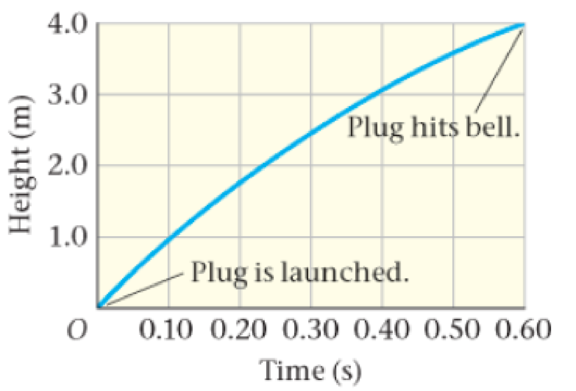
Problem 1CQ: You take your dog on a walk to a nearby park. On the way, your dog takes many short side trips to... Problem 2CQ: Does an odometer in a car measure distance or displacement? Explain. Problem 3CQ: An astronaut orbits Earth in the space shuttle. In one complete orbit, is the magnitude of the... Problem 4CQ: After a tennis match the players dash to the net to congratulate one another. If they both run with... Problem 5CQ: Does a speedometer measure speed or velocity? Explain. Problem 6CQ: Is it possible for a car to circle a racetrack with constant velocity? Can it do so with constant... Problem 7CQ: For what kinds of motion are the instantaneous and average velocities equal? Problem 8CQ: Assume that the brakes in your car create a constant deceleration, regardless of how fast you are... Problem 9CQ: The velocity of an object is zero at a given instant of time. (a) Is it possible for the objects... Problem 10CQ: If the velocity of an object is nonzero, can its acceleration be zero? Give an example if your... Problem 11CQ: Is it possible for an object to have zero average velocity over a given interval of time, yet still... Problem 12CQ: A batter hits a pop fly straight up. (a) Is the acceleration of the ball on the way up different... Problem 13CQ: A person on a trampoline bounces straight upward with an initial speed of 4.5 m/s. What is the... Problem 14CQ: A volcano shoots a lava bomb straight upward. Does the displacement of the lava bomb depend on (a)... Problem 1PCE: Referring to Figure 2-27, you walk from your home to the library, then to the park. (a) What is the... Problem 2PCE: In Figure 2-27, you walk from the park to your friends house, then back to your house. What are your... Problem 3PCE: The two tennis players shown in Figure 2-28 walk to the net to congratulate one another. (a) Find... Problem 4PCE: The golfer in Figure 2-29 sinks the ball in two putts, as shown. What are (a) the distance traveled... Problem 5PCE: A jogger runs on the track shown in Figure 2-30. Neglecting the curvature of the corners, (a) what... Problem 6PCE: Predict/Calculate A child rides a pony on a circular track whose radius is 5.25 m. (a) Find the... Problem 7PCE: Predict/Explain You drive your car in a straight line at 15 m/s for 10 kilometers, then at 25 m/s... Problem 8PCE: Predict/Explain You drive your car in a straight line at 15 m/s for10 minutes, then at25 m/s for... Problem 9PCE: Usain Bolt of Jamaica set a world record in 2009 for the 200-meter dash with a time of 19.19 seconds... Problem 10PCE: BIO Kangaroos have been clocked at speeds of 65 km/h. (a) How far can a kangaroo hop in 3.2 minutes... Problem 11PCE: Rubber Ducks A severe storm on January 10, 1992, caused a cargo ship near the Aleutian Islands to... Problem 12PCE: Radio waves travel at the speed of light, approximately 186,000 miles per second. How much time does... Problem 13PCE: It was a dark and stormy night, when suddenly you saw a flash of lightning. Six and a half seconds... Problem 14PCE: BIO Nerve Impulses The human nervous system can propagate nerve impulses at about 102 m/s. Estimate... Problem 15PCE: A finch rides on the back of a Galapagos tortoise, which walks at the stately pace of 0.060 m/s.... Problem 16PCE: You jog at 9.1 km/h for 5.0 km, then you jump into a car and drive an additional 13 km. With what... Problem 17PCE: A dog runs back and forth between its two owners, who are walking toward one another (Figure 2-31).... Problem 18PCE: BIO Predict/Calculate Blood flows through a major artery at 1.0 m/s for 0.50 s, then at 0.60 m/s for... Problem 19PCE: BIO Predict/Calculate Blood flows through a major artery at 1.0 m/s over a distance of 0.50 m, then... Problem 20PCE: In heavy rush-hour traffic you drive in a straight line at 12 m/s for 1.5 minutes, then you have to... Problem 21PCE: Predict/Calculate An expectant father paces back and forth, producing the position-versus-time graph... Problem 22PCE: The position of a particle as a function of time is given by x = (5 m/s) t + (3 m/s2) t2. (a) Plot x... Problem 23PCE: The position of a particle as a function of time is given by x = (6 m/s) t + (2 m/s2) t2. (a) Plot x... Problem 24PCE: Predict/Calculate A tennis player moves back and forth along the baseline while waiting for her... Problem 25PCE: On your wedding day you leave for the church 30.0 minutes before the ceremony is to begin, which... Problem 26PCE: The position-versus-time plot of a boat positioning itself next to a dock is shown in Figure 2-34.... Problem 27PCE: The position of a particle as a function of time is given by x = (2.0 m/s) t + (3.0 m/s3) t3. (a)... Problem 28PCE: The position of a particle as a function of time is given by x = (2.00 m/s) t + (3.00 m/s3) t3. (a)... Problem 29PCE: Predict/Explain On two occasions you accelerate uniformly from rest along an on-ramp in order to... Problem 30PCE: A 747 airliner reaches its takeoff speed of156 mi/h in 35.2 s. What is the magnitude of its average... Problem 31PCE: At the starting gun, a runner accelerates at1.9 m/s2 for 5.2 s The runner's acceleration is zero for... Problem 32PCE: A jet makes a landing traveling due east with a speed of 70.6 m/s If the jet comes to rest in 13.0... Problem 33PCE: A car is traveling due north at 23.6 m/s. Find the velocity of the car after 7.10 s if its... Problem 34PCE: A motorcycle moves according to the velocity-versus-time graph shown in Figure 2-35. Find the... Problem 35PCE: A person on horseback moves according to the velocity-versus-time graph shown in Figure 2-36. Find... Problem 36PCE: Running with an initial velocity of +9.2 m/s, a horse has an average acceleration of 1.81 m/s2 How... Problem 37PCE: Predict/Calculate Assume that the brakes in your car create a constant deceleration of 4.2 m/s2... Problem 38PCE: As a train accelerates away from a station, it reaches a speed of 4.7 m/s in 5.0 s. If the trains... Problem 39PCE: A particle has an acceleration of +6.24 m/s2 for 0.450 s. At the end of this time the particles... Problem 40PCE: Landing with a speed of 71.4 m/s, and traveling due south, a jet comes to rest in 949 m. Assuming... Problem 41PCE: When you see a traffic light turn red, you apply the brakes until you come to a stop. If your... Problem 42PCE: A ball is released at the point x = 2 m on an inclined plane with a nonzero initial velocity. After... Problem 43PCE: Starting from rest, a boat increases its speed to 4.82 m/s with constant acceleration. (a) What is... Problem 44PCE: The position of a car as a function of time is given by x = (50 m) + (5.0 m/s) t + (10 m/s2) t2 (a)... Problem 45PCE: The position of a ball as a function of time is given by x = (5.0 m/s) t + (10 m/s2) t2. (a) What... Problem 46PCE: BIO A cheetah can accelerate from rest to 25 0 m/s in 6.22 s. Assuming constant acceleration, (a)... Problem 47PCE: A sled slides from rest down an icy slope. Measurements taken from a video show that the distance... Problem 48PCE: A child slides down a hill on a toboggan with an acceleration of 1.6 m/s2. If she starts at rest,... Problem 49PCE: The Detonator On a ride called the Detonator at Worlds of Fun in Kansas City, passengers accelerate... Problem 50PCE: Jules Verne In his novel From the Earth to the Moon (1865), Jules Verne describes a spaceship that... Problem 51PCE: BIO Bacterial Motion Approximately 0.1% of the bacteria in an adult humans intestines are... Problem 52PCE: Two cars drive on a straight highway. At time t = 0, car 1 passes mile marker 0 traveling due east... Problem 53PCE: A Meteorite Strikes On October 9, 1992, a 27-pound meteorite struck a car in Peekskill, NY, leaving... Problem 54PCE: A rocket blasts off and moves straight upward from the launch pad with constant acceleration. After... Problem 55PCE: Predict/Calculate You are driving through town at 12.0 m/s when suddenly a ball rolls out in front... Problem 56PCE: Predict/Calculate You are driving through town at 16 m/s when suddenly a car backs out of a driveway... Problem 57PCE: BIO Predict/Calculate A Tongues Acceleration When a chameleon captures an insect, its tongue can... Problem 58PCE: BIO Surviving a Large Deceleration On July 13, 1977, while on a test drive at Britains Silverstone... Problem 59PCE: A boat is cruising in a straight line at a constant speed of 2.6 m/s when it is shifted into... Problem 60PCE: A model rocket rises with constant acceleration to a height of 4.2 m, at which point its speed is... Problem 61PCE: The infamous chicken is dashing toward home plate with a speed of 5.7 m/s when he decides to hit the... Problem 62PCE: A bicyclist is finishing his repair of a flat tire when a friend rides by with a constant speed of... Problem 63PCE: A car in stop-and-go traffic starts at rest, moves forward 22 m in 8.0 s, then comes to rest again.... Problem 64PCE: A car and a truck are heading directly toward one another on a straight and narrow street, but they... Problem 65PCE: Suppose you use videos to analyze the motion of penguins as they slide from rest down three... Problem 66PCE: At the edge of a roof you throw ball 1 upward with an initial speed v0; a moment later you throw... Problem 67PCE: A cliff diver drops from rest to the water below. How many seconds does it take for the diver to go... Problem 68PCE: For a flourish at the end of her act, a juggler tosses a single ball high in the air. She catches... Problem 69PCE: Soaring Shaun During the 2014 Olympic games, snowboarder Shaun White rose 6.4 m vertically above the... Problem 70PCE: BIO Gulls are often observed dropping clams and other shellfish from a height to the rocks below, as... Problem 71PCE: A volcano launches a lava bomb straight upward with an initial speed of 28 m/s. Taking upward to be... Problem 72PCE: An Extraterrestrial Volcano The first active volcano observed outside the Earth was discovered in... Problem 73PCE: BIO Measure Your Reaction Time Heres something you can try at homean experiment to measure your... Problem 74PCE: Predict/Explain A carpenter on the roof of a building accidentally drops her hammer. As the hammer... Problem 75PCE: Predict/Explain Figure 2-40 shows a v-versus-t plot for the hammer dropped by the carpenter in... Problem 76PCE: A ball is thrown straight upward with an initial speed v0. When it reaches the top of its flight at... Problem 77PCE: On a hot summer day in the state of Washington while kayaking, I saw several swimmers jump from a... Problem 78PCE: Highest Water Fountain The USAs highest fountain of water is located, appropriately enough, in... Problem 79PCE: Wrongly called for a foul, an angry basketball player throws the ball straight down to the floor. If... Problem 80PCE: To celebrate a victory, a pitcher throws her glove straight upward with an initial speed of 6.5 m/s.... Problem 81PCE: Predict/Calculate Standing at the edge of a cliff 30.5 m high, you drop a ball. Later, you throw a... Problem 82PCE: You shoot an arrow into the air. Two seconds later (2.00 s) the arrow has gone straight upward to a... Problem 83PCE: While riding on an elevator descending with a constant speed of 3.0 m/s, you accidentally drop a... Problem 84PCE: A hot-air balloon is descending at a rate of 2.3 m/s when a passenger drops a camera. If the camera... Problem 85PCE: A model rocket blasts off and moves upward with an acceleration of 12 m/s2 until it reaches a height... Problem 86PCE: BIO The southern flying squirrel (Glaucomys volans) can reduce its free-fall acceleration by... Problem 87PCE: Hitting the High Striker A young woman at a carnival steps up to the high striker, a popular test of... Problem 88PCE: While sitting on a tree branch 10.0 m above the ground, you drop a chestnut. When the chestnut has... Problem 89GP: An astronaut on the Moon drops a rock straight downward from a height of 1.25 m. If the acceleration... Problem 90GP: Taipei 101 An elevator in the Taipei 101 skyscraper can start from rest and accelerate to a maximum... Problem 91GP: A Supersonic Waterfall Geologists have learned of periods in the past when the Strait of Gibraltar... Problem 92GP: A juggler throws a ball straight up into the air. If the ball returns to its original position in... Problem 93GP: CE At the edge of a roof you drop ball A from rest, and at the same instant your friend throws ball... Problem 94GP: CE Two balls start their motion at the same time, with ball A dropped from rest and ball B thrown... Problem 95GP: CE Refer to the position-versus-time plot in Figure 2-44 for the following questions: (a) Is the... Problem 96GP: Drop Tower NASA operates a 2.2-second drop tower at the Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, Ohio. At... Problem 97GP: The velocity-versus-time graph for an object moving in a straight line is given in Figure 2. (a)... Problem 98GP: At the 13th green of the U.S. Open you need to make a 23.5-ft putt to win the tournament. When you... Problem 99GP: A glaucous-winged gull, ascending straight upward at 5.20 m/s, drops a shell when it is 12.5 m above... Problem 100GP: A doctor, preparing to give a patient an injection, squirts a small amount of liquid straight upward... Problem 101GP: A hot-air balloon has just lifted off and is rising at the constant rate of 2.0 m/s. Suddenly one of... Problem 102GP: Astronauts on a distant planet throw a rock straight upward and record its motion with a video... Problem 103GP: BIO A Jet-Propelled Squid Squids can move through the water using a form of jet propulsion. Suppose... Problem 104GP: A ball, dropped from rest, covers three-quarters of the distance to the ground in the last second of... Problem 105GP: You drop a ski glove from a height h onto fresh snow, and it sinks to a depth d before coming to... Problem 106GP: To find the height of an overhead power line, you throw a ball straight upward. The ball passes the... Problem 107GP: Sitting in a second-story apartment, a physicist notices a ball moving straight upward just outside... Problem 108PP: Bam!Apollo 15 Lands on the Moon The first word spoken on the surface of the Moon after Apollo 15... Problem 109PP: Bam!Apollo 15 Lands on the Moon The first word spoken on the surface of the Moon after Apollo 15... Problem 110PP: Bam!Apollo 15 Lands on the Moon The first word spoken on the surface of the Moon after Apollo 15... Problem 111PP: Bam!Apollo 15 Lands on the Moon The first word spoken on the surface of the Moon after Apollo 15... Problem 112PP: Referring to Example 2-17 Suppose the speeder (red car) is traveling with a constant speed of 25... Problem 113PP: Referring to Example 2-17 The speeder passes the position of the police car with a constant speed of... Problem 114PP: Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 2-21 (a) In Example 2-21, the bag of sand is released at 20.0... Problem 115PP: Referring to Example 2-21 Suppose the balloon is descending with a constant speed of 4.2 m/s when... format_list_bulleted


 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning




