
Binomial model* Over the coming year, Ragwort’s stock price will halve to $50 from its current level of $100 or it will rise to $200. The one-year interest rate is 10%.
- a. What is the delta of a one-year call option on Ragwort stock with an exercise price of $100?
- b. Use the replicating-portfolio method to value this call.
- c. In a risk-neutral world, what is the probability that Ragwort stock will rise in price?
- d. Use the risk-neutral method to check your valuation of the Ragwort option.
- e. If someone told you that in reality there is a 60% chance that Ragwort’s stock price will rise to $200, would you change your view about the value of the option? Explain.
a.
To compute: The delta of one year call option on R stock with a strike price of $100.
Explanation of Solution
The formula to calculate delta is:
The calculation of delta is as follows:
b.
To discuss: Apply the replicating portfolio technique to value this call.
Explanation of Solution
The replicating portfolio technique of valuing call is as follows.
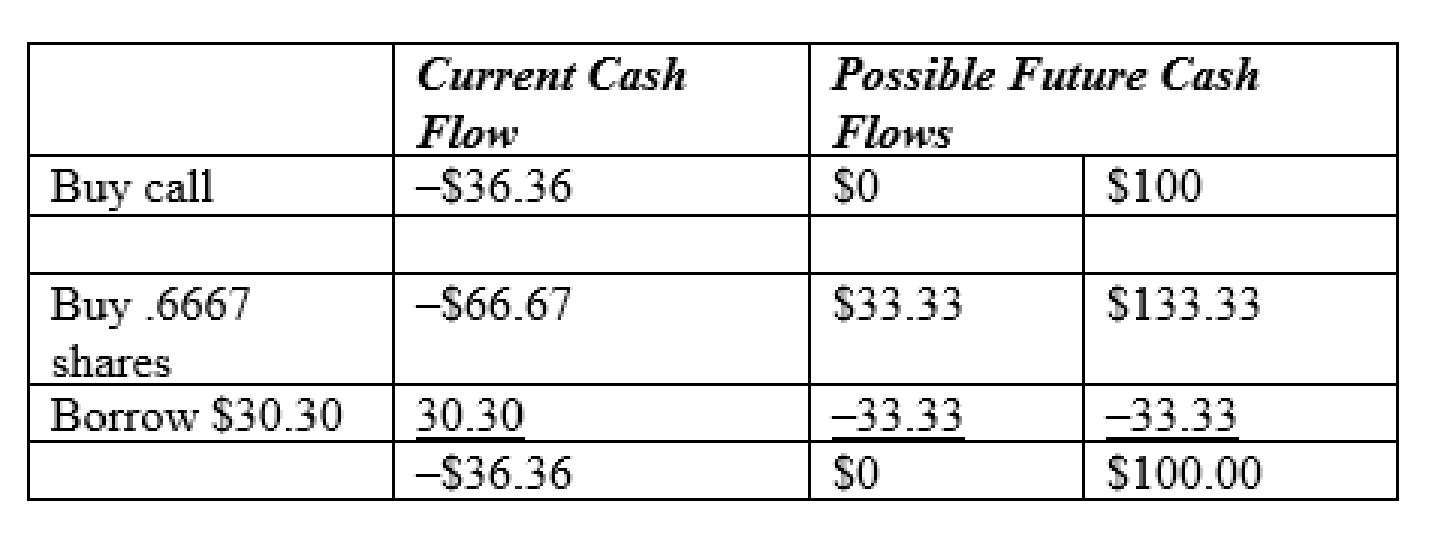
c.
To discuss: The probability of increasing stock R price in a risk neutral world.
Explanation of Solution
The probability of increasing stock R calculated as follows:
The computation as follows:
Foot note: The probability is calculated on the basis of expected return.
d.
To compute: The value of stock R using the risk neutral method.
Explanation of Solution
The option value is calculated using the following formula:
Hence, the value of call is $36.36
e.
To discuss: Whether person X change his option regarding the value of option.
Explanation of Solution
Person X does not change his opinion regarding the value of option. The chance of price increase is most likely higher than the risk- neutral probability, but it does not aid to value the option.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Principles of Corporate Finance
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Operations Management: Processes and Supply Chains (12th Edition) (What's New in Operations Management)
Marketing: An Introduction (13th Edition)
Intermediate Accounting (2nd Edition)
Horngren's Accounting (12th Edition)
Principles Of Taxation For Business And Investment Planning 2020 Edition
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
 Pfin (with Mindtap, 1 Term Printed Access Card) (...FinanceISBN:9780357033609Author:Randall Billingsley, Lawrence J. Gitman, Michael D. JoehnkPublisher:Cengage Learning
Pfin (with Mindtap, 1 Term Printed Access Card) (...FinanceISBN:9780357033609Author:Randall Billingsley, Lawrence J. Gitman, Michael D. JoehnkPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Fundamentals Of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781337902571Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals Of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781337902571Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781285065137Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781285065137Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781305635937Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781305635937Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning





