
Concept explainers
Subpart (a):
Production possibilities frontier of Mexico and United States.
Subpart (a):
Explanation of Solution
The production possibilities frontier of Mexico and United States is shown in Figure 1 below:
Figure 1 shows the
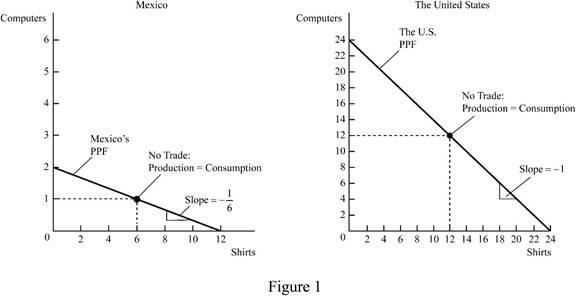
In Figure 1, the left side diagram shows PPF of Mexico and right side diagram shows the PPF of US. The vertical axis of both measures the number of computers produced by Mexico and United States, and the horizontal axis measures the number of shirts. Mexico produces 2 computers and 12 shirts, and United States produces 24 computers and 24 shirts.
Concept introduction:
Production possibilities frontier (PPF): PPF refers to the different combination of goods and services that can be produced efficiently with the given resources by a country. Any points inside the PPF represent inefficient usage of the resources, and any points outside the PPF represent that it is not attainable with the available resources.
Subpart (b):
Calculation of opportunity cost .
Subpart (b):
Explanation of Solution
The equation to calculate the opportunity cost is shown below.
Substitute the respective values in Equation (1) to calculate the opportunity cost of producing a shirt in Mexico.
Opportunity cost of producing a shirt in Mexico is 0.1666.
Substitute the respective values in Equation (1) to calculate the opportunity cost of producing a shirt in United States.
Opportunity cost of producing a shirt in United States is 1.
Mexico has to produce more number of shirts. This is because when comparing the opportunity cost of producing a shirt in both countries, Mexico has the lowest opportunity cost.
Concept introduction:
Opportunity cost: Opportunity cost refers to the value of forgone goods and services to consume the other goods and services.
Sub part (c):
Calculation of opportunity cost.
Sub part (c):
Explanation of Solution
Substitute the respective values in Equation (1) to calculate the opportunity cost of producing a computer in Mexico.
The opportunity cost of producing a computer in Mexico is 6.
Substitute the respective values in Equation (1) to calculate the opportunity cost of producing a computer in United States.
Opportunity cost of producing a computer in United States is 1.
United States has to produce more number of computers. This is because when comparing the opportunity of producing a computer in both countries, United States has the lowest opportunity cost.
Concept introduction:
Opportunity cost: Opportunity cost refers to the value of forgone goods and services to consume the other goods and services.
Sub part (d):
Production possibility frontier.
Sub part (d):
Explanation of Solution
On the basis of opportunity cost of producing a shirt and a computer in both countries, Mexico has a
Figure 2 shows the PPF of trade alliance between United States and Mexico.
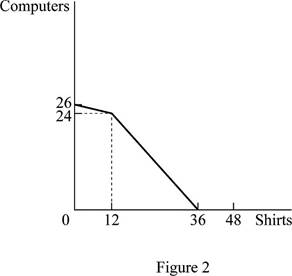
In Figure 2, the vertical axis measures the volume of production of computers and the horizontal axis measures the volume of production of shirts. United States produces 24 units of computer and Mexico produces 1 unit. In the case of shirt, Mexico produces 12 units and United States produces 24 units.
Concept introduction:
Production possibilities frontier (PPF): PPF refers to the different combination of goods and services that can be produced efficiently with the given resources by a country. Any points inside the PPF represent inefficient usage of the resources, and any points outside the PPF represent that it is not attainable with the available resources.
Sub part (e):
Production possibility frontier.
Sub part (e):
Explanation of Solution
The trade alliance after the entrance of Haiti is shown below:
Figure 3 shows the PPF of trade alliance of Haiti, Mexico, and United States.
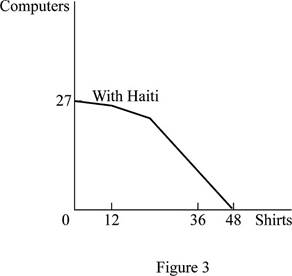
In Figure 3, the vertical axis measures the volume of production of computers and the horizontal axis measures the volume of production of shirts. This is the new PPF after the trade alliance of Haiti with the trade alliance between Mexico and United States. Haiti is producing 1 unit of computer and 12 units of shirt.
Concept introduction:
Production possibilities frontier (PPF): PPF refers to the different combination of goods and services that can be produced efficiently with the given resources by a country. Any points inside the PPF represent inefficient usage of the resources, and any points outside the PPF represent that it is not attainable with the available resources.
Sub part (f):
Production possibility frontier.
Sub part (f):
Explanation of Solution
The PPF of trade alliance of existing three countries and many countries who join the trade alliance is shown below.
Figure 4 shows the PPF for trade alliance between infinity numbers of countries.
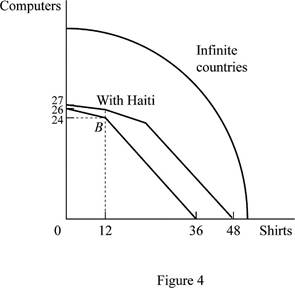
In Figure 4, the vertical axis measures the volume of production of computers and the horizontal axis measures the volume of production of shirts. The first curve represents that PPF is the trade alliance between Mexico and United States. The second curve represents that PPF is the trade alliance between Mexico, United States with Haiti. The third curve represents the PPF of trade alliance between infinity numbers of countries.
Concept introduction:
Production possibilities frontier (PPF): PPF refers to the different combination of goods and services that can be produced efficiently with the given resources by a country. Any points inside the PPF represent inefficient usage of the resources, and any points outside the PPF represent that it is not attainable with the available resources.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Sapling Learning Single-Course Homework-Only for Principles of Microeconomics (Access Card)
- In a small open economy with a floating exchange rate, the supply of real money balances is fixed and a rise in government spending ______ Group of answer choices Raises the interest rate so that net exports must fall to maintain equilibrium in the goods market. Cannot change the interest rate so that net exports must fall to maintain equilibrium in the goods market. Cannot change the interest rate so income must rise to maintain equilibrium in the money market Raises the interest rate, so that income must rise to maintain equilibrium in the money market.arrow_forwardSuppose a country with a fixed exchange rate decides to implement a devaluation of its currency and commits to maintaining the new fixed parity. This implies (A) ______________ in the demand for its goods and a monetary (B) _______________. Group of answer choices (A) expansion ; (B) contraction (A) contraction ; (B) expansion (A) expansion ; (B) expansion (A) contraction ; (B) contractionarrow_forwardAssume a small open country under fixed exchanges rate and full capital mobility. Prices are fixed in the short run and equilibrium is given initially at point A. An exogenous increase in public spending shifts the IS curve to IS'. Which of the following statements is true? Group of answer choices A new equilibrium is reached at point B. The TR curve will shift down until it passes through point B. A new equilibrium is reached at point C. Point B can only be reached in the absence of capital mobility.arrow_forward
- A decrease in money demand causes the real interest rate to _____ and output to _____ in the short run, before prices adjust to restore equilibrium. Group of answer choices rise; rise fall; fall fall; rise rise; fallarrow_forwardIf a country's policy makers were to continously use expansionary monetary policy in an attempt to hold unemployment below the natural rate , the long urn result would be? Group of answer choices a decrease in the unemployment rate an increase in the level of output All of these an increase in the rate of inflationarrow_forwardA shift in the Aggregate Supply curve to the right will result in a move to a point that is southwest of where the economy is currently at. Group of answer choices True Falsearrow_forward
- An oil shock can cause stagflation, a period of higher inflation and higher unemployment. When this happens, the economy moves to a point to the northeast of where it currently is. After the economy has moved to the northeast, the Federal Reserve can reduce that inflation without having to worry about causing more unemployment. Group of answer choices True Falsearrow_forwardThe long-run Phillips Curve is vertical which indicates Group of answer choices that in the long-run, there is no tradeoff between inflation and unemployment. that in the long-run, there is no tradeoff between inflation and the price level. None of these that in the long-run, the economy returns to a 4 percent level of inflation.arrow_forwardSuppose the exchange rate between the British pound and the U.S. dollar is £1 = $2.00. The U.S. government implementsU.S. government implements a contractionary fiscal policya contractionary fiscal policy. Illustrate the impact of this change in the market for pounds. 1.) Using the line drawing tool, draw and label a new demand line. 2.) Using the line drawing tool, draw and label a new supply line. Note: Carefully follow the instructions above and only draw the required objects.arrow_forward
- Just Part D please, this is for environmental economicsarrow_forward3. Consider a single firm that manufactures chemicals and generates pollution through its emissions E. Researchers have estimated the MDF and MAC curves for the emissions to be the following: MDF = 4E and MAC = 125 – E Policymakers have decided to implement an emissions tax to control pollution. They are aware that a constant per-unit tax of $100 is an efficient policy. Yet they are also aware that this policy is not politically feasible because of the large tax burden it places on the firm. As a result, policymakers propose a two- part tax: a per unit tax of $75 for the first 15 units of emissions an increase in the per unit tax to $100 for all further units of emissions With an emissions tax, what is the general condition that determines how much pollution the regulated party will emit? What is the efficient level of emissions given the above MDF and MAC curves? What are the firm's total tax payments under the constant $100 per-unit tax? What is the firm's total cost of compliance…arrow_forward2. Answer the following questions as they relate to a fishery: Why is the maximum sustainable yield not necessarily the optimal sustainable yield? Does the same intuition apply to Nathaniel's decision of when to cut his trees? What condition will hold at the equilibrium level of fishing in an open-access fishery? Use a graph to explain your answer, and show the level of fishing effort. Would this same condition hold if there was only one boat in the fishery? If not, what condition will hold, and why is it different? Use the same graph to show the single boat's level of effort. Suppose you are given authority to solve the open-access problem in the fishery. What is the key problem that you must address with your policy?arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





