
Concept explainers
(a)
To determine: Sketch of a labeled voltaic cell and the concentration of the solution.
(a)
Answer to Problem 1DE
The labeled sketch of the voltaic cell is,
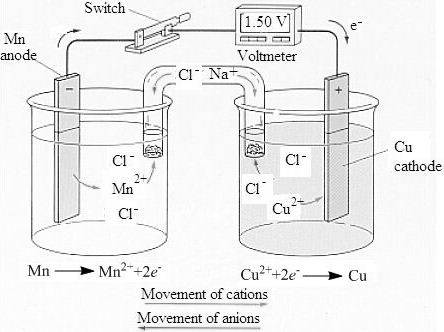
The concentration of the copper and the manganese ion is
Explanation of Solution
Given
The electrical potential output of the cell is
The external device draws the current of
The electric potential of the cell is calculated as,
According to the above equation, the difference in the oxidation and the reduction potential should be
The standard oxidation potential of manganese is
Therefore, the pair of manganese and copper is used to construct a voltaic cell with manganese being anode at which oxidation takes place and copper being cathode at which reduction takes place.
The standard reduction potential is the potential of the electrode dipped in the aqueous solution of its ion of concentration
Therefore, the concentration of the copper and the manganese ion is
We are given the beaker of the capacity of
The volume of the solution of manganese and copper ion is assumed to be
The labeled sketch of the voltaic cell is,
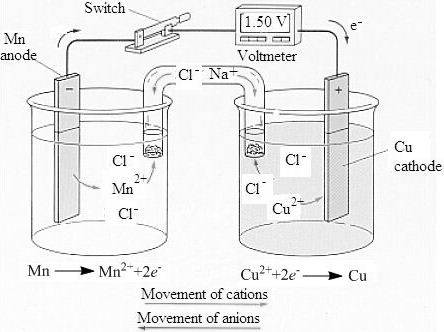
- Figure. 1
The mass of the manganese in the
Substitute the value of molar concentration, molar mass and the volume of the solution of manganese in the above equation.
The mass of the copper in the
Substitute the value of molar concentration, molar mass and the volume of the solution of copper in the above equation.
Therefore, the mass of manganese and copper present in the
The concentration of the copper and the manganese ion is
(b)
To determine: The concentration of manganese and copper ion in the solution after
(b)
Answer to Problem 1DE
Explanation of Solution
Given
The electrical potential output of the cell is
The external device draws the current of
The charge transport is calculated by the formula,
Substitute the value of current and time in the above formula,
Charge on each electron is
The moles of electron present in
Substitute the value of charge transfer, charge on each electron and Avogadro’s number in the above formula.
Two electron transfer takes place by oxidation and reduction of manganese and copper, respectively.
Therefore, the change in moles of manganese and copper is:
The initial concentration of the ions is
Thus, one mole of ion is present in one liter of the solution and
The number of moles of manganese ion increase due to oxidation of metal. Therefore, the molar concentration of manganese ion in
The number of moles of copper ion increase due to oxidation of metal. Therefore, the molar concentration of copper ion in
Thus, the concentration of manganese and copper ion after two hours is
The concentration of manganese and copper ion after two hours is
(c)
To determine: The voltage that a cell register at the end of the discharge.
(c)
Answer to Problem 1DE
Explanation of Solution
Given
The electrical potential output of the cell is
The external device draws the current of
The concentration of manganese and copper ion after two hours is
The standard oxidation potential of manganese is
The standard reduction potential is the potential of the electrode dipped in the aqueous solution of its ion of concentration
Thus, one mole of manganese ion gives the oxidation potential of
Therefore,
One mole of copper ion gives the reduction potential of
Therefore,
The electric potential of the cell at discharge is calculated as,
Substitute the value of oxidation and reduction potential in the above equation.
Thus, the end cell potential is
The end cell potential is
(d)
To determine: The time taken for the reactant of one cell to get completely consumed.
(d)
Answer to Problem 1DE
Explanation of Solution
Given
The electrical potential output of the cell is
The external device draws the current of
The charge transport is calculated by the formula,
Substitute the value of current and time in the above formula,
Charge on each electron is
The moles of electron present in
Substitute the value of charge transfer, charge on each electron and Avogadro’s number in the above formula.
Two electron transfer takes place by oxidation and reduction of manganese and copper, respectively.
Therefore, the change in moles of manganese and copper is
Charge is directly proportional to time at constant current flow.
The charge transferred is
The total initial concentration of the reactant of one half cell is one molar.
Therefore, the charge transfer of one molar takes place in
The charge transfer of one molar takes place in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
EBK CHEMISTRY:CENTRAL SCIENCE
- Would the following organic synthesis occur in one step? Add any missing products, required catalysts, inorganic reagents, and other important conditions. Please include a detailed explanation and drawings showing how the reaction may occur in one step.arrow_forwardBelow is the SN1 reaction of (S)-3-chlorocyclohexene and hydroxide (OH). Draw the missing curved arrows, lone pairs of electrons, and nonzero formal charges. In the third box, draw the two enantiomeric products that will be produced. 5th attempt Please draw all four bonds at chiral centers. Draw the two enantiomeric products that will be produced. Draw in any hydrogen at chiral centers. 1000 4th attempt Feedback Please draw all four bonds at chiral centers. 8. R5 HO: See Periodic Table See Hint H Cl Br Jid See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forwardShow that a molecule with configuration π4 has a cylindrically symmetric electron distribution. Hint: Let the π orbitals be equal to xf and yf, where f is a function that depends only on the distance from the internuclear axis.arrow_forward
- (a) Verify that the lattice energies of the alkali metal iodides are inversely proportional to the distances between the ions in MI (M = alkali metal) by plotting the lattice energies given below against the internuclear distances dMI. Is the correlation good? Would a better fit be obtained by plotting the lattice energies as a function of (1 — d*/d)/d, as theoretically suggested, with d* = 34.5 pm? You must use a standard graphing program to plot the graph. It generates an equation for the line and calculates a correlation coefficient. (b) From the graph obtained in (a), estimate the lattice energy of silver iodide. (c) Compare the results of (b) with the experimental value of 886 kJ/mol. If they do not agree, explain the deviation.arrow_forwardCan I please get help with #3 & 4? Thanks you so much!arrow_forwardA solution consisting of 0.200 mol methylbenzene, C,H,CH,, in 500. g of nitrobenzene, CH,NO₂, freezes at 3.2°C. Pure nitrobenzene freezes at 6.0°C. The molal freezing point constant of nitrobenzene is _ °C/m. a) 2.8 b) 3.2 c) 5.6 d) 7.0 e) 14.0arrow_forward
- Below is the SN1 reaction of (S)-3-chlorocyclohexene and hydroxide ("OH). Draw the missing curved arrows, lone pairs of electrons, and nonzero formal charges. In the third box, draw the two enantiomeric products that will be produced. 2nd attempt Please draw all four bonds at chiral centers. 0 D Draw the missing curved arrow notation. Add lone pairs of electrons and nonzero formal charges. + 노 V 1st attempt Feedback Please draw all four bonds at chiral centers. See Periodic Table See Hint F P 41 H Br See Periodic Table See Hint H Larrow_forwardHow close are the Mulliken and Pauling electronegativity scales? (a) Now that the ionization energies and electron affinities have been defined, calculate the Mulliken and Pauling electronegativities for C, N, O and F. Compare them. (Make the necessary adjustments to the values, such as dividing the ionization energies and electron affinities by 230kj/mol) (b) Plot both sets of electronegativities against atomic number (use the same graph). (c) Which scale depends most consistently on position in the Periodic Table?arrow_forwardBelow is the SN2 reaction between 2-bromopropane and iodide (I). Draw the mechanism arrows in the first box to reflect electron movements. In both boxes, add lone pairs of electrons and nonzero formal charges. 4th attempt Feedback 3rd attempt Feedback 1 -Br H :Bri :Br: ili See Periodic Table See Hint ini See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forward
- When 4-chloro-1-butanol is placed in sodium hydride, a cyclization reaction occurs. 3rd attempt 2 HO NaH CI D Draw the curved arrow notation to form the intermediate. 4 2 H₂ See Periodic Table See Hint =arrow_forwardSketch, qualitatively, the potential energy curves of the N-N bond of N2H4, N2 and N3- graph. Explain why the energy at the minimum of each curve is not the same.arrow_forward(a) Show that the lattice energies are inversely proportional to the distance between ions in MX (M = alkali metal, X = halide ions) by plotting the lattice energies of KF, KCl, and KI against the internuclear distances, dMX. The lattice energies of KF, KCl, and KI are 826, 717, and 645 kJ/mol, respectively. Does the correlation obtained correlate well? You will need to use a standard graphing program to construct the graph (such as a spreadsheet program). It will generate an equation for the line and calculate a correlation coefficient. (b) Estimate the lattice energy of KBr from your graph. (c) Find an experimental value for the lattice energy of KBr in the literature, and compare this value with the one calculated in (b). Do they agree?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





