
Two forces are applied as shown to a hook. Determine graphically the magnitude and direction of their resultant using (a) the parallelogram law, (b) the triangle rule.
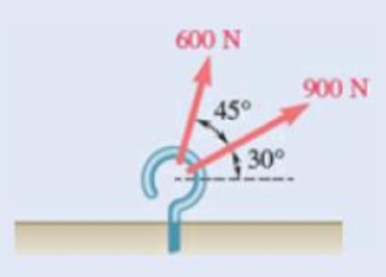
Fig. P2.1
(a)
The magnitude and direction of the resultant force on the hook graphically using the parallelogram law.
Answer to Problem 2.1P
The magnitude of the resultant force on the hook determined graphically using the parallelogram law is
Explanation of Solution
Force is a vector and the addition of vectors can be done using parallelogram law. The parallelogram law of vector addition says that if a parallelogram is constructed using two vectors by taking them as the adjacent sides of the parallelogram by attaching them on the same point, then the diagonal passing through that point gives the sum of the two vectors.
The forces acting on the hook are taken as the adjacent sides of the parallelogram. The diagram is shown in figure 1. In the figure,
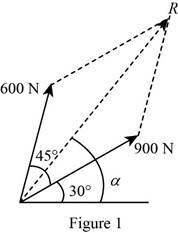
The length of the diagonal of the parallelogram gives the magnitude of the resultant vector and the angle the diagonal makes with the horizontal gives the direction.
Conclusion:
The length of the diagonal is measured to be
Thus, the magnitude of the resultant force on the hook determined graphically using the parallelogram law is
(b)
The magnitude and direction of the resultant force on the hook graphically using the triangle rule.
Answer to Problem 2.1P
The magnitude of the resultant force on the hook determined graphically using the triangle rule is
Explanation of Solution
Force is a vector and one of the graphical methods to obtain the resultant of two vectors is triangle rule. The triangle rule says that the sum of two vectors can be found by arranging the vectors in tip-to-tail fashion and then connecting the tail of the first vector with the tip of the second.
The forces acting on the hook are arranged in tip-to-tail fashion by placing the tail of
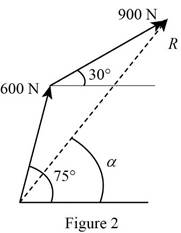
The length of the third side of the triangle formed gives the magnitude of the resultant force. The direction of the resultant force is specified by the angle the third side of the triangle makes with the horizontal.
Conclusion:
The length of the third side of the triangle is measured to be
Thus, the magnitude of the resultant force on the hook determined graphically using the triangle rule is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Starting Out with C++: Early Objects (9th Edition)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
- Box A has a mass of 15 kilograms and is attached to the 20 kilogram Box B using the cord and pulley system shown. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the boxes and surface is 0.2 and the moment of inertia of the pulley is 0.5 kg * m^2. Both boxes are 0.25 m long and 0.25 m high. The cord is attached to the bottom of Box A and the middle of box B. After 2 seconds, how far do the boxes move? A From бро Barrow_forwardSign in PDF Lecture W09.pdf PDF MMB241 - Tutorial L9.pdf File C:/Users/KHULEKANI/Desktop/mmb241/MMB241%20-%20Tutorial%20L9.pdf II! Draw | I│Alla | Ask Copilot + 4 of 4 | D TQ9. If motor M exerts a force of F (10t 2 + 100) N determine the velocity of the 25-kg crate when t kinetic friction between the crate and the plane are μs The crate is initially at rest. on the cable, where t is in seconds, 4s. The coefficients of static and 0.3 and μk = 0.25, respectively. M 3 TQ10. The spring has a stiffness k = 200 N/m and is unstretched when the 25-kg block is at A. Determine the acceleration of the block when s = 0.4 m. The contact surface between the block and the plane is smooth. 0.3 m F= 100 N F= 100 N k = 200 N/m σ Q Q ☆ ا الى 6 ☑arrow_forwardmy ID# is 016948724 please solve this problem step by steparrow_forwardMY ID#016948724 please solve the problem step by spetarrow_forward1 8 4 For the table with 4×4 rows and columns as shown Add numbers so that the sum of any row or column equals .30 Use only these numbers: .1.2.3.4.5.6.10.11.12.12.13.14.14arrow_forwardMY ID# 016948724 please solve this problem step by steparrow_forwardThe pickup truck weighs 3220 Ib and reaches a speed of 30 mi/hr from rest in a distance of 200 ft up the 10-percent incline with constant acceleration. Calculate the normal force under each pair of wheels and the friction force under the rear driving wheels. The effective coefficient of friction between the tires and the road is known to be at least 0.8.arrow_forward1. The figure shows a car jack to support 400kg (W=400kg). In the drawing, the angle (0) varies between 15 and 70 °. The links are machined from AISI 1020 hot-rolled steel bars with a minimum yield strength of 380MPa. Each link consists of two bars, one on each side of the central bearings. The bars are 300mm in length (/) and 25 mm in width (w). The pinned ends have the buckling constant (C) of 1.4 for out of plane buckling. The design factor (nd) is 2.5. (1) Find the thickness (t) of the bars and the factor of safety (n). (2) Check if the bar is an Euler beam. Darrow_forward(Read image)arrow_forwardUNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL DE SAN ANTONIO ABAD DEL CUSCO PRIMER EXAMEN PARCIAL DE MECÁNICA DE FLUIDOS I ............ Cusco, 23 de setiembre de 2024 AP. Y NOMBRES: ........ 1.- Para el tanque de la figura: a) Calcule la profundidad de la hidrolina si la profundidad del agua es de 2.8 m y el medidor del fondo del tanque da una lectura de 52.3kPa. b) Calcule la profundidad del agua si la profundidad de la hidrolina es 6.90 m y el medidor de la parte inferior del tanque registra una lectura de 125.3 kPa. Hidrolina Sp=0.90 Abertura Agua sup suge to but amulor quit y 2.- Calcule la magnitud de la fuerza resultante sobre el área A-B y la ubicación del centro de presión. Señale la fuerza resultante sobre el área y dimensione su ubicación con claridad. 3.5 ft 12 in: Oil (38-0.93) 14 in 8 inarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





