
The budget constraint of the consumer.
Explanation of Solution
The budget constraint is the constraint which is due to the budget of the individual. The human wants and needs are unlimited and when the budget of the individual is not unlimited, it will lead to the constraint of needs and this constraint raised due to the limited budget is known as the budget constraint of the individual. Thus, a budget constraint will represent all the possible combinations of two commodities that an individual can consume at the given market prices and with all his income in hand.
Here, the income of the person is given as $3,000, the
Thus, when she spends all her income on cheese, she can buy 500 pounds of cheese. When she spends all her income on the wine, the quantity can be calculated by replacing the price of cheese with that of wine as follows:
Thus, when she spends all her income on wine, she can receive 1,000 glasses of wine.
The budget constraint represents all the combinations of these two goods ranging between 500 pounds of cheese and no wine to no cheese and 1,000 glasses of wine. The vertical axis represents wine and the horizontal represents cheese on our diagram. The 500 pounds of cheese and no wine point represent the horizontal intercept and the no cheese and 1,000 glasses of wine represent the vertical intercept. The budget constraint can be drawn as follows:
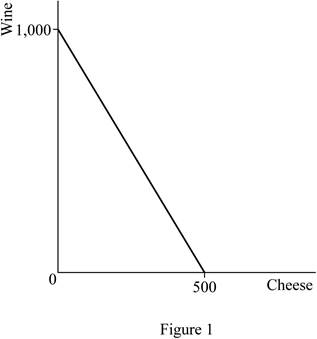
The slope of the budget constraint is the rise over the run. It can be calculated by dividing the negative vertical intercept (represented by –b) by the horizontal intercept (represented by a) as follows:
Thus, the slope of the budget constraint is -2.
Concept introduction:
Budget constraint: It represents all the combinations of two goods that the consumer can consume with the given price level and the income in the hands of the individual.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
EBK PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS
- In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. 8. How does monetary policy supposedly translate into changes in AD?arrow_forwardIn a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. 2. Carefully explain either Keynes’ “cookie jar” motive for holding money or the “saw-toothed model’s” motive for holding a safety stock.arrow_forwardIn a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. 7.Carefully explain the Fisher equation for interest rates. What insight does it provide?arrow_forward
- In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. 3. Describe the general architecture of the Federal Reserve System.arrow_forwardIn a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. 1. Define money. Carefully explain the three functions of money.arrow_forwardIn a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. 5.Draw the Federal Reserve System’s Balance Sheet and briefly explain each of the main (highlighted in the PowerPoints and text) components.arrow_forward
- In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. 9. What are monetary rules? How are they carried out and what is the difference between monetary rules and discretionary behavior?arrow_forwardIn a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. 4. What is interest payment on reserve balances used for? How does it work?arrow_forwardA linear programming computer package is needed. As part of the settlement for a class action lawsuit, Hoxworth Corporation must provide sufficient cash to make the following annual payments (in thousands of dollars). Year 1 2 3 4 5 6 Payment 170 195 220 265 295 440 The annual payments must be made at the beginning of each year. The judge will approve an amount that, along with earnings on its investment, will cover the annual payments. Investment of the funds will be limited to savings (at 4% annually) and government securities, at prices and rates currently quoted in The Wall Street Journal. Hoxworth wants to develop a plan for making the annual payments by investing in the following securities (par value = $1,000). Funds not invested in these securities will be placed in savings. Security Current Price Rate (%) Years to Maturity 1 $1,055 6.750 3 2 $1,000 5.125 4 Assume that interest is paid annually. The plan will be submitted to the judge and, if approved,…arrow_forward
- On the 1st of April 2018, the South African National Treasury increase the value-added tax rate from 14% to 15%. This policy change had a wide-ranging impact on society. Discuss some of the benefits and drawbacks of making use of this type of tax to generate government revenue and what we may expect in terms of its impact on inflation and GDP growth within the economy. Please use some of the economics graphs to explain some scenariosarrow_forwardEskom is South Africa’s monopoly power producer which the majority of South Africans depend on. Suppose there is extensive deregulation in the power industry. What is the impact of this deregulation on the industry? Help me on discussing the new market structure as well as the impact on supply and demand. Use the relevant diagrams.arrow_forwardDiscuss the impact of exchange rate volatility on the economy and its impact on your organisation. Make use of the relevant diagrams.arrow_forward
 Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305971493Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305971493Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning

 Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning





