
Concept explainers
Statement of
Direct method: The direct method uses the cash basis of accounting for the preparation of the statement of cash flows. It takes into account those revenues and expenses for which cash is either received or paid.
Cash flows from operating activities: Cash flows from operating activity represent the net cash flows from the general operation of the business by comparing the cash receipt and cash payments.
Cash Receipts: It encompasses all the cash receipts from sale of goods and on account receivable.
Cash Payments: It encompasses all the cash payments that are made to suppliers of goods and all expenses that are paid.
The below table shows the way of calculation of cash flows from operating activities:
| Cash flows from operating activities (Direct method) |
| Add: Cash receipts. |
| Cash receipt from customer |
| Less: Cash payments: |
| To supplier |
| For operating expenses |
| Income tax expenses |
| Net cash provided from or used by operating activities |
Table (1)
Cash flows from investing activities: Cash provided by or used in investing activities is a section of statement of cash flows. It includes the purchase or sale of equipment or land, or marketable securities, which is used for business operations.
The below table shows the way of calculation of cash flows from investing activities:
| Cash flows from investing activities |
| Add: Proceeds from sale of fixed assets |
| Sale of marketable securities / investments |
| Deduct: Purchase of fixed assets/long-lived assets |
| Purchase of marketable securities |
| Net cash provided from or used by investing activities |
Table (2)
Cash flows from financing activities: Cash provided by or used in financing activities is a section of statement of cash flows. It includes raising cash from long-term debt or payment of long-term debt, which is used for business operations.
The below table shows the way of calculation of cash flows from financing activities:
| Cash flows from financing activities |
| Add: Issuance of common stock |
| Proceeds from borrowings |
| Proceeds from issuance of debt |
| Issuance of bonds payable |
| Deduct: Payment of dividend |
| Repayment of debt |
| Interest paid |
| Redemption of debt |
| Repurchase of stock |
| Net cash provided from or used by financing activities |
Table (3)
T-Account: For all the business transactions,
To Prepare: T-account for
Explanation of Solution
Cash Account: (all amounts are in 000s)
| Cash Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Operatingactivities: | December 31, 2016 | Operatingactivities: | |||
| From customers | 414 | To suppliers of goods | 200 | |||
| From investment revenue | 3 | To employees | 78 | |||
| From sale of cash equivalents | 2 | For insurance | 3 | |||
| For bond interest | 21 | |||||
| For income taxes | 35 | |||||
| Investing activities: | Investing activities: | |||||
| Sale of machine components | 17 | Purchase of long-term investment | 25 | |||
| Purchase of land | 23 | |||||
| Financing activities: | Financing activities: | |||||
| Sale of |
75 | Retirement of bonds | 60 | |||
| Payment of dividends | 22 | |||||
| Purchase of treasury stock | 9 | |||||
| Balance | 35 | |||||
Table (4)
| Accounts Receivable Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Decrease in accounts receivable | 4 | ||||
| Balance | 4 | |||||
Table (5)
Prepaid Insurance:
| Prepaid InsuranceAccount | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Decrease in accounts receivable | 4 | ||||
| Balance | 4 | |||||
Table (6)
Inventory:
| Inventory Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Increase in inventory | 5 | ||||
| Balance | 5 | |||||
Table (7)
Investment Revenue Receivable:
| Investment Revenue ReceivableAccount | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Increase in investment revenue receivable | 2 | ||||
| Balance | 2 | |||||
Table (8)
Long-Term Investment:
| Long-Term Investment Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Increase in long-term investment | 31 | ||||
| Purchase of long-term investment | 6 | |||||
| Balance | 25 | |||||
Table (9)
Land:
| Land Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Increase in land | 46 | ||||
| Balance | 46 | |||||
Building and Equipment:
| Building and Equipment Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Increase in building and equipment | 12 | ||||
| December 31, 2016 | Balance | 82 | December 31, 2016 | Machine cost | 70 | |
Table (10)
| Accumulated Depreciation Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Accumulated depreciation | 23 | ||||
| Depreciation | 35 | December 31, 2016 | Balance | 12 | ||
Table (11)
Patent:
| Patent Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Decrease in patent | 2 | ||||
| Balance | 2 | |||||
Table (12)
Accounts Payable:
| Accounts Payable Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Decrease in accounts payable | 15 | ||||
| Balance | 15 | |||||
Table (13)
Salaries Payable:
| Salaries Payable Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Decrease in salary payable | 5 | ||||
| Balance | 5 | |||||
Table (14)
Bond Interest Payable:
| Bond Interest Payable Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Increase in interest payable | 4 | ||||
| Balance | 4 | |||||
Table (15)
Income Tax Payable:
| Income Tax PayableAccount | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Decrease in income tax payable | 2 | ||||
| Balance | 2 | |||||
Table (16)
| Deferred Tax Liability Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Increase in income tax payable | 3 | ||||
| Balance | 3 | |||||
Table (17)
Notes Payable:
| Notes Payable Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Notes payable | 23 | ||||
| Balance | 23 | |||||
Table (18)
Lease Liability:
| Lease Liability Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Lease liability | 82 | ||||
| Balance | 82 | |||||
Table (19)
Bonds Payable:
| Bonds Payable Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Decrease in Bonds payable | 60 | ||||
| Balance | 60 | |||||
Table (20)
Discount on Bonds:
| Discount on Bonds Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Discount on bond | 3 | ||||
| Balance | 3 | |||||
Table (21)
Common stock:
| Common stock Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Common stock | 20 | ||||
| Balance | 20 | |||||
Table (22)
Paid-in Capital:
| Paid-in Capital Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Paid-in capital | 10 | ||||
| Balance | 10 | |||||
Table (23)
Preferred Stock:
| Preferred Stock Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Preferred stock | 75 | ||||
| Balance | 75 | |||||
Table (24)
| Retained Earnings Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2016 | Balance of retained earnings | 15 | |||
| Payment of cash dividend | 22 | Balance | 67 | |||
| Retained earning | 30 | |||||
Table (25)
Treasury Stock:
| Treasury Stock Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Treasury stock | 9 | ||||
| Balance | 9 | |||||
Table (26)
Sales:
| Sales Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Sales revenue | 410 | ||||
| Balance | 410 | |||||
Table (27)
Investment Revenue:
| Investment Revenue Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 |
Investment revenue |
11 | ||||
| Balance | 11 | |||||
Table (28)
Gain on Sale of Treasury Bills:
| Gain on Sale of Treasury Bills Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Gain on sale of treasury bill | 2 | ||||
| Balance | 2 | |||||
Table (29)
Cost of Goods Sold:
| Cost of Goods Sold Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Cost of Goods Sold | 180 | ||||
| Balance | 180 | |||||
Table (30)
Salaries Expense:
| Salaries Expense Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Salaries Expense | 73 | ||||
| Balance | 73 | |||||
Table (31)
Depreciation Expense:
| Depreciation Expense Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Depreciation Expense | 12 | ||||
| Balance | 12 | |||||
Table (32)
Patent Amortization Expense:
| Patent Amortization ExpenseAccount | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Patent amortization expense | 2 | ||||
| Balance | 2 | |||||
Table (33)
Insurance Expense:
| Insurance Expense Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Insurance expense | 7 | ||||
| Balance | 7 | |||||
Table (34)
Bond Interest Expense:
| Bond Interest ExpenseAccount | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Bond Interest Expense | 28 | ||||
| Balance | 28 | |||||
Table (35)
Income Tax Expense:
| Income Tax Expense Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Income Tax Expense | 36 | ||||
| Balance | 36 | |||||
Table (36)
Loss on Machine Damage:
| Loss on Machine Damage Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Loss on machine damage | 18 | ||||
| Balance | 18 | |||||
Table (37)
Net income (income summary):
| Net Income (income summary)Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Net income | 67 | ||||
| Balance | 67 | |||||
Table (38)
To Prepare: The statement of cash flows from operating activities using direct method for A Company for the year ended December 31, 2016.
Answer to Problem 21.21P
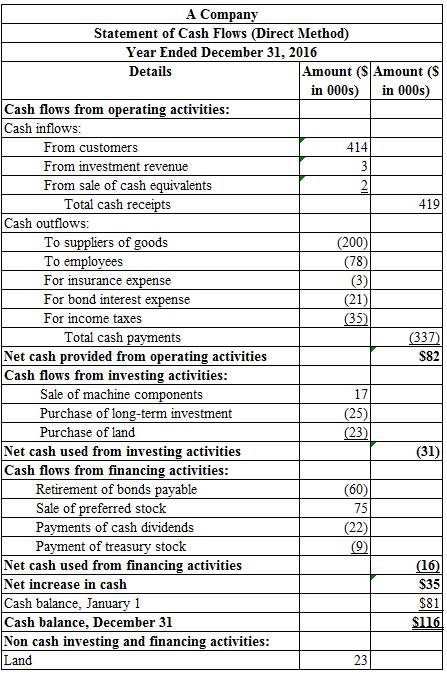
Figure (1)
Explanation of Solution
Working notes:
Calculate the amount of cash received from customers:
Calculate the amount of investment revenue:
Calculate the amount of cash paid to suppliers:
Calculate the amount of cash paid to employees:
Calculate the amount of cash paid for insurance:
Calculate the amount of cash paid for bond interest:
Calculate the amount of cash paid for income taxes:
Calculate the amount of retirement of bonds payable:
Calculate the amount of cash dividend:
Step 1: Calculate the amount of totaldividend.
Step 2: Calculate the amount of stock dividend.
Step 3: Calculate the amount of cash dividend:
The statement of cash flows of Company S shows opening balance of cash flows in the year 2015 as $81million and the closing balance of cash in the year 2016 as $116 million.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
INTERMEDIATE ACCT.-CONNECT PLUS ACCESS
- Please given correct answer for General accounting question I need step by step explanationarrow_forwardThe following VAT balances were extracted from the subsidiary journals of Africa Traders as at 28 February 2024. R Cash receipts journal VAT input 556,50 VAT output 14 676,48 Cash payments journal VAT input 9 375,12 VAT output 642,78 Purchases journal VAT 6 260,40 Sales journal VAT 8 037,12 Purchases returns journal VAT 871,75 Sales returns journal VAT 902,32 On 1 February 2024, the VAT input account had a debit opening balance of R14 768 and the VAT output account had a credit opening balance of R14 154. Calculate the closing balance of the VAT output account as at 28 February 2024arrow_forwardHelp me tutor to solve questions. Give correct general accounting answerarrow_forward
- Hi expert please given correct answer with accountingarrow_forwardVista Motors has a total asset turnover of 2.9, a net profit margin of 6.25 percent, and an equity multiplier of 3.6. Calculate Vista's return on equity (ROE) using the DuPont equation. (Financial accounting)arrow_forwardWhat is the gross margin? Financial accountingarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





