![OWLv2 for Moore/Stanitski's Chemistry: The Molecular Science, 5th Edition, [Instant Access], 1 term (6 months)](https://s3.amazonaws.com/compass-isbn-assets/textbook_empty_images/large_textbook_empty.svg)
Concept explainers
An
- (a) Identify the element and give its symbol.
- (b) Give the element’s
atomic number . - (c) Give the mass number of the isotope.
- (d) This element has two naturally occurring isotopes. Given the information in the table, calculate the atomic weight of the element.
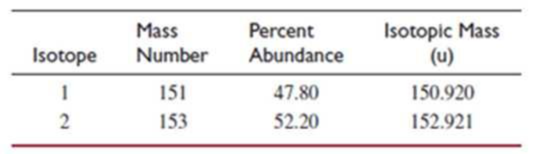
- (e) In which region of the periodic table is the element found? Explain your answer.
- (f) Is the element a metal, metalloid, or nonmetal? Explain your answer.
- (g) This element, used in compact fluorescent light bulbs and computer screens, has an atomic radius of 180 pm. Calculate how long the chain of atoms would be if all the atoms in a 1.25-mg sample of this element were put into a row.
(a)
Interpretation:
The isotope of an element contains 63 protons and 91 neutrons. The element has to be identified and the symbol of the element has to be given.
Explanation of Solution
Number of protons of the element is 63.
Number of neutrons of the element is 91.
The atomic number is same as that of number of protons, 63. Also the number of protons is same as that number of electrons in an uncharged atom. The element is Europium with a symbol of
(b)
Interpretation:
The atomic number of element with 63 protons and 91 neutrons has to be given.
Explanation of Solution
Number of protons of the element is 63.
The atomic number is same as that of number of protons, 63.
Atomic number
(c)
Interpretation:
The mass number of the isotope with 63 protons and 91 neutrons has to be given.
Explanation of Solution
Number of protons of the element is 63.
Number of neutrons of the element is 91.
Atomic number
Mass number is the sum of atomic number of the element and number of neutrons.
Isotope’s mass number
(d)
Interpretation:
The element has two naturally occurring isotopes. From the table given the atomic weight of the element has to be calculated.
Explanation of Solution
Every 10000 atoms of the element contain 4780 atoms of the
(e)
Interpretation:
The region in which the element is found in periodic table has to be explained.
Explanation of Solution
The element is found in the lanthanide series because it shows up in the row labeled “Lanthanides”.
(f)
Interpretation:
The given element is a metal, metalloid or non-metal has to be found and the answer has to be explained.
Explanation of Solution
The element Europium is a transition metal.
(g)
Interpretation:
The element given has an atomic radius of
Explanation of Solution
The atomic radius is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
OWLv2 for Moore/Stanitski's Chemistry: The Molecular Science, 5th Edition, [Instant Access], 1 term (6 months)
- What is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- please help me with my homeworkarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forward
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





