
Concept explainers
Credit Policy at Howlett Industries
Sterling Wyatt, the president of Howlett Industries, has been exploring ways of improving the company’s financial performance. Howlett manufactures and sells office equipment to retailers. The company’s growth has been relatively slow in recent years, but with an expansion in the economy, it appears that sales may increase more rapidly in the future. Sterling has asked Andrew Preston, the company’s treasurer, to examine Howlett’s credit policy to see if a change can help increase profitability.
The company currently has a policy of net 30. As with any credit sales, default rates are always of concern. Because of Howlett’s screening and collection process, the default rate on credit is currently only 1.6 percent. Andrew has examined the company’s credit policy in relation to other vendors, and he has found three available options.
The first option is to relax the company’s decision on when to grant credit. The second option is to increase the credit period to net 45, and the third option is a combination of the relaxed credit policy and the extension of the credit period to net 45. On the positive side, each of the three policies under consideration would increase sales. The three policies have the drawbacks that default rates would increase, the administrative costs of managing the firm’s receivables would increase, and the receivables period would increase. The effect of the credit policy change would impact all four of these variables to different degrees. Andrew has prepared the following table outlining the effect on each of these variables:
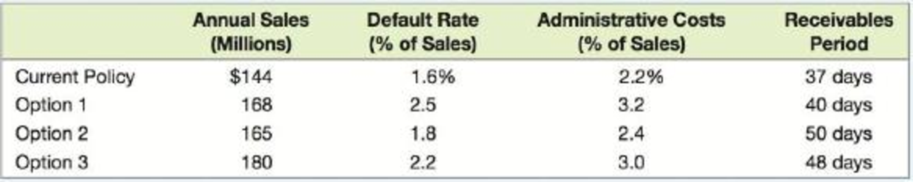
Howlett’s variable costs of production are 45 percent of sales, and the relevant interest rate is a 6 percent effective annual rate.
1. Which credit policy should the company use?
To evaluate: The credit policy of the firm.
Introduction:
Credit policy refers to a set of procedures that include the terms and conditions for providing goods on credit and principles for making collections.
Answer to Problem 1M
Company H should select Option 1, because it has the highest net present value (NPV) of $34,226,117.98 compared to other two options.
Explanation of Solution
The formula to calculate the average daily sales under current policy:
Hence, the average sales under current policy is $394,520.55.
The formula to calculate average daily variable costs under current policy:
Hence, the variable costs under current policy is $177,534.25.
The formula to calculate the average daily default under current policy:
Hence, the average daily default under current policy is $6312.33.
The formula to calculate average daily administrative cost under current policy:
Hence, the average administrative costs under current policy is $8,679.45.
The formula to calculate the interest rate for the collection period:
Hence, the interest rate is 0.61%.
The formula to calculate the net present value (NPV) under current policy:
Hence, the NPV under current policy is $32,936,321.48.
Option 1:
The formula to calculate the average daily sales under option 1:
Hence, the average daily sales under option 1 is $460,273.97.
The formula to calculate average daily variable costs under option 1:
Hence, the average daily variable costs under option 1 is $207,123.29.
The formula to calculate average daily default under option 1:
Hence, average daily default under option 1 is $11,506.85.
The formula to calculate average daily administrative cost under option 1:
Hence, the average daily administrative costs under option 1 is $14,728.77.
The formula to calculate interest rate for the for collection period:
Hence, the interest rate is 0.659%.
The formula to calculate the net present value (NPV) under option 1:
Hence, the NPV under option 1 is $34,226,117.98.
Option 2:
The formula to calculate the average daily sales under option 2:
Hence, the average daily sales under option 2 is $452,054.79.
The formula to calculate average daily variable costs under option 2:
Hence, the average daily variable costs under option 2 is $203,424.66.
The formula to calculate average daily default under option 2:
Hence, the average daily default under option 2 is $8,136.99.
The formula to calculate average daily administrative cost under option 2:
Hence, the average daily administrative costs under option 2 is $10,849.32.
The formula to calculate interest rate for the for collection period:
Hence, the interest rate is 0.852%.
The formula to calculate NPV under option 2:
Hence, the NPV under option 2 is $27,632,189.89.
Option 3:
The formula to calculate the average daily sales under current policy:
Hence, the average daily sales under option 3 is $493,150.68.
The formula to calculate average daily variable costs under option 3:
Hence, the average daily variable costs under option 3 is $221,917.81.
The formula to calculate average daily default under option 3:
Hence, the average daily default under option 3 is $10,849.32.
The formula to calculate average daily administrative cost under option 3:
Hence, the average daily administrative costs under option 3 is $14,794.52.
The formula to calculate interest rate for collection period:
Hence, the interest rate is 0.792%.
The formula to calculate NPV under option 3:
Hence, the NPV under option 3 is $30,786,798.099.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Connect 1 Semester Access Card for Fundamentals of Corporate Finance
- No AI Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of common stock? A) Voting rights B) Dividends C) Guaranteed return on investment D) Ownership in the companyarrow_forwardWhich of the following would be considered an example of an operating activity in a cash flow statement? A) Issuance of common stock B) Borrowing from a bank C) Payment for goods sold D) Purchase of equipmentarrow_forwardNo chatgpt!! What does the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio measure? A) Profit margin B) Dividend yield C) Market valuation relative to earnings D) Return on equityarrow_forward
- I need help in this question!! What does the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio measure? A) Profit margin B) Dividend yield C) Market valuation relative to earnings D) Return on equityarrow_forwardWhat does the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio measure? A) Profit margin B) Dividend yield C) Market valuation relative to earnings D) Return on equityarrow_forwardWhat is the risk-free rate typically associated with? A) Corporate bonds B) Government securities C) Real estate investments D) Equitiesarrow_forward
- No chatgpt! Which of the following financial instruments is used to hedge against interest rate risk? A) Futures contracts B) Treasury bills C) Interest rate swaps D) Corporate bondsarrow_forwardWhich of the following financial instruments is used to hedge against interest rate risk? A) Futures contracts B) Treasury bills C) Interest rate swaps D) Corporate bondsarrow_forwardNeed assistance! Which of the following is the best description of a dividend? A) The amount a company spends on research and development B) A payment made to shareholders from company profits C) The price of a company’s stock D) The cost of producing goods for salearrow_forward
- I need help in this question! Which of the following is the best description of a dividend? A) The amount a company spends on research and development B) A payment made to shareholders from company profits C) The price of a company’s stock D) The cost of producing goods for salearrow_forwardNo AI Which of the following is the best description of a dividend? A) The amount a company spends on research and development B) A payment made to shareholders from company profits C) The price of a company’s stock D) The cost of producing goods for saleNeed help!arrow_forwardDo not use ChatGPT! Which of the following is the best description of a dividend? A) The amount a company spends on research and development B) A payment made to shareholders from company profits C) The price of a company’s stock D) The cost of producing goods for salearrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning





