
Concept explainers
Figure 21−9 shows a compound gear train. Gears B and C are keyed to the same shaft; therefore, they turn at the same speed. Gear A and gear C are driving gears. Gear B and gear D are driven gears. Set up a proportion for each problem and determine the unknown values, x, y, and z in the table. Round the answers to 1 decimal place where necessary.
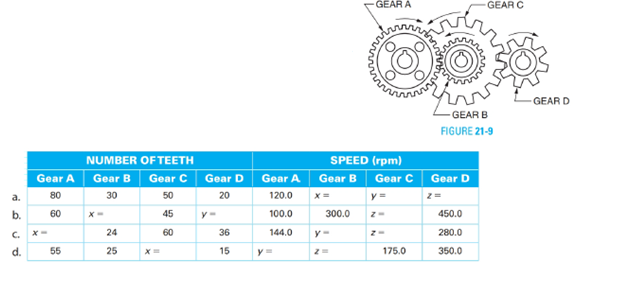
(a)
To find the speed of the different gears given in the problem.
Answer to Problem 16A
Speed of gear B is
Speed of gear C is
Speed of gear D is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
A gear and pinion arrangement is given as below.
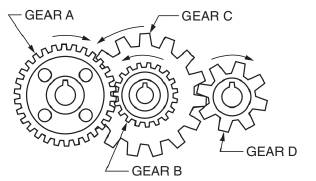
Calculation:
We have been given below information,
As we know that in a gear arrangement,
13
So,
Hence, speed of gear B is
Since, gear B and C are on same shaft. So, speed of both gear is equal.
Therefore, speed of gear C is
Again,
Hence, speed of gear D is
Thus, speed of gear B is
Speed of gear C is
Speed of gear D is
(b)
To find the number of teeth in the gear and the speed of the gear.
Answer to Problem 16A
Number of teeth in gear B is
Number of teeth in gear D is
Speed of gear C is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
A gear and pinion arrangement is given as below.
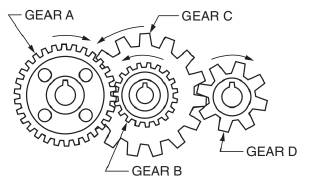
Calculation:
We have been given below information,
As we know that in a gear arrangement,
So,
Hence, number of teeth in gear B is
Since, gear B and C are on same shaft. So, speed of both gear is equal.
Therefore, speed of gear C is
Again,
Hence, number of teeth in gear D is
Thus, number of teeth in gear B is
Number of teeth in gear D is
Speed of gear C is
(c)
To find the number of teeth as well as speed of the gear.
Answer to Problem 16A
Number of teeth in gear A is
Speed of gear B is
Speed of gear C is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
A gear and pinion arrangement is given as below.
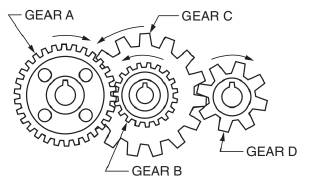
Calculation:
We have been given below information,
As we know that in a gear arrangement,
So,
Since, gear B and C are on same shaft. So, speed of both gear is equal. i.e.
Again,
Hence, speed of gear B and gear C is
Putting,
Thus, number of teeth in gear A is
Speed of gear B is
Speed of gear C is
(d)
To find the speed of the different gears and the number of teeth.
Answer to Problem 16A
Number of teeth in gear C is
Speed of gear A is
Speed of gear B is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
A gear and pinion arrangement is given as below.
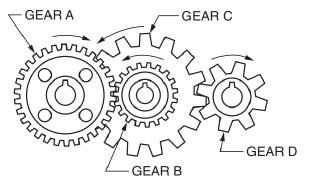
Calculation:
We have been given below information,
As we know that in a gear arrangement,
So,
Since, gear B and C are on same shaft. So, speed of both gear is equal. i.e.
Putting
Hence, speed of gear A is
Again,
Hence, number of teeth in gear C is
Thus, number of teeth in gear C is
Speed of gear A is
Speed of gear B is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Mathematics For Machine Technology
- Let v₁ = (2,-3,7,8), v2 = (3, 10, -6, 14), v3 = (0, 19, -2, 16), and v₁ = (9, -2, 1, 10). Is the set {V1, V2, V3, V4} a basis for R4? Of the two sets S = {(3x-5y, 4x + 7y, x+9y): x, y = R} and T = {2x-3y+z, -7x-3y²+z, 4x + 3z): x, y, z = R} which is a subspace of R3? (S, T, both, neither) Justify.arrow_forwardFind a basis and dimension for the null space of the following matrix: 3 -2 0 7 -2 1-1 1 5 3 19-2 8 06 1 -2 -4 -5-6 -9 4-6 11 6 Find a basis and dimension for the column space of the same matrix (above).arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- please answer the questions below ands provide the required codes in PYTHON. alsp provide explanation of how the codes were executed. Also make sure you provide codes that will be able to run even with different parameters as long as the output will be the same with any parameters given. these questions are not graded. provide accurate codes pleasearrow_forwardCould you please help me answer the follwoing questionsarrow_forwardWhat is Poisson probability? What are 3 characteristics of Poisson probability? What are 2 business applications of Poisson probability? Calculate the Poisson probability for the following data. x = 3, lambda = 2 x = 2, lambda = 1.5 x = 12, lambda = 10 For the problem statements starting from question 6 onward, exercise caution when entering data into Microsoft Excel. It's essential to carefully evaluate which value represents x and which represents λ. A call center receives an average of 3 calls per minute. What is the probability that exactly 5 calls are received in a given minute? On average, 4 patients arrive at an emergency room every hour. What is the probability that exactly 7 patients will arrive in the next hour? A production line produces an average of 2 defective items per hour. What is the probability that exactly 3 defective items will be produced in the next hour? An intersection experiences an average of 1.5 accidents per month. What is the probability that…arrow_forward
- (Nondiagonal Jordan form) Consider a linear system with a Jordan form that is non-diagonal. (a) Prove Proposition 6.3 by showing that if the system contains a real eigenvalue 入 = O with a nontrivial Jordan block, then there exists an initial condition with a solution that grows in time. (b) Extend this argument to the case of complex eigenvalues with Reλ = 0 by using the block Jordan form Ji = 0 W 0 0 3000 1 0 0 1 0 ω 31 0arrow_forwardYou manage a chemical company with 2 warehouses. The following quantities of Important Chemical A have arrived from an international supplier at 3 different ports: Chemical Available (L) Port 1 400 Port 2 110 Port 3 100 The following amounts of Important Chemical A are required at your warehouses: Warehouse 1 Warehouse 2 Chemical Required (L) 380 230 The cost in£to ship 1L of chemical from each port to each warehouse is as follows: Warehouse 1 Warehouse 2 Port 1 £10 Port 2 £20 Port 3 £13 £45 £28 £11 (a) You want to know how to send these shipments as cheaply as possible. For- mulate this as a linear program (you do not need to formulate it in standard inequality form) indicating what each variable represents. (b) Suppose now that all is as in the previous question but that only 320L of Important Chemical A are now required at Warehouse 1. Any excess chemical can be transported to either Warehouse 1 or 2 for storage, in which case the company must pay only the relevant transportation…arrow_forwardSuppose we have a linear program in standard equation form maximize cx subject to Ax = b, x > 0. and suppose u, v, and w are all optimal solutions to this linear program. (a) Prove that z = u+v+w is an optimal solution. (b) If you try to adapt your proof from part (a) to prove that that u+v+w is an optimal solution, say exactly which part(s) of the proof go wrong. (c) If you try to adapt your proof from part (a) to prove that u+v-w is an optimal solution, say exactly which part(s) of the proof go wrong.arrow_forward
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9780998625713Author:Lynn Marecek, MaryAnne Anthony-SmithPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
Elementary AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9780998625713Author:Lynn Marecek, MaryAnne Anthony-SmithPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,





