
Interpretation:
The given set of compounds should be arranged in their increasing acidity order.
Concept introduction:
Acidity of the compound is the measure of strength of the acid. If the acid forms a more stable conjugate base after deprotonation then that acid is said to be more acidic. The number and the strength of electron withdrawing group attached to the carbon that bears the removable proton determine the acidity of compound.
Answer to Problem 35PP
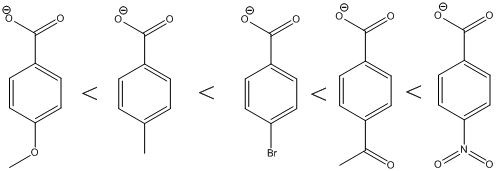
The ranking of the given set of compounds in increasing acidity order of (a) and (b) is,
Explanation of Solution
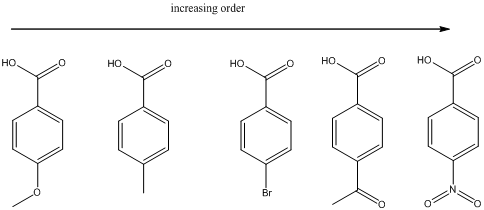
(a)
To find: The increasing acidity order for the given set of compounds.
Determine the acidic proton and electron withdrawing groups that is available
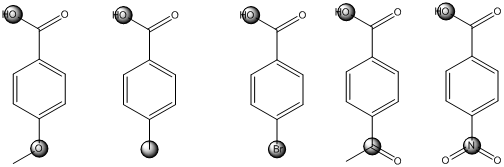
The centers that is highlighted in the above structures has the hydrogen which is more susceptible for deprotonations and delocalization. Because the electron withdrawing groups involve the delocalization step. Electron withdrawing groups stabilize the conjugate base while electron-donating groups destabilize the conjugate base. Substituents that are closer to the
Closer the electron withdrawing group more is the acidity and vice versa.
Each of these carboxylic acids is a para-substituted benzoic acids. The relative acid strength depends on the electron withdrawing or electron donating capacity of the substituent.
* Electron withdrawing groups pull electron density away from the ring, thus stabilizing the anionic charge on the conjugate base, thus giving a stronger acid.
* Electron donating groups donate electron density to the ring, thus stabilizing the anionic charge on the conjugate base, resulting a weaker acid.
The carboxylic acids are arranged in order of increasing acid strength.
*Methoxy and methyl groups are strongly and weakly electron donating respectively and bromine atom is weakly electron withdrawing.
*A carbonyl group and a nitro group in the given carboxylic acid is moderate and strong electron withdrawing groups respectively. deprotonated structure of the given carboxylic acid is drawn above. The more closer the electron withdrawing group to the carboxylate ion, the conjugate is more stabilized. From this we can confirm that p-methoxybenzoic acid < p-methylbenzoic acid< p-bromobenzoic acid<p-acetylbenzoic acid<p-nitrobenzoic acid.
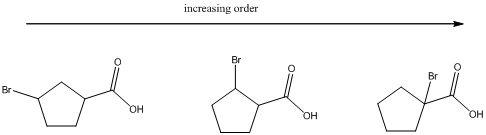
(b)
To find: The increasing acidity order for the given set of compounds.
Determine the acidic proton and electron withdrawing groups that is available
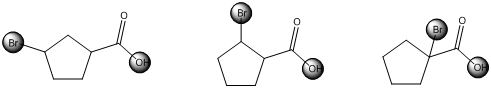
The centers that is highlighted in the above structures has the hydrogen which is more susceptible for deprotonations and delocalization. Because the electron withdrawing groups involve the delocalization step. Electron withdrawing groups stabilize the conjugate base while electron-donating groups destabilize the conjugate base. Substituents that are closer to the carboxylic acid have a greater affect on acidity.
Closer the electron withdrawing group more is the acidity and vice versa.
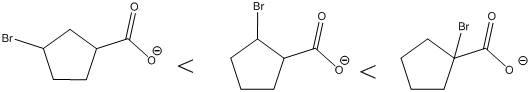
Each of these carboxylic acids is a bromine-substituted cyclopentanoic acids. The relative acid strength depends on the electron withdrawing or electron donating capacity of the substituent.
* Electron withdrawing groups pull electron density away from the ring, thus stabilizing the anionic charge on the conjugate base, thus giving a stronger acid.
* Electron donating groups donate electron density to the ring, thus stabilizing the anionic charge on the conjugate base, resulting a weaker acid.
The carboxylic acids are arranged in order of increasing acid strength.
*Bromine atom is a weakly electron withdrawing atom, it is closer to the carboxylic acid, the more it stabilizes the anionic charge on the conjugate base.
*The deprotonated structure of the given carboxylic acid is drawn above. In the first structure the compound has the electron withdrawing group, namely bromine in this case is at
Conclusion
The increasing order of acidity is ranked using the resonance structure of the formed conjugate base, and the order is


Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRYPKGDRL+MLCRL MDL
- Problem 6-17 Look at the following energy diagram: Energy Reaction progress (a) Is AG for the reaction positive or negative? Label it on the diagram. (b) How many steps are involved in the reaction? (c) How many transition states are there? Label them on the diagram. Problem 6-19 What is the difference between a transition state and an intermediate? Problem 6-21 Draw an energy diagram for a two-step reaction with Keq > 1. Label the overall AG°, transition states, and intermediate. Is AG° positive or negative? Problem 6-23 Draw an energy diagram for a reaction with Keq = 1. What is the value of AG° in this reaction?arrow_forwardProblem 6-37 Draw the different monochlorinated constitutional isomers you would obtain by the radical chlorination of the following compounds. (b) (c) Problem 6-39 Show the structure of the carbocation that would result when each of the following alkenes reacts with an acid, H+. (a) (b) (c)arrow_forwardPlease draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts and the carboxylic side productarrow_forward
- predict the product formed by the reaction of one mole each of cyclohex-2-en-1-one and lithium diethylcuprate. Assume a hydrolysis step follows the additionarrow_forwardPlease handwriting for questions 1 and 3arrow_forwardIs (CH3)3NHBr an acidic or basic salt? What happens when dissolved in aqueous solution? Doesn't it lose a Br-? Does it interact with the water? Please advise.arrow_forward
- © Macmilla Finish resonance structure 3 Select Draw Templates More C H N 0 H H S Erase Which structure is the most stable (lowest energy) resonance contributor? The structure with the positive charge on nitrogen and negative charges on oxygen and sulfur. All structures are equal in stability. The structure with the positive charge on nitrogen and negative charges on sulfur and carbon. The structure with the positive charge on nitrogen and negative charges on oxygen and carbon. Q2Qarrow_forwardThree pure compounds are formed when 1.00 g samples of element x combine with, respectively, 0.472 g, 0.630 g, and 0.789 g of element z. The first compound has the formula x2Z3. find the empricial formula of the other two compoundsarrow_forwardDraw the product and the mechanism A. excess H*; 人 OH H*; B. C. D. excess OH ✓ OH H*; H₂O 1. LDA 2. H*arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





