.
It is also said that at present she only spends 30 percent of her income on the dining hall meal, which means that the income spent on dining hall meal is only $18 and that spend on cup o' soup is $42. At this income spending distribution, she can purchase 3 units of dining hall meals and 21 units of cup o' soup meals. This new point can be illustrated as point B and it can be represented as follows:
Concept introduction:
Budget constraint: Budget constraint is defined as the possible combination of goods and services that is purchased at a given price level with the entire income.
Normal good: The goods whose quantity demanded increases, when the income of the consumer increases and vice versa.
Inferior good: The goods whose quantity demanded falls, when the income of the consumer increases and vice versa.
Giffen goods: They are the special cases of inferior goods in which an income effect overweighs the substitution effect.
Subpart (c):
The budget constraint and trade-off.
Subpart (c):
Explanation of Solution
The initial price of cup o' soup was $1.5, and the new price after the increase is $2. The initial quantity demanded of cup o' soup was 20 units; whereas after the increased price of the commodity, the quantity demanded is 21 units. This shows that the demand for the commodity will increase, when the price of the commodity increases. This shows that the cup o' soup is an inferior good for which the income effect overweighs the substitution effect.
Concept introduction:
Budget constraint: Budget constraint is defined as the possible combination of goods and services that is purchased at a given price level with the entire income.
Normal good: The goods whose quantity demanded increases, when the income of the consumer increases and vice versa.
Inferior good: The goods whose quantity demanded falls, when the income of the consumer increases and vice versa.
Giffen goods: They are the special cases of inferior goods in which an income effect overweighs the substitution effect.
Subpart (d):
The budget constraint and trade-off.
Subpart (d):
Explanation of Solution
The initial price of cup o' soup was $1.5, and the new price after the increase is $2. The initial quantity demanded of cup o' soup was 20 units denoted by point A; whereas after the increased price of the commodity, the quantity demanded is 21 units denoted by point B. This shows that the demand for the commodity will increase, when the price of the commodity increases. Thus, these two points can be graphically illustrated as follows:
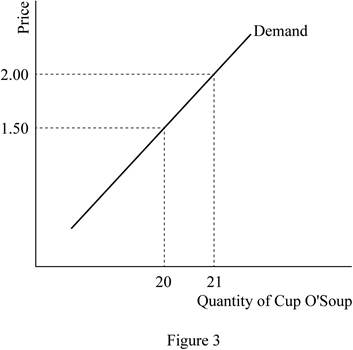
Here, the demand for the cup o' soup increases, when its price increases, which means that the commodity is an inferior good. However at the same time, the income effect overweighs the substitution effect for the commodity, which is a special case of inferior goods, known as the Giffen goods. Thus, the cup o' soup is a Giffen good.
Concept introduction:
Budget constraint: Budget constraint is defined as the possible combination of goods and services that is purchased at a given price level with the entire income.
Normal good: The goods whose quantity demanded increases, when the income of the consumer increases and vice versa.
Inferior good: The goods whose quantity demanded falls, when the income of the consumer increases and vice versa.
Giffen goods: They are the special cases of inferior goods in which an income effect overweighs the substitution effect.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Bundle: Principles of Microeconomics, Loose-Leaf Version, 7th + Aplia, 1 term Printed Access Card
- < Files 9:10 Fri Mar 21 Chapter+11-Public+Goods+and+Common+Res... The Economic Catch-22 By Robert J. Samuelson We are now in the "blame phase" of the economic cycle. As the housing slump deepens and financial markets swing erratically, we've embarked on the usual search for culprits. Who got us into this mess? Our investigations will doubtlessly reveal, as they already have, much wishful thinking and miscalculation. They will also find incompetence, predatory behavior and probably some criminality. But let me suggest that, though inevitable and necessary, this exercise is also simplistic and deceptive. -- business It assumes that, absent mistakes and misdeeds, we might remain in a permanent paradise of powerful income and wealth growth. The reality, I think, is that the economy follows its own Catch-22: By taking prosperity for granted, people perversely subvert prosperity. The more we managers, investors, consumers - think that economic growth is guaranteed and that risk and…arrow_forward2.) Using the line drawing tool, plot and label the isocost line. Carefully follow the instructions above, and only draw the required objects. FILL IN BLANK d. Now suppose the price of labour rises to $5 per unit, but the firm still wants to produce 500 tires per day. Explain how a cost-minimizing firm adjusts to this change (with no change in technology). A cost-minimizing firm will be producing on ▼ The samedifferently slopedparallel isocost line. The firm will use ▼ moresameless labour and ▼ less the same amount of more capital and produce on ▼ a higher point on the same a lower point on the same a lower a higher isoquant curve.arrow_forwardQK Using the graph on the right, determine how the firm should change the quantity of the production factors in order to reduce the costs. The firm that is producing at point A can reduce its costs for producing 2000 units by employing A. same capital and more labour. B. less capital and more labour. ○ C. less capital and the same labour. D. more capital and more labour. OE. more capital and less labour. C A B Q =4000 Q = 2000 C Isocost line QLarrow_forward
- PL Suppose the price ratio is the same along isocost PK lines A and B. In the figure at right, the difference between isocost line A and isocost line B is that A. the total cost is larger along B. B. the total cost is larger along A. OC. labour is relatively more expensive along A. ○ D. the level of output is lower along A. OE. both capital and labour are relatively cheaper along A. Capital B Labourarrow_forwardUsing the graph on the right, determine the per unit prices of capital and labour. 20- Given the information provided about the isocost lines, we know that the per unit price of capital is TC=$100 and the per unit price of labour is 16- TC $80 ○ A. $50; $20 ○ B. $2; $5 ○ C. $5; $2 ○ D. $20; $50 E. not determinable; not determinable Quantity of K 12 TC $60 TC $40 0 10 20 30 Quantity of L 40arrow_forwardThe diagram to the right contains isocost lines A and B. If the price of capital is the same for both lines, then the difference between isocost line A and isocost line B is that OA. the total cost is larger along B. B. the level of output is lower along A. C. both capital and labour are cheaper along A. OD. labour is more expensive along A. ○ E. labour is more expensive along B. Capital Labourarrow_forward
- For the firm whose cost curves are shown at right, the minimum efficient scale is ○ A. between 60 and 140 units of production. OB. about 20 units of production. OC. about 60 units of production. OD. about 100 units of production. OE. the level of fixed cost corresponding to SRATC2. SRATC₁ LRAC SRATC4 SRATC₂ SRATC3 เนด เad iso C 20 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 Output per Periodarrow_forwardSRATC₂ SRATC3 In the figure, increasing long-run average total costs for the firm are confined to the output range OA. where the LRAC curve is downward sloping. B. above 80 units of output. O C. above 50 units of output. OD. between 50 and 80 units of output. SRATC₁ OE. between 10 and 100 units of output. ---- SRATC LRAC 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Output per Periodarrow_forwardFor the firm whose cost curves are shown at right, the minimum efficient scale is OA. between 10 and 50 units of production. OB. about 80 units of production. O C. the level of fixed cost corresponding to SRATC₁. OD. about 10 units of production. ○ E. about 50 units of production. Cost per Unit SRATC₁ LRAC SRATC2 SRATC4 SRATC3 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 Output per Period 90 100arrow_forward
- • 3 different people working at any companies under the BPO industry in the Philippines. • What are the 3 different Vision, Mission, Duties and Responsibilities and Career Path of these people in their companies under the BPO industry?arrow_forwardModule 6 ⚫(1902) Buckner C X | (1902) How to d x (1902) Buckner F X (1902) Productic X WP Videoplayer Canvas Login | Ir x | + Σ R mybrcc.instructure.com/courses/417310/discussion_topics/3420114?module_item_id=20155705 Spring 2025 Home Announcements Modules Syllabus Grades 8 People BRCC-_Library DLASC Module 6 Discussion - Business Costs Relaunch to update For this discussion, think about where you work or a business you have a significant amount of knowledge about. What is a common product that the business sells? What are the main costs the business has to incur in order to be able to sell that product? Which of these costs are fixed and which are variable? How much additional costs would be incurred if it were to sell one additional unit of that product (marginal cost)? Write a discussion thread about this business, the product it commonly sells, and your answers to the above questions. Also, respond to at least two threads created by your classmates. In these responses, share what…arrow_forwardRefer to the video to answer the following: • what are all the key policies or all the strategies the Philippine government should prioritize to accelerate sustainable economic growth? • these should consider the Philippines current economic challenges, including inflation, unemployment, and the need for digital transformation. "The Philippines' Strong Economic Growth" (YouTube link: https://youtu.be/1YtEoGp2ZeM?siJQfIv5kbu0txVsLL.)arrow_forward
 Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning


 Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning





