
Concept explainers
a.
To compute: The rate of
Introduction:
Rate of return: When the annual income earned through an investment is expressed as a proportion in the form of percentage of the original investment, it is called as rate of return.
a.
Answer to Problem 6PS
The table comparing the
| Particulars | Amount (in $) when stock price is $80 | Amount (in $ ) when stock price is $100 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $110 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $120 |
| Rate of return in percentages | -20% | 0 | 10% | 20% |
Explanation of Solution
Stock price S0=$100
Call option with exercise price X=$100
Call option’s selling price C=$10
Call option’s expiration=1 year
Available amount for investment=$10000
Let us follow the following steps to calculation the rate of return.
Step 1: Calculation of investment amount:
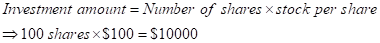
So, therefore in each case of price variation at an expiry period of 1 year i.e., at, $80, $100, $110, $120 the investment amount will $10000.
Step 2: Calculation of
| Particulars | Amount (in $) when stock price is $80 | Amount (in $ ) when stock price is $100 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $110 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $120 |
| Profit/ Loss per share when the current price is $100. (Stock price after 1 year − Current price) | 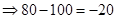 | 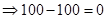 | 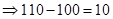 | 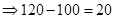 |
| Profit/Loss per total shares | 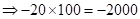 | 0 | 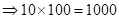 | 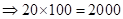 |
Step 3: Calculation of rate of return in different prices at maturity
Calculation of rate of return:
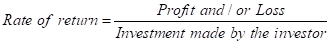
The same formula is used in calculations shown in the table.
| Particulars | Amount (in $) when stock price is $80 | Amount (in $ ) when stock price is $100 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $110 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $120 |
| Rate of return | 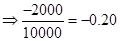 | 0 | 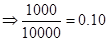 | 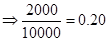 |
| Rate of return in percentages (Rate of return *100) | 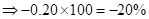 | 0 | 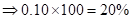 | 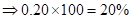 |
The maximum profit earned is 20 % and maximum loss to be borne is -20% when all of the investment amount is invested in stocks by the investor.
b.
To compute: The rate of return when the investment amount is invested in the stock options.
Introduction:
Rate of return: When the annual income earned through an investment is expressed as a proportion in the form of percentage of the original investment, it is called as rate of return.
b.
Answer to Problem 6PS
The table comparing the rate of return in percentages at different stock prices at maturity is as follows:
| Particulars | Amount (in $) when stock price is $80 | Amount (in $ ) when stock price is $100 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $110 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $120 |
| Rate of return in percentages | -300% | -100% | 0 | 100% |
Explanation of Solution
Stock price S0=$100
Call option with exercise price X=$100
Call option’s selling price C=$10
Call option’s expiration=1 year
Available amount for investment=$10000\
Let us follow the following steps to calculate the rate of return in this alternative.
Step 1: Calculation of investment amount:
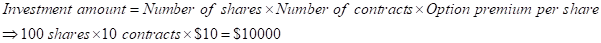 So, therefore in each case of price variation at an expiry period of 1 year i.e., at, $80, $100, $110, $120 the investment amount will $10000.
So, therefore in each case of price variation at an expiry period of 1 year i.e., at, $80, $100, $110, $120 the investment amount will $10000.
Step 2: Calculation of profit/loss in different maturity prices
Note1: Calculation of profit/loss for long call= Stock price at maturity − Strike Price- Option premium paid by the investor
| Particulars | Amount (in $) when stock price is $80 | Amount (in $ ) when stock price is $100 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $110 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $120 |
| Payoff per share when the strike price is $100. (Payoff=Stock price after 1 year − Strike price) | 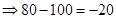 | 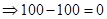 | 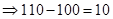 | 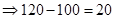 |
| Option premium per share paid by the investor | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Profit/Loss per share (Note 1) |  | 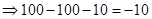 | 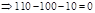 | 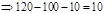 |
| Profit/Loss for 10 contracts | 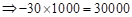 | 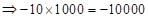 | 0 | 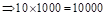 |
Calculation of value of total contracts:
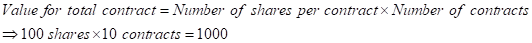
The same is used in all price variation cases in the above table.
Step 3: Calculation of rate of return:
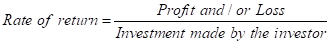
The same formula is used in calculations shown in the table.
| Particulars | Amount (in $) when stock price is $80 | Amount (in $ ) when stock price is $100 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $110 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $120 |
| Rate of return | 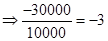 | 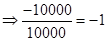 | 0 | 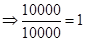 |
| Rate of return in percentages (Rate of return *100) | 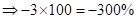 | 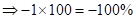 | 0 | 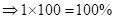 |
In this alternative, a maximum return of 100% and maximum loss to be borne is 300%. The reason is simple. It is a type of insurance contract where investor pays a premium and exercise the option only when required.
c.
To compute: The rate of return when $1000 is invested in options and $9000 is invested in
Introduction:
Money market fund: There are many types of securities in which the investment can be made. When the investor has the intention of investing in short term debt securities he/she can always opt for the money market fund. The money market fund is supposed to be an open-minded type of mutual fund. These are managed to maintain the net asset value’s stability at the highest point and at the same time pay the sufficient dividend to the investors in the form of dividends.
c.
Answer to Problem 6PS
The combined weighted average rate of return at different stock prices at maturity is as follows:
| Particulars | Amount (in $) when stock price is $80 | Amount (in $ ) when stock price is $100 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $110 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $120 |
| Weighted average rate of return from options contract | -30 | -10 | 0 | 10 |
| Weighted average rate of return from money market fund | 3.60 | 3.6 | 3.6 | 3.6 |
| Total | -26.40 | -6.40 | 3.60 | 13.60 |
Explanation of Solution
Stock price S0=$100
Call option with exercise price X=$100
Call option’s selling price C=$10
Call option’s expiration=1 year
Available amount for investment=$10000
Let us follow the following steps to calculate the rate of return in this alternative
Step 1: Calculation of investment amount when $1000 is invested in options contract
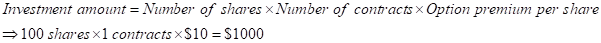 The same amount is applicable in all prices at maturity.
The same amount is applicable in all prices at maturity.
Step2: Calculation of Profit/Loss at different prices at maturity:
| Particulars | Amount (in $) when stock price is $80 | Amount (in $ ) when stock price is $100 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $110 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $120 |
| Payoff per share when the strike price is $100. (Payoff=Stock price after 1 year − Strike price) | 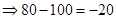 | 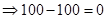 | 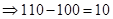 | 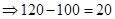 |
| Option premium per share paid by the investor | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Profit/Loss per share (Note 1) |  | 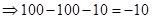 | 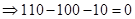 | 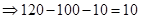 |
| Profit/Loss for 1 contracts | 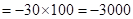 | 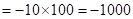 | 0 | 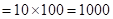 |
Calculation of value of total contracts:
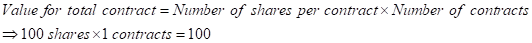
The same is used in all price variation cases in the above table.
Step 3: Calculation of rate of return:
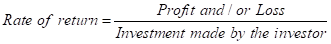
The same formula is used in calculations shown in the table.
| Particulars | Amount (in $) when stock price is $80 | Amount (in $ ) when stock price is $100 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $110 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $120 |
| Rate of return | 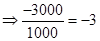 | 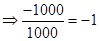 | 0 | 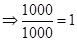 |
| Rate of return (profit/loss amount) in percentages (Rate of return *100) | 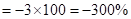 | 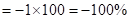 | 0 | 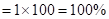 |
Step 4: Calculation of Weighted average rate of return- Note 2
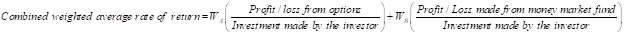
Calculation of weighted average rate of return for option contract:
| Particulars | Amount (in $) when stock price is $80 | Amount (in $ ) when stock price is $100 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $110 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $120 |
Weight of option contract investment 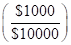 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
Weighted average rate of return 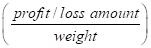 | 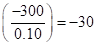 | 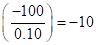 | 0 | 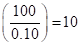 |
Calculation of Profit/Loss of investment in money market fund at different price at maturity:
| Particulars | Amount (in $) when stock price is $80 | Amount (in $ ) when stock price is $100 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $110 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $120 |
Return from money market fund 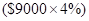 | 360 | 360 | 360 | 360 |
Rate of return 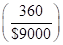 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| Rate of return in percentages (Rate of return *100) | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
Weight of option contract investment 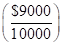 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.90 |
Weighted average rate of return 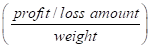 | 3.60 | 3.6 | 3.6 | 3.6 |
Step5: Calculation of combined weighted average rate of return:
| Particulars | Amount (in $) when stock price is $80 | Amount (in $ ) when stock price is $100 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $110 | Amount (in $) when stock price is $120 |
| Weighted average rate of return from options contract | -30 | -10 | 0 | 10 |
| Weighted average rate of return from money market fund | 3.60 | 3.6 | 3.6 | 3.6 |
| Total | -26.40 | -6.40 | 3.60 | 13.60 |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Investments, 11th Edition (exclude Access Card)
- Which of the following would be expected to hold its value best during a time of inflation? A certificate of deposit. A corporate bond. A house.arrow_forwardWhat is a budget? A spending plan showing sources and uses of income. A limit on spending that cannot be exceeded. The amount of money that a credit card will let youarrow_forwardThe Pan American Bottling Co. is considering the purchase of a new machine that would increase the speed of bottling and save money. The net cost of this machine is $60,000. The annual cash flows have the following projections: Year 1 ........... 2 ........... 3 ........... 4 ........... 5 ........... Cash Flow $23,000 26,000 29,000 15,000 8,000 a. If the cost of capital is 13 percent, what is the net present value of selecting a new machine? I need to see the work. I can't use Excel to solve the problem. Excel doesn't help me solve Part a.arrow_forward
- Pat and Chris have identical interest-bearing bank accounts that pay them $15 interest per year. Pat leaves the $15 in the account each year, while Chris takes the $15 home to a jar and never spends any of it. After five years, who has more money? Pat. Chris. They both have the same amount. Don’t knowarrow_forwardAssume a firm has earnings before depreciation and taxes of $200,000 and no depreciation. It is in a 25 percent tax bracket. a. Compute its cash flow using the following format: Earnings before depreciation and taxes _____Depreciation _____Earnings before taxes _____Taxes @ 25% _____Earnings after taxes _____Depreciation _____Cash Flow _____ b. Compute the cash flow for the company if depreciation is $200,000. Earnings before depreciation and taxes _____Depreciation _____Earnings before taxes _____Taxes @ 25% _____Earnings after taxes _____Depreciation _____Cash Flow _____ c. How large a cash flow benefit did the depreciation provide?arrow_forwardAssume a $40,000 investment and the following cash flows for two alternatives. Year Investment X Investment Y 1 $6,000 $15,000 2 8,000 20,000 3 9,000 10,000 4 17,000 — 5 20,000 — Which of the alternatives would you select under the payback method?arrow_forward
- The Short-Line Railroad is considering a $140,000 investment in either of two companies. The cashflows are as follows:Year Electric Co. Water Works1.................. $85,000 $30,0002.................. 25,000 25,0003.................. 30,000 85,0004–10............ 10,000 10,000a. Using the payback method, what will the decision be?b. Using the Net Present Value method, which is the better project? The discount rate is 10%.arrow_forwardWhat is corporate finance explain its important?arrow_forwardWhat is corporate finance? can you explain more?arrow_forward
- General accounting problem.arrow_forwardWhat do you know about corporate finance? tell me about thisarrow_forwardWhich of the following is the primary function of insurance? Making risk disappear. Pooling and sharing risk among the insured. Making someone else pay for an accident or loss. Don’t know.arrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





