
Concept explainers
Statement of
Direct method: The direct method uses the cash basis of accounting for the preparation of the statement of cash flows. It takes into account those revenues and expenses for which cash is either received or paid.
Cash flows from operating activities: Cash flows from operating activity represent the net cash flows from the general operation of the business by comparing the cash receipt and cash payments.
Cash Receipts: It encompasses all the cash receipts from sale of goods and on account receivable.
Cash Payments: It encompasses all the cash payments that are made to suppliers of goods and all expenses that are paid.
The below table shows the way of calculation of cash flows from operating activities:
| Cash flows from operating activities (Direct method) |
| Add: Cash receipts. |
| Cash receipt from customer |
| Less: Cash payments: |
| To supplier |
| For operating expenses |
| Income tax expenses |
| Net cash provided from or used by operating activities |
Table (1)
Cash flows from investing activities: Cash provided by or used in investing activities is a section of statement of cash flows. It includes the purchase or sale of equipment or land, or marketable securities, which is used for business operations.
The below table shows the way of calculation of cash flows from investing activities:
| Cash flows from investing activities |
| Add: Proceeds from sale of fixed assets |
| Sale of marketable securities / investments |
| Deduct: Purchase of fixed assets/long-lived assets |
| Purchase of marketable securities |
| Net cash provided from or used by investing activities |
Table (2)
Cash flows from financing activities: Cash provided by or used in financing activities is a section of statement of cash flows. It includes raising cash from long-term debt or payment of long-term debt, which is used for business operations.
The below table shows the way of calculation of cash flows from financing activities:
| Cash flows from financing activities |
| Add: Issuance of common stock |
| Proceeds from borrowings |
| Proceeds from issuance of debt |
| Issuance of bonds payable |
| Deduct: Payment of dividend |
| Repayment of debt |
| Interest paid |
| Redemption of debt |
| Repurchase of stock |
| Net cash provided from or used by financing activities |
Table (3)
T-Account: For all the business transactions,
To Prepare: T-account for
Explanation of Solution
Cash Account: (all amounts are in 000s)
| Cash Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Operatingactivities: | December 31, 2016 | Operatingactivities: | |||
| From customers | 203 | To suppliers of goods | 132 | |||
| From dividend received | 2 | To employees | 28 | |||
| For interest | 5 | |||||
| For income taxes | 18 | |||||
| Investing activities: | Investing activities: | |||||
| Sale of building | 7 | Purchase of long-term investment | 5 | |||
| Purchase of equipment | 15 | |||||
| Financing activities: | Financing activities: | |||||
| Sale of bonds payable | 25 | Payment of dividends | 13 | |||
| Purchase of |
8 | |||||
| Balance | 13 | |||||
Table (4)
Accounts Receivable:
| Accounts Receivable Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Decrease in accounts receivable | 3 | ||||
| Balance | 3 | |||||
Table (5)
Inventory:
| Inventory Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Increase in inventory | 5 | ||||
| Balance | 5 | |||||
Table (6)
Dividend Receivable:
| Dividend ReceivableAccount | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Increase in dividend receivable | 1 | ||||
| Balance | 1 | |||||
Table (7)
Long-Term Investment:
| Long-Term InvestmentAccount | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Increase in long-term investment | 5 | ||||
| Balance | 5 | |||||
Table (8)
Land:
| Land Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Increase in land | 30 | ||||
| Balance | 30 | |||||
Table (9)
Building and Equipment:
| Building and Equipment Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Decrease in building and equipment | 25 | ||||
| December 31, 2016 | Purchase of equipment | 15 | Balance | 40 | ||
Table (10)
| Accumulated Depreciation Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Accumulated depreciation | 25 | ||||
| Depreciation | 30 | December 31, 2016 | Balance | 5 | ||
Table (11)
Accounts Payable:
| Accounts Payable Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Decrease in accounts payable | 7 | ||||
| Balance | 7 | |||||
Table (12)
Salary Payable:
| Salary Payable Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Decrease in salary payable | 3 | ||||
| Balance | 3 | |||||
Table (13)
Interest Payable:
| Interest Payable Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Increase in interest payable | 2 | ||||
| Balance | 2 | |||||
Table (14)
Income Tax Payable:
| Income Tax PayableAccount | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Decrease in income tax payable | 1 | ||||
| Balance | 1 | |||||
Table (15)
Notes Payable:
| Notes Payable Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Notes payable | 30 | ||||
| Balance | 30 | |||||
Table (16)
Bonds Payable:
| Bonds Payable Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Bonds payable | 25 | ||||
| Balance | 25 | |||||
Table (17)
Discount on Bonds:
| Discount on BondsAccount | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Discount on bond | 1 | ||||
| Balance | 1 | |||||
Table (18)
Common stock:
| Common stock Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Common stock | 10 | ||||
| Balance | 10 | |||||
Table (19)
Paid-in Capital:
| Paid-in Capital Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Paid-in capital | 4 | ||||
| Balance | 4 | |||||
Table (20)
| Retained Earnings Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Balance of retained earnings | 2 | December 31, 2016 | |||
| Payment of cash dividend | 13 | Balance | 25 | |||
| Retained earning | 14 | |||||
Table (21)
Treasury Stock:
| Treasury Stock Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Treasury stock | 8 | ||||
| Balance | 8 | |||||
Table (22)
Sales:
| Sales Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Sales revenue | 200 | ||||
| Balance | 200 | |||||
Table (23)
Dividend Revenue:
| Dividend RevenueAccount | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Dividend revenue | 3 | ||||
| Balance | 3 | |||||
Table (24)
Cost of Goods Sold:
| Cost of Goods Sold Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Cost of Goods Sold | 120 | ||||
| Balance | 120 | |||||
Table (28)
Salaries Expense:
| Salaries ExpenseAccount | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Salaries Expense | 25 | ||||
| Balance | 25 | |||||
Table (29)
Depreciation Expense:
| Depreciation Expense Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Depreciation Expense | 5 | ||||
| Balance | 5 | |||||
Table (30)
| Bad debt Expense Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Bad debt Expense | 3 | ||||
| Balance | 3 | |||||
Table (31
Interest Expense:
| Interest ExpenseAccount | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | InterestExpense | 8 | ||||
| Balance | 8 | |||||
Table (32)
Loss on Sale of Building:
| Loss on Sale of BuildingAccount | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Loss on sale of building | 3 | ||||
| Balance | 3 | |||||
Table (33)
Income Tax Expense:
| Income Tax Expense Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Income Tax Expense | 17 | ||||
| Balance | 17 | |||||
Table (34)
Net income (income summary):
| Net Income (income summary)Account | ||||||
| Date | Details |
Debit ($) | Date | Details |
Credit ($) |
|
| December 31, 2016 | Net income | 25 | ||||
| Balance | 25 | |||||
Table (35)
To Prepare: The statement of cash flows using direct method for D Company for the year ended December 31, 2016.
Answer to Problem 21.19P
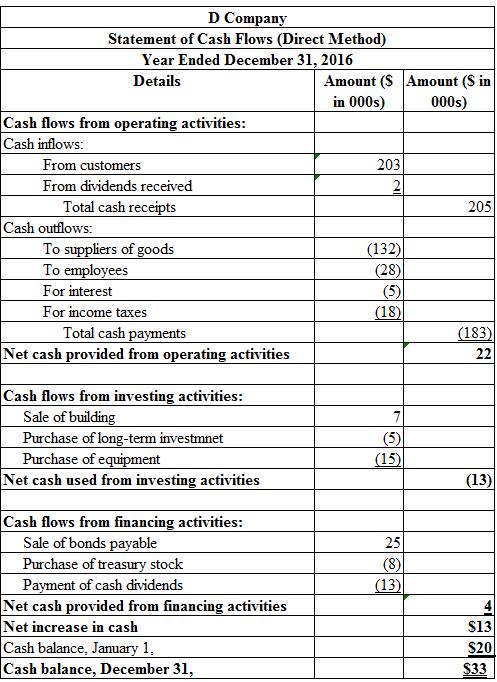
Figure (1)
Explanation of Solution
Working notes:
Calculate the amount of cash received from customers:
Calculate the amount of dividend received:
Calculate the amount of cash paid to suppliers:
Calculate the amount of cash paid to employee expenses:
Calculate the amount of cash paid for interest expense:
Calculate the amount of cash paid for income taxes:
Calculate the amount of purchaseof long-term investment:
Calculate the amount of proceeds from sale of bonds payable:
Hence, the opening cash balance is $20 million and closing cash balance is $33 million.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
INTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING
- If beginning and ending work in process inventories are $12,500 and $21,700, respectively, and cost of goods manufactured is $215,000, what is the total manufacturing cost for the period? HELParrow_forwardI need help with this solution and general accounting questionarrow_forwardCompute the gross profitarrow_forward
- Can you solve this general accounting problem with appropriate steps and explanations?arrow_forwardWhich of the following is an example of a non-operating income item? a) Sales revenueb) Interest incomec) Wages expensed) Cost of goods soldarrow_forwardDuring October, Department X started and completed 92,000 units and also finished 28,000 units that were 60% completed on September 30. On October 31, Department X's ending inventory consisted of 25,000 units that were 40% completed. All manufacturing costs are incurred at a uniform rate throughout Department X's production process. Compute the number of equivalent full units of production for Department X during October. (FIFO Method)arrow_forward
- If beginning and ending work in process inventories are $12,500 and $21,700, respectively, and cost of goods manufactured is $215,000, what is the total manufacturing cost for the period?arrow_forwardCorrect Answerarrow_forwardI need guidance with this general accounting problem using the right accounting principles.arrow_forward
- Hello tutor solve this question and accounting questionarrow_forwardWhat is goodwill in accounting? a) The value of a company’s brand and reputationb) The excess of the fair value of assets acquired over their book valuec) The amount a company earns from its operationsd) The cost of capital used in financing a businessarrow_forwardI am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with appropriate explanations.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





