
Concept explainers
Subpart (a):
Production possibilities frontier of Mexico and United States.
Subpart (a):
Explanation of Solution
The production possibilities frontier of Mexico and United States is shown in Figure 1 below:
Figure 1 shows the
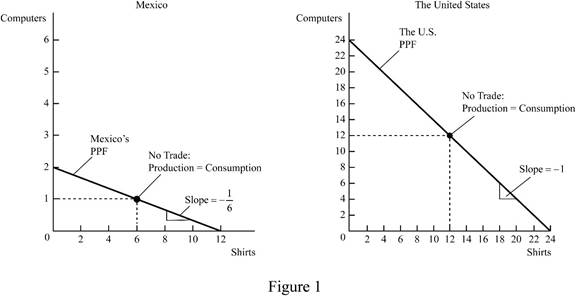
In Figure 1, the left side diagram shows PPF of Mexico and right side diagram shows the PPF of US. The vertical axis of both measures the number of computers produced by Mexico and United States, and the horizontal axis measures the number of shirts. Mexico produces 2 computers and 12 shirts, and United States produces 24 computers and 24 shirts.
Concept introduction:
Production possibilities frontier (PPF): PPF refers to the different combination of goods and services that can be produced efficiently with the given resources by a country. Any points inside the PPF represent inefficient usage of the resources, and any points outside the PPF represent that it is not attainable with the available resources.
Subpart (b):
Calculation of
Subpart (b):
Explanation of Solution
The equation to calculate the opportunity cost is shown below.
Substitute the respective values in Equation (1) to calculate the opportunity cost of producing a shirt in Mexico.
Opportunity cost of producing a shirt in Mexico is 0.1666.
Substitute the respective values in Equation (1) to calculate the opportunity cost of producing a shirt in United States.
Opportunity cost of producing a shirt in United States is 1.
Mexico has to produce more number of shirts. This is because when comparing the opportunity cost of producing a shirt in both countries, Mexico has the lowest opportunity cost.
Concept introduction:
Opportunity cost: Opportunity cost refers to the value of forgone goods and services to consume the other goods and services.
Sub part (c):
Calculation of opportunity cost.
Sub part (c):
Explanation of Solution
Substitute the respective values in Equation (1) to calculate the opportunity cost of producing a computer in Mexico.
The opportunity cost of producing a computer in Mexico is 6.
Substitute the respective values in Equation (1) to calculate the opportunity cost of producing a computer in United States.
Opportunity cost of producing a computer in United States is 1.
United States has to produce more number of computers. This is because when comparing the opportunity of producing a computer in both countries, United States has the lowest opportunity cost.
Concept introduction:
Opportunity cost: Opportunity cost refers to the value of forgone goods and services to consume the other goods and services.
Sub part (d):
Production possibility frontier.
Sub part (d):
Explanation of Solution
On the basis of opportunity cost of producing a shirt and a computer in both countries, Mexico has a
Figure 2 shows the PPF of trade alliance between United States and Mexico.
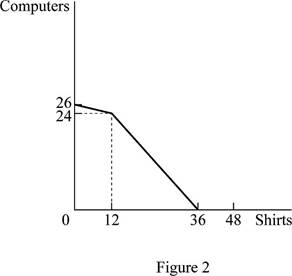
In Figure 2, the vertical axis measures the volume of production of computers and the horizontal axis measures the volume of production of shirts. United States produces 24 units of computer and Mexico produces 1 unit. In the case of shirt, Mexico produces 12 units and United States produces 24 units.
Concept introduction:
Production possibilities frontier (PPF): PPF refers to the different combination of goods and services that can be produced efficiently with the given resources by a country. Any points inside the PPF represent inefficient usage of the resources, and any points outside the PPF represent that it is not attainable with the available resources.
Sub part (e):
Production possibility frontier.
Sub part (e):
Explanation of Solution
The trade alliance after the entrance of Haiti is shown below:
Figure 3 shows the PPF of trade alliance of Haiti, Mexico, and United States.
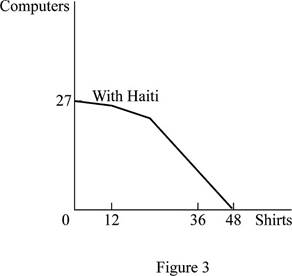
In Figure 3, the vertical axis measures the volume of production of computers and the horizontal axis measures the volume of production of shirts. This is the new PPF after the trade alliance of Haiti with the trade alliance between Mexico and United States. Haiti is producing 1 unit of computer and 12 units of shirt.
Concept introduction:
Production possibilities frontier (PPF): PPF refers to the different combination of goods and services that can be produced efficiently with the given resources by a country. Any points inside the PPF represent inefficient usage of the resources, and any points outside the PPF represent that it is not attainable with the available resources.
Sub part (f):
Production possibility frontier.
Sub part (f):
Explanation of Solution
The PPF of trade alliance of existing three countries and many countries who join the trade alliance is shown below.
Figure 4 shows the PPF for trade alliance between infinity numbers of countries.
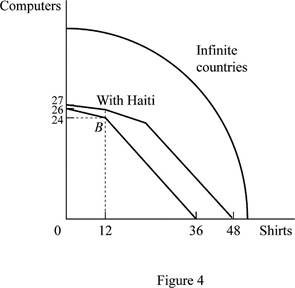
In Figure 4, the vertical axis measures the volume of production of computers and the horizontal axis measures the volume of production of shirts. The first curve represents that PPF is the trade alliance between Mexico and United States. The second curve represents that PPF is the trade alliance between Mexico, United States with Haiti. The third curve represents the PPF of trade alliance between infinity numbers of countries.
Concept introduction:
Production possibilities frontier (PPF): PPF refers to the different combination of goods and services that can be produced efficiently with the given resources by a country. Any points inside the PPF represent inefficient usage of the resources, and any points outside the PPF represent that it is not attainable with the available resources.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK MODERN PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS
- Production efficiency is most concerned with Choice of inputs in production process Quantity of outputs resulting from the production process The technological process of production All of the abovearrow_forwardChoose all of the following that are assumed to be constant while constructing the production possibilities curve Technology Precise mix of inputs Institutional arrangements like judicial protection of business contracts Outputsarrow_forwardA point that lies OUTSIDE of the PPC can be achieved if A major technological innovation increases production efficiency A sudden influx of resources e.g., massive immigration of trained nurses Economic reform resulting in greater protection of intellectual property rights All of the above Only options 1 and 2arrow_forward
- The marginal benefit from each successive unit of medical care consumed declines BECAUSE each successive unit is more expensive to produce True Falsearrow_forwardIn the Human Capital approach, estimated monetary worth of life is MOST SENSITIVE to which key indicator Discount rate Social security payroll taxes Labour market earnings Workplace injury compensationarrow_forwardOver the last few decades out-of-pocket costs have formed a DECLINING proportion of total consumer expenditure on medical care True Falsearrow_forward
- Cost benefit analyses often assumes the following about consumers EXCEPT Consumers have clear preferences among choices they are exposed to Consumers purposely choose actions that result in higher satisfaction Consumers factor in uncertainty of outcomes in their decision-making regarding net benefits and costs Consumers lack information about attributes of market goods that are necessary for ranking their choice setarrow_forwardThe TRUE relationship between MARGINAL utility and an individual’s stock of health can be best described as a scatter plot True Falsearrow_forwardMany health economists believe that the United States spends its MARGINAL dollars on healthcare in a highly wasteful manner. This view is also known as “flat of the curve” medicine. True Falsearrow_forward
- Increasing provision of out-of-pocket cost calculators by major insurers are attempts to REDUCE price transparency for consumers True Falsearrow_forwardA price hike for medical goods/services that have an inelastic (i.e., <1) own-price elasticity of demand will tend to yield lower revenues True Falsearrow_forwardRisk Loving people are willing to pay insurance premiums that exceed their expected losses True Falsearrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





