
DRAW IT Show where the following antibiotics work: ciprofloxacin, tetracvcline, streptomycin, vancomycin, polymyxin B, sulfanilamide, rifampin, erythromycin.
To review:
Themode of action of given antibiotics in a bacterial cell.
Concept introduction:
The antibiotics can either act as a bacteriostatic (prevent growth of bacteria) or bactericidal (kill bacteria) agents. These drugs with a specific mode of action inhibits the essential biological processes of the target pathogen, including disruption of plasma membrane permeability, inhibition of cell wall, protein and nucleic acid synthesis, and inhibition of essential metabolites synthesis.
Answer to Problem 1R
Correct answer:
| ANTIBIOTICS | MODE OF ACTION |
| Ciprofloxacin | Inhibition of the nucleic acid replication |
| Tetracycline | Inhibition of the protein synthesis |
| Streptomycin | Inhibition of the protein synthesis |
| Vancomycin | Inhibition of the cell wall synthesis |
| Polymyxin B | Injury to the plasma membrane |
| Sulfanilamide | Inhibition of the essential metabolite synthesis |
| Rifampin | Inhibition of the nucleic acid transcription |
| Erythromycin | Inhibition of the protein synthesis |
Explanation of Solution
Diagram:
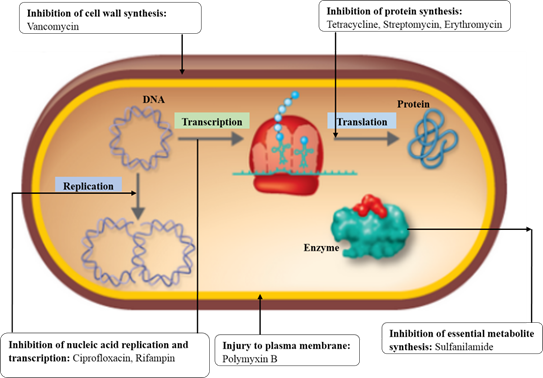
Explanation:
The mechanism of action of the given antibacterial drugs:
Ciprofloxacin – A broad spectrum of the bactericidal agent inhibits the bacterial enzyme DNA gyrase and blocks DNA synthesis. The DNA gyrase is an essential enzyme which is specifically involved in the introduction of negative supercoiling.
Tetracycline – A broad spectrum of the bacteriostatic agent prevents the attachment of aminoacyl tRNA from binding to bacterial 30S ribosome. By binding to the 30S subunit of bacterial ribosome, the tetracycline blocks the association of aminoacyl tRNA with the acceptor site.
Streptomycin – A broad spectrum of the bactericidal agent by acting on 70S ribosome inhibits the protein synthesis. It binds to the 30S subunit of bacterial ribosome and disrupts the protein synthesis (initiation and elongation step).
Vancomycin – A broad spectrum of the antibacterial agent inhibits the assembly of cell wall of bacteria. The N-acetylmuramic acid (NAG) and N-acetylglucosamine (NAM) monomers are the the building blocks of peptidoglycan cell wall. By binding to NAG and NAM, the vancomycin prevents the action of transpeptidase enzyme which is involved in the cross-linking of peptidoglycan.
Polymyxin B – A broad spectrum of the bactericidal agent with a cationic detergent action disrupts the permeability of the plasma membrane.
Sulfanilamide – A broad spectrum of the bacteriostatic agent acts as a competitive inhibitor of p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA). The sulfanilamide with a similar chemical structure competitively prevents the action of PABA and inhibits the folic acid biosynthesis. This arrests the bacterial growth and ultimately results in the elimination of the bacteria.
Rifampin – A broad spectrum of the bactericidal agent specifically inhibits the function of RNA polymerase in the bacteria. Rifampin forms a stable complex with the enzyme, thereby inhibits its activity in the nucleic acid transcription.
Erythromycin – A broad spectrum of the antibacterial agent inhibits the protein synthesis by binding to the bacterial 50S ribosome. It inhibits the activity of peptidyl transferase and intervenes with the amino acid translocation and protein assembly.
The specific site of action of the given antibacterial agents, namely cell wall synthesis (vancomycin), protein synthesis (tetracycline, streptomycin, erythromycin), essential metabolite synthesis (sulfanilamide), nucleic acid synthesis (ciprofloxacin), nucleic acid transcription (rifampin), and plasma membrane integrity (polymyxin B) is shown.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Microbiology: An Introduction (13th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
- If using animals in medical experiments could save human lives, is it ethical to do so? In your answer, apply at least one ethical theory in support of your position.arrow_forwardYou aim to test the hypothesis that the Tbx4 and Tbx5 genes inhibit each other's expression during limb development. With access to chicken embryos and viruses capable of overexpressing Tbx4 and Tbx5, describe an experiment to investigate whether these genes suppress each other's expression in the limb buds. What results would you expect if they do repress each other? What results would you expect if they do not repress each other?arrow_forwardYou decide to delete Fgf4 and Fgf8 specifically in the limb bud. Explain why you would not knock out these genes in the entire embryo instead.arrow_forward
- You implant an FGF10-coated bead into the anterior flank of a chicken embryo, directly below the level of the wing bud. What is the phenotype of the resulting ectopic limb? Briefly describe the expected expression domains of 1) Shh, 2) Tbx4, and 3) Tbx5 in the resulting ectopic limb bud.arrow_forwardDesign a grafting experiment to determine if limb mesoderm determines forelimb / hindlimb identity. Include the experiment, a control, and an interpretation in your answer.arrow_forwardThe Snapdragon is a popular garden flower that comes in a variety of colours, including red, yellow, and orange. The genotypes and associated phenotypes for some of these flowers are as follows: aabb: yellow AABB, AABb, AaBb, and AaBB: red AAbb and Aabb: orange aaBB: yellow aaBb: ? Based on this information, what would the phenotype of a Snapdragon with the genotype aaBb be and why? Question 21 options: orange because A is epistatic to B yellow because A is epistatic to B red because B is epistatic to A orange because B is epistatic to A red because A is epistatic to B yellow because B is epistatic to Aarrow_forward
- A sample of blood was taken from the above individual and prepared for haemoglobin analysis. However, when water was added the cells did not lyse and looked normal in size and shape. The technician suspected that they had may have made an error in the protocol – what is the most likely explanation? The cell membranes are more resistant than normal. An isotonic solution had been added instead of water. A solution of 0.1 M NaCl had been added instead of water. Not enough water had been added to the red blood cell pellet. The man had sickle-cell anaemia.arrow_forwardA sample of blood was taken from the above individual and prepared for haemoglobin analysis. However, when water was added the cells did not lyse and looked normal in size and shape. The technician suspected that they had may have made an error in the protocol – what is the most likely explanation? The cell membranes are more resistant than normal. An isotonic solution had been added instead of water. A solution of 0.1 M NaCl had been added instead of water. Not enough water had been added to the red blood cell pellet. The man had sickle-cell anaemia.arrow_forwardWith reference to their absorption spectra of the oxy haemoglobin intact line) and deoxyhemoglobin (broken line) shown in Figure 2 below, how would you best explain the reason why there are differences in the major peaks of the spectra? Figure 2. SPECTRA OF OXYGENATED AND DEOXYGENATED HAEMOGLOBIN OBTAINED WITH THE RECORDING SPECTROPHOTOMETER 1.4 Abs < 0.8 06 0.4 400 420 440 460 480 500 520 540 560 580 600 nm 1. The difference in the spectra is due to a pH change in the deoxy-haemoglobin due to uptake of CO2- 2. There is more oxygen-carrying plasma in the oxy-haemoglobin sample. 3. The change in Mr due to oxygen binding causes the oxy haemoglobin to have a higher absorbance peak. 4. Oxy-haemoglobin is contaminated by carbaminohemoglobin, and therefore has a higher absorbance peak 5. Oxy-haemoglobin absorbs more light of blue wavelengths and less of red wavelengths than deoxy-haemoglobinarrow_forward
- With reference to their absorption spectra of the oxy haemoglobin intact line) and deoxyhemoglobin (broken line) shown in Figure 2 below, how would you best explain the reason why there are differences in the major peaks of the spectra? Figure 2. SPECTRA OF OXYGENATED AND DEOXYGENATED HAEMOGLOBIN OBTAINED WITH THE RECORDING SPECTROPHOTOMETER 1.4 Abs < 0.8 06 0.4 400 420 440 460 480 500 520 540 560 580 600 nm 1. The difference in the spectra is due to a pH change in the deoxy-haemoglobin due to uptake of CO2- 2. There is more oxygen-carrying plasma in the oxy-haemoglobin sample. 3. The change in Mr due to oxygen binding causes the oxy haemoglobin to have a higher absorbance peak. 4. Oxy-haemoglobin is contaminated by carbaminohemoglobin, and therefore has a higher absorbance peak 5. Oxy-haemoglobin absorbs more light of blue wavelengths and less of red wavelengths than deoxy-haemoglobinarrow_forwardWhich ONE of the following is FALSE regarding haemoglobin? It has two alpha subunits and two beta subunits. The subunits are joined by disulphide bonds. Each subunit covalently binds a haem group. Conformational change in one subunit can be transmitted to another. There are many variant ("mutant") forms of haemoglobin that are not harmful.arrow_forwardWhich ONE of the following is FALSE regarding haemoglobin? It has two alpha subunits and two beta subunits. The subunits are joined by disulphide bonds. Each subunit covalently binds a haem group. Conformational change in one subunit can be transmitted to another. There are many variant ("mutant") forms of haemoglobin that are not harmful.arrow_forward
- Essentials of Pharmacology for Health ProfessionsNursingISBN:9781305441620Author:WOODROWPublisher:Cengage
 Microbiology for Surgical Technologists (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781111306663Author:Margaret Rodriguez, Paul PricePublisher:Cengage LearningBasic Clinical Lab Competencies for Respiratory C...NursingISBN:9781285244662Author:WhitePublisher:Cengage
Microbiology for Surgical Technologists (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781111306663Author:Margaret Rodriguez, Paul PricePublisher:Cengage LearningBasic Clinical Lab Competencies for Respiratory C...NursingISBN:9781285244662Author:WhitePublisher:Cengage





