
a.
Determine the unit contribution margin and break-even point in units and break-even point in dollar sales.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Contribution Margin:
The process or theory which is used to judge the benefit given by each unit of the goods produced is called as contribution margin.
The contribution margin is the difference between the selling price and the cost of the product.
Formula to compute the unit contribution margin:
Calculate the contribution margin per unit:
Step 1: Calculate the variable cost per unit.
Step 2: Calculate the contribution margin per unit.
Calculate the break-even volume in units:
Step 1: Calculate the total monthly fixed costs.
Step 2: Calculate the break-even volume in units.
Working note:
Calculate the amount of
Calculate the break-even volume in dollars:
b.
Draw a monthly cost-volume-profit graph for the sales volume up to 800 units per machine per month.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Cost-Volume- Profit Analysis (CVP Analysis): This analysis is helpful in determining that how any type of change in cost determines company’s income.
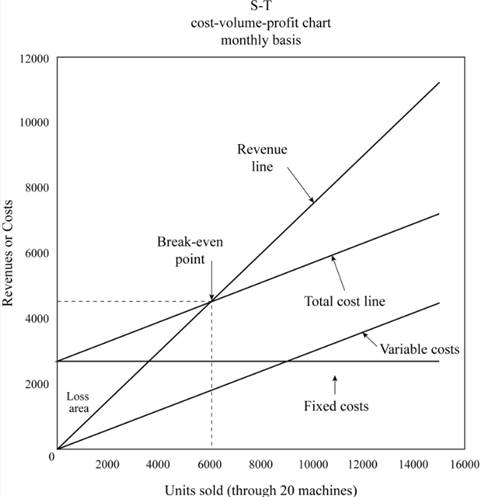
c.
Compute the sales volume in units and in dollars per month.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Compute the sales volume in units:
Step 1: Calculate the total desired contribution margin.
Step 2: Calculate the sales volume in units.
Working note:
Calculate the amount of desired operating income:
Compute the sales volume in dollars:
d.
Determine the changes in break-even volume in units.
d.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the changes in break-even volume in units:
Working notes:
Calculate the amount of new monthly fixed costs:
Calculate the new contribution margin per unit:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Gen Combo Looseleaf Financial And Managerial Accounting; Connect Access Card
- Can you help me solve this general accounting question using the correct accounting procedures?arrow_forwardHonda Corporation had beginning raw materials inventory of $34,500. During the period, the company purchased $128,000 of raw materials on account. If the ending balance in raw materials was $22,700, the amount of raw materials transferred to work in process inventory is? Helparrow_forwardGet correct answer with general accounting questionarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





