
(a)
The magnetic force on side 2 and 4 at the instant shown in Figure 20.7.
(a)
Answer to Problem 74P
The magnetic force on side 2 at the instant shown in Figure 20.7 is
Explanation of Solution
In side 2, current flows into the page and in side 4, current flows out of the page.
Given that the current in the system is,
Write the expression for the magnetic force due to the current carrying loop.
Here,
Use equation (I) in (III).
The direction of the magnetic force is determined using the right-hand rule, and applying right hand rule yields that the magnetic force on side 2 is directed downward and that on side 4 is directed upward.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnetic force on side 2 at the instant shown in Figure 20.7 is
(b)
The reason for which the magnetic forces on side 1 and 3 do not cause a torque about the axis of rotation.
(b)
Answer to Problem 74P
The magnetic forces on side 1 and 3 are always parallel to the axis of rotation, and hence they cannot produce a torque about the axis.
Explanation of Solution
If the forces acting on a body is parallel to the axis of rotation of the body, the forces cannot produce a torque on the body. In the given system, the magnetic forces on side 1 and 3 are parallel to the axis of rotation. Hence, they cannot cause a torque about the axis.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnetic forces on side 1 and 3 are always parallel to the axis of rotation, and hence they cannot produce a torque about the axis.
(c)
The torque on the loop about its axis of rotation.
(c)
Answer to Problem 74P
The torque on the loop about its axis of rotation is
Explanation of Solution
The diagram depicting the forces on the loop is shown in Figure 1.
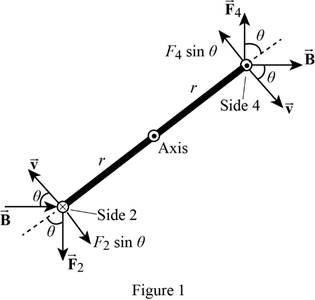
Write the expression for the total torque on the loop using the diagram.
Here,
The magnitude of magnetic force
Write the expression for the angular displacement.
Here,
From part (a) the magnetic force is obtained as,
Use equation (VI) and (VII) in(V).
The direction of forces indicates that the torque on the loop is in the counter clockwise direction.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the torque on the loop about its axis of rotation is
(d)
Whether the magnetic torque make the loop increase or decrease its
(d)
Answer to Problem 74P
In the absence of other torques the magnetic torque make the loop decrease its angular velocity.
Explanation of Solution
In the given system, the loop has the angular velocity in the clockwise direction whereas the torque exerted by the magnetic force is obtained as in the counterclockwise direction. Since the direction of magnetic torque is opposite to the direction of the angular velocity, the magnetic torque would tend to decrease the angular speed of the loop.
Conclusion:
Therefore, in the absence of other torques the magnetic torque make the loop decrease its angular velocity.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Physics
- A man holds a double-sided spherical mirror so that he is looking directly into its convex surface, 33 cm from his face. The magnification of the image of his face is +0.17. What will be the image distance when he reverses the mirror (looking into its concave surface), maintaining the same distance between the mirror and his face? Be sure to include the algebraic sign (+ or -) with your answer.arrow_forwardHow do you draw a diagram of the ruler and mass system in equilibrium identifying the anti-clockwise torque and clockwise torque? How do I calculate the anti-clockwise torque and the clockwise torque of the system with the ruler and the washers, does it come from the data in table 4? Please help, thank you!arrow_forwardExample Double pane windows have two panes of glass (n = 1.5), with a layer of air sandwiched between them. If light from outside enters the first pane at an angle of 25° from the surface normal, what angle does it enter the house at? ☑ 3 5arrow_forward
- Did your experiment results in Data Table 3 verify, to within a reasonable experimental error, the condition of equilibrium of Equation 6: Στanti-clockwise = Στclockwise? Support your response with experimental data. What does this Σ mean? My results do not show they are equal to each other, what does this mean then, and what does the data show? Thanks!arrow_forwardmicro wave.arrow_forwardmicro wave.arrow_forward
- kerjakanarrow_forwardAn object is placed 37.4cm in front of a diverging lens with a focal length of 18.1 cm. Please provide your answers in units of cm if necessary. bookmark_border1.0p3a Find the image distance. Answer Updated 6 days ago Show feedback bookmark_border1.0p3b Is the image real or virtual? Real Virtual Updated 6 days ago Show feedback bookmark_border1.0p3c Suppose the object is brought to a distance of 10.3 cm in front of the lens. Where is the image now with respect to its previous location? (Note: Ensure the sign convention you use is consistent by treating all image distances on the object side of the lens as negative.) Answer Updated 7 minutes ago Show feedback bookmark_border1.0p3d How has the height of the image changed if the object is 84.2 cm tall? Answerarrow_forwardn object is placed 37.4cm in front of a diverging lens with a focal length of 18.1 cm. Please provide your answers in units of cm if necessary. bookmark_border1.0p3a Find the image distance. Answer Updated 6 days ago Show feedback bookmark_border1.0p3b Is the image real or virtual? Real Virtual Updated 6 days ago Show feedback bookmark_border1.0p3c Suppose the object is brought to a distance of 10.3 cm in front of the lens. Where is the image now with respect to its previous location? (Note: Ensure the sign convention you use is consistent by treating all image distances on the object side of the lens as negative.) Answer Updated just now Show feedback bookmark_border1.0p3d How has the height of the image changed if the object is 84.2 cm tall? Answerarrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





