
Concept explainers
1 (a)
Calculate the annual rental amounts.
1 (a)
Explanation of Solution
Compute the annual rental amount of Company L, as follows:
Therefore, annual rental amount is $67,673.02.
1 (b)
Explain the way Company T should compute the present value of the lease rights and additional information required to make such calculation.
1 (b)
Explanation of Solution
To determine the present value of the lease rights, Company T should multiply the annual rental payment of $67,673.02 by the PV factor for 6 periods in advance at x%. That x% would be lesser than 14% or incremental borrowing rate of the Company T. Thus the incremental borrowing rate for Company T is the required additional information to compute the PV of lease rights.
2.
Prepare the table summarizing the lease and interest receipts that would be suitable for Company L.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the table summarizing the lease and interest receipts that would be suitable for Company L:
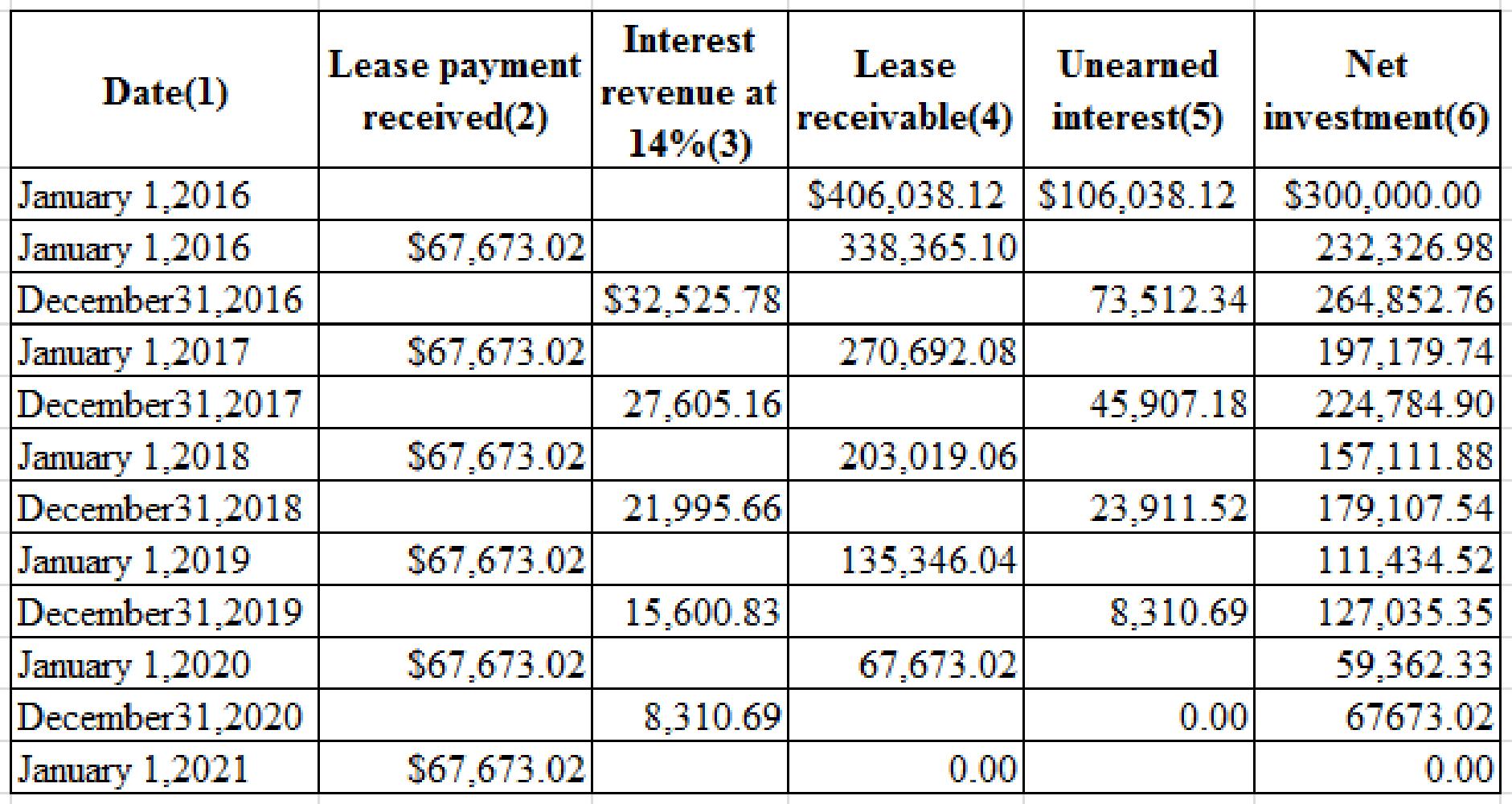
Table (1)
Notes for the above table:
The aforesaid table would also be suitable for Company T, if the incremental borrowing rate is
3.
Prepare
3.
Explanation of Solution
Journal: Journal is the method of recording monetary business transactions in chronological order. It records the debit and credit aspects of each transaction to abide by the double-entry system.
Rules of Debit and Credit: Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
- Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and
stockholders’ equities . - Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, expenses.
Prepare journal entries suitable for Company L and Company T for the years 2016 and 2017:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| January 1,2016 | Leased Equipment | 300,000.00 | ||
| Capital Lease Obligation | 300,000.00 | |||
| (To record the capital lease at inception) | ||||
| January 1,2016 | Capital Lease Obligation | 67,673.02 | ||
| Cash | 67,673.02 | |||
| (To record the capital lease payment) | ||||
| During Year | Insurance Expense | 700.00 | ||
| Property Tax Expense | 800.00 | |||
| Cash | 1,500.00 | |||
| (To record the payment for executory costs) | ||||
| December 31, 2016 | 50,000.00 | |||
| | 50,000.00 | |||
| (To record the depreciation expense) | ||||
| December 31, 2016 | Interest Expense | 32,525.78 | ||
| Accrued Interest on Capital Lease Obligation | 32,525.78 | |||
| (To record the interest expense) | ||||
| January 1,2017 | Accrued Interest on Capital Lease Obligation | 32,525.78 | ||
| Capital Lease Obligation | 35,147.24 | |||
| Cash | 67,673.02 | |||
| (To record the payment of accrued interest and lease payment) | ||||
| During Year | Insurance Expense | 600.00 | ||
| Property Tax Expense | 750.00 | |||
| Cash | 1,350.00 | |||
| (To record the payment for executory costs) | ||||
| December 31, 2017 | Depreciation Expense: Leased Equipment | 50,000.00 | ||
| Accumulated Depreciation: Equipment | 50,000.00 | |||
| (To record the depreciation expense) | ||||
| December 31, 2017 | Interest Expense | 27,605.16 | ||
| Accrued Interest on Capital Lease Obligation | 27,605.16 | |||
| (To record the interest expense) |
Table (2)
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| January 1,2016 | Equipment Leased to Others | 300,000.00 | ||
| Cash | 300,000.00 | |||
| (To record the payment of capital lease at inception) | ||||
| January 1,2016 | Lease Receivable | 406,038.12 | ||
| Equipment Leased to Others | 300,000.00 | |||
| Unearned Interest: Leases | 106,038.12 | |||
| (To record the lease receivable in a capital lease) | ||||
| January 1,2016 | Cash | 67,673.02 | ||
| Lease Receivable | 67,673.02 | |||
| (To record the receipt lease payment) | ||||
| December31, 2016 | Unearned Interest: Leases | 32,525.78 | ||
| Interest Revenue: Leases | 32,525.78 | |||
| (To recognize the interest revenue for the year) | ||||
| January 1,2017 | Cash | 67,673.02 | ||
| Lease Receivable | 67,673.02 | |||
| (To record the receipt lease payment) | ||||
| December 31, 2017 | Unearned Interest: Leases | 27,605.16 | ||
| Interest Revenue: Leases | 27,605.16 | |||
| (To recognize the interest revenue for the year) |
Table (3)
4.
Prepare income statements and ending balance sheets for both Company L and Company T for the year 2016 and 2017 with appropriate notes.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Income statements and ending balance sheets for Company T:
| Company T | ||
| Comparative Income statement(Partial) | ||
| For the year ended December 31 | ||
| 2017 | 2016 | |
| Interest Expense | $27,605.16 | $32,525.78 |
| Insurance Expense | 600.00 | 700.00 |
| Property Tax Expense | 750.00 | 800.00 |
| Depreciation Expense | 50,000.00 | 50,000.00 |
| Comparative Balance Sheet(Partial) | ||
| As on December 31 | ||
| 2017 | 2016 | |
| Assets | ||
| Leased equipment less accumulated depreciation | ||
| (Notes 1 and 2) | $200,000.00 | $250,000.00 |
| Liabilities | ||
| Current: | ||
| Capital Lease Obligation | $67,673.02 | $67,673.02 |
| Non-Current: | ||
| Capital Lease Obligation(Notes 1 and 2) | $157,111.88 | $197,179.74 |
Table (4)
Note 1: Description of Leasing Equipment:
Company T is leasing heavy equipment from Company L. The lease term is 6 years and 4 years are still remaining. There are no restrictions and no purchase option too in the lease. The heavy equipment reverts to Company L once the lease period is over.
Note 2: Capital Leases:
The leased property details are as follows:
| 31.12.2017 | 31.12.2016 | |
| Heavy Equipment | $300,000.00 | $300,000.00 |
| Less: Accumulated amortization | $100,000.00 | $50,000.00 |
| Balance | $200,000.00 | $250,000.00 |
Table (5)
Compute the present value of net lease payments under capital leases with future lease payments as of December 31, 2017 as per the following schedule:
| December 31 | Amount($) | |
| 2018 | 67,673.02 | |
| 2019 | 67,673.02 | |
| 2020 | 67,673.02 | |
| 2021 | 67,673.02 | |
| Total Lease Payments | $270,692.08 | |
| Less: Amount that represent interest | (45,907.18) | |
| Present value of lease payments(net) | $224,784.90 | |
Table (6)
Income statements and ending balance sheets for Company L:
| Company L | ||
| Comparative Income statement(Partial) | ||
| For the year ended December 31st | ||
| 2017 | 2016 | |
| Revenue: | ||
| Interest Revenue: Leases | 27,605.16 | 32,525.78 |
| Comparative Balance Sheet(Partial) | ||
| As on December 31st | ||
| 2017 | 2016 | |
| Current Assets | ||
| Net investment in direct financing leases | ||
| (Notes 1 and 2) | $67,673.02 | $67,673.02 |
| Non-Current Assets: | ||
| Net Investment in direct financing leases | ||
| (Notes1 and 2) | $157,111.88 | $197,179.74 |
Table (7)
Note 1: Description of leasing arrangements:
Company L has leased the heavy equipment to Company T. The lease term is 6 years and 4 years are remaining. The heavy equipment reverts to Company L after the expiry of the lease.
Note 2: Net Investment in direct financing leases:
Following are the components of net investments in direct financing leases as on December 31 of the years as depicted in the schedule below:
| 2017 | 2016 | |
| Total lease payment receivable | $270,692.08 | $338,365.10 |
| Less: Unearned interest: leases | 45,907.18 | 73,512.34 |
| Total lease payment receivable(net) | $224,784.90 | $264,852.76 |
Table (8)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting and Analysis (Looseleaf)
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning

