
Concept explainers
1.
To prepare: Sale budget of D Company.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Statement that shows the sales budget of D Company
| D Company | ||||
| Sales Budget | ||||
| Particulars | January ($) | February ($) | March ($) | Total ($) |
| Sales unit (A) | 7,000 | 9,000 | 11,000 | 27,000 |
| Selling price Per unit (B) | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 |
| Total sales | 385,000 | 495,000 | 605,000 | 1,485,000 |
| Table (1) | ||||
2.
To prepare: Purchase budget of D Company.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Statement that shows the purchase budget of D Company
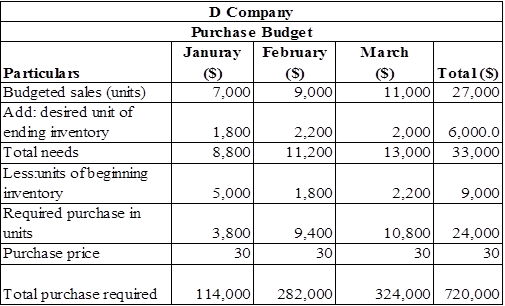
Table (2)
3.
To prepare: Selling expense budget of D Company.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Statement that shows the selling expense budget of D Company,
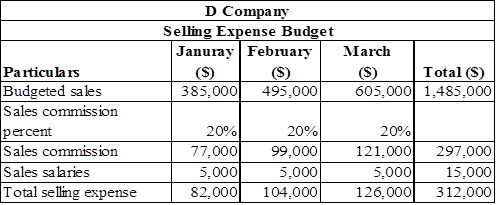
Table (3)
4.
To prepare: General and administrative expense budget of D Company.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Statement that shows the General and administrative expense budget of D Company
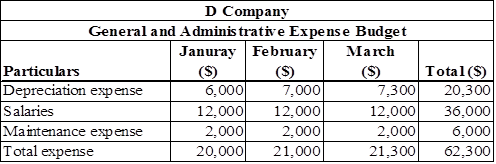
Table (4)
Working notes:
Statement that shows the
| Particulars | January ($) | February ($) | March ($) | |
| Equipment in Beginning | 540,000 | 576,000 | 672,000 | |
| Add: Purchase of Equipment | 36,000 | 96,000 | 28,800 | |
| Less: equipment at the end | 576,000 | 672,000 | 700,800 | |
| Depreciation | 6,000 | 7,000 | 7,300 | |
| Table (5) | ||||
5.
To prepare: Capital expenditure budget of D Company.
5.
Explanation of Solution
Statement that shows the capital expenditure budget of D Company
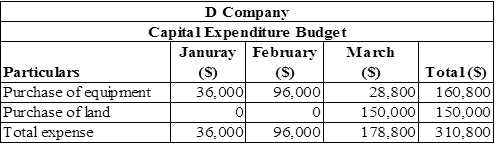
Table (6)
6.
To prepare:
6.
Explanation of Solution
Statement that shows the Cash budget of D Company
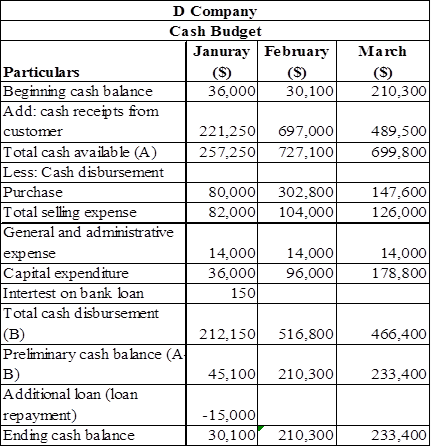
Table (7)
Working notes:
Calculation of expected cash collection
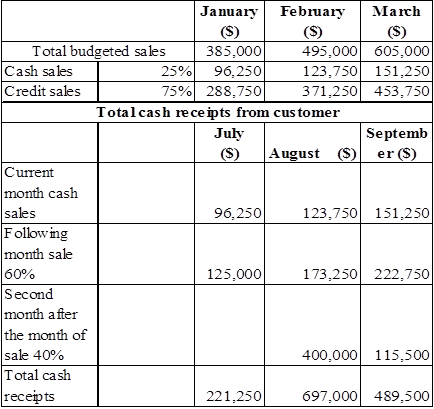
Table (8)
Calculation of cash payment from purchase,
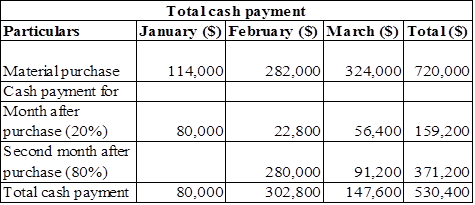
Table (9)
7.
To prepare:
7.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare income statement.
| D Company | ||||
| Income Statement | ||||
| For three months ended March 31,2018 | ||||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) | ||
| Sales | 1,485,000 | |||
| Less: Cost of goods sold | 810,000 | |||
| Gross profit | 675,000 | |||
| Less: Operating expenses | ||||
| Total selling expense | 312,000 | |||
| General administrative salary | 62,300 | |||
| Interest on bank loan | 150 | |||
| Total operating expense | 374,450 | |||
| Earnings before taxes (A) | 300,550 | |||
| Less: Income tax | 120,220 | |||
| Net income | 180,330 | |||
| Table (10) | ||||
Thus, budgeted net income of D Company is $180,330.
8.
To prepare: Budgeted
8.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare balance sheet
| D Company | ||||
| Balance sheet | ||||
| For three months ended March 31,2018 | ||||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | |||
| Assets | ||||
| Cash | 233,400 | |||
| 602,250 | ||||
| Inventory | 60,000 | |||
| Total current assets | 895,650 | |||
| Equipment | 523,000 | |||
| Land | 150,000 | |||
| Net equipment | ||||
| Total Assets | 1,568,650 | |||
| Liabilities and | ||||
| Liabilities | ||||
| Accounts Payable | 549,600 | |||
| Income tax payable | 120,220 | |||
| Total liabilities | 669,820 | |||
| Stockholder’s Equity | ||||
| Common Stock | 472,500 | |||
| 426,330 | ||||
| Total stockholders’ equity | 898,830 | |||
| Total Liabilities and Stockholder’s equity | 1,568,650 | |||
| Table (11) | ||||
Working Notes:
Calculation of retained earnings,
Hence, the total of the balance sheet of the D Company as on March 31, 2018 is of $1,568,650.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
GEN CMB FINCL MGRL ACCT CNCT >BI<
- Stevenson Corporation reported a pretax book income of $500,000 in 2022. Included in the computation were favorable temporary differences of $60,000, unfavorable temporary differences of $25,000, and favorable permanent differences of $50,000. What is the book equivalent of taxable income for Stevenson Corporation?arrow_forwardSaxbury Corporation's relevant range of activity is 3,000 units to 7,000 units. When it produces and sells 5,000 units, its average costs per unit are as follows: Direct Materials Direct Labor Average Cost per Unit $5.30 $3.65 Variable Manufacturing Overhead $1.50 Fixed Manufacturing Overhead $3.90 Fixed Selling Expense $0.75 Sales Commissions $0.50 Variable Administrative Expense $0.50 Fixed Administrative Expense $0.60 If the selling price is $22.90 per unit, what is the contribution margin per unit sold?arrow_forwardAccounting 12arrow_forward
- Please provide correct answerarrow_forwardAn asset's book value is $19,000 on December 31, Year 5. The asset has been depreciated at an annual rate of $4,000 on the straight-line method. Assuming the asset is sold on December 31, Year 5 for $16,000, the company should record: a. A loss on sale of $3,000. b. Neither a gain nor a loss is recognized in this type of transaction. c. A gain on sale of $3,000. d. A gain on sale of $3,000. e. A loss on sale of $3,000.arrow_forwardI want answerarrow_forward
- On December 31, Strike Company decided to sell one of its batting cages. The initial cost of the equipment was $215,000 with accumulated depreciation of $185,000. Depreciation has been taken up to the end of the year. The company found a company that is willing to buy the equipment for $30,000. What is the amount of the gain or loss on this transaction? a. Gain of $30,000 b. Loss of $30,000 c. No gain or loss d. Cannot be determinedarrow_forwardWhat is the level of its accounts receivable?arrow_forwardKindly help me with general accounting questionarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





