
Concept explainers
a)
To compute: The labor productivity and multifactor productivity for each unit.
Introduction: Labor productivity is the measure of productivity of a worker during a period of time. It the ratio of total output to the total productivity hours.
a)
Answer to Problem 7P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Unit | Employees | Customer processed/day |
| A | 4 | 36 |
| B | 5 | 40 |
| C | 8 | 60 |
| D | 3 | 20 |
Hourly wage=$25Overhead=1.0×Labor costMaterial cost=$5 per customer
Formula:
Multifactor Productivity=OutputTotal costLabor Productivity=Customersper dayEmployeesTotal cost=Labor cost+Overhead cost+Material cost
Laborcost=Number of workers ×8 hours×$25/hourOverhead cost=Labor cost×1.00Material cost=Customers×$5/customer
Calculation of multifactor productivity:
| Unit | Employees | Customer processed/day | Labor cost | Overhead cost | Material cost | Total cost | Labor productivity | MFP (2decimal) | MFP (3decimal) |
| A | 4 | 36 | 800 | 800 | 180 | 1780 | 9 | 0.02 | 0.020 |
| B | 5 | 40 | 1000 | 1000 | 200 | 2200 | 8 | 0.02 | 0.018 |
| C | 8 | 60 | 1600 | 1600 | 300 | 3500 | 7.5 | 0.02 | 0.017 |
| D | 3 | 20 | 600 | 600 | 100 | 1300 | 6.6666667 | 0.02 | 0.015 |
Table 1
Excel Worksheet:
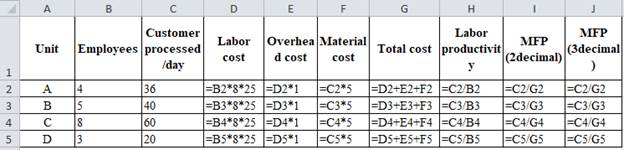
Calculation of multifactor productivity:
Unit A:
Labor cost is calculated by multiplying number of workers (4) with 8working hours and 25 hourly wages which gives 800.
Overhead cost is calculated by multiplying Labor cost of 800 with 1.0 which gives 800.
Material cost is calculated by multiplying 36 with 5 which gives 180.
Total cost is calculated by adding labor cost of 800, overhead cost of 800 and material cost of 180 which yields 1780.
Labor productivity is calculated by dividing 36 with 4 which yields 9.
Multifactor productivity is calculated by dividing 36 with the total cost of 1,780 which yields 0.02 (2-decimal) and 0.020 (3 decimal).
Same procedure is followed for unit B, C and D the result is shown in table 1.
Hence, multifactor productivity has dropped from 0.020 to 0.015.
b)
To compute: The labor productivity and multifactor productivity for each unit.
Introduction: Multifactor productivity is also referred as total factor productivity. It is the measure of economic performance by comparing the amount of goods and services produced to the total input used to produce the output.
b)
Answer to Problem 7P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Every employee process on additional customers.
| Unit | Employees | Customer processed/day |
| A | 4 | 40 |
| B | 5 | 45 |
| C | 8 | 68 |
| D | 3 | 23 |
Hourly wage=$25Overhead=1.0×Labor costMaterial cost=$5 per customer
Formula:
Multifactor Productivity=OutputTotal costLabor Productivity=Customersper dayEmployeesTotal cost=Labor cost+Overhead cost+Material cost
Laborcost=Number of workers ×8 hours×$25/hourOverhead cost=Labor cost×1.00Material cost=Customers×$5/customer
Calculation of multifactor productivity:
| Unit | Employees | Customer processed/day | Labor cost | Overhead cost | Material cost | Total cost | Labor productivity | MFP (2decimal) | MFP (3decimal) |
| A | 4 | 40 | 800 | 800 | 200 | 1800 | 10 | 0.02 | 0.022 |
| B | 5 | 45 | 1000 | 1000 | 225 | 2225 | 9 | 0.02 | 0.020 |
| C | 8 | 68 | 1600 | 1600 | 340 | 3540 | 8.5 | 0.02 | 0.019 |
| D | 3 | 23 | 600 | 600 | 115 | 1315 | 7.6666667 | 0.02 | 0.017 |
Table 2
Excel Worksheet:
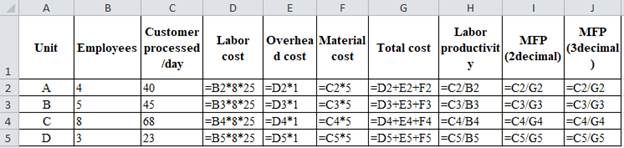
Calculation of multifactor productivity:
Unit A:
Labor cost is calculated by multiplying number of workers (4) with 8 working hours and 25 hourly wages which gives 800.
Overhead cost is calculated by multiplying Labor cost of 800 with 1.0 which gives 800.
Material cost is calculated by multiplying 40 with 5 which gives 200.
Total cost is calculated by adding labor cost of 800, overhead cost of 800 and material cost of 200 which yields 1800.
Labor productivity is calculated by dividing 40 with 4 which yields 10.
Multifactor productivity is calculated by dividing 40 with the total cost of 1,800 which yields 0.02 (2-decimal) and 0.022 (3 decimal).
Same procedure is followed for unit B, C and D the result is shown in table 2.
Hence, multifactor productivity has dropped from 0.022to 0.017.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
- SIPOC Process Supplier Machines Quality Group Leader Double Output Customers Inputs Solutions End of batch Inspection verification Scrap evaluation Sampling Verification Batch complete Evaluation Completed Quality Group Leader Samplings verified Quality Samplings verified Quality Barcode programed Mechanic Parameters registered Quality Line verified Quality Line Verified Quality Second verification Barcode Parameters Line Inspection Second Line Inspection Lot and Expiration Date Quality Quality Mechanic Mechanic Quality Machines Quality Group Leader Quality Quality Quality Batch Verification Process complete Revision Review Sampling Verification Barcode Scanner Machine Parameters Line Clearance Line Clearance Machine Remove Lot Status Verification Close floor Final MFG Review Final QA Review Close Batch Machine removed Lot verified Floor closed MFG Reviewed Process reviewed Batch closed Mechanic Group Leader Quality Quality Quality Group Leaderarrow_forwardAn assessment of gender leadership and corporate culture.Kindly provide the following, citing it using in-text referencing: • A thorough exploration of gender dynamics and concepts.• Creating a clear plan to address gender bias and promote inclusive leadership.• An examination of female leadership dynamics and their impact on performance. • Comprehensive justification behind the proposal.arrow_forwardAssessment of Strategic Leadership and Global Context Provide the below in detail:· A comprehensive analysis of the current strategy,· Develop a new comprehensive strategic leadership framework that tackles the challenges of leading a global company while balancing global standards and responding to local context and challenges.· Justify a framework by drawing on and applying relevant theories of strategic leadership and global management.· It needs substantial depth and detail.· Conduct a critical evaluation of strategic leadership in a global context.arrow_forward
- Assessing Leadership Ethics and Cross-cultural DiversityProvide the below with in-cite text referencing:- Investigate ethical issues and how they influence diversity and cross-cultural leadership.• Develop an ethical decision-making model that addresses cross-cultural concerns in emerging markets, such as Africa.· Conduct comprehensive analysis and modelling if necessary.- Provide a thorough ethical analysis that considers cross-cultural issues.· Careful evaluation of potential outcomes.- The proposed ethical decision-making technique is both novel and defendable.· Promoting diversity and recognising cross-cultural differences.arrow_forwardNeed help, have no idea where to start and love help upon a paper idea with no AI and soemthing original please.arrow_forwardAbout the Assignment In this course, you learned how a business chooses a positioning strategy in the marketplace and focuses on these areas by evaluating management's use of production types, creating effective productivity, and analyzing the competitiveness of production. Now you will choose a retail organization and propose a positioning marketing strategy that analyzes the organizational management decisions related to any competitiveness of cost, quality, flexibility, speed, innovation, and/or service. Prompt Choose an organization that focuses on one of these areas in the market: competitiveness of cost, quality, flexibility, speed, innovation, and/or service. An example would be choosing ALDI or LIDL. Their cost marketing positioning strategy is providing customers with international goods for a lower price and, in turn, saving business fees by not providing bagging products for free. (This is just an example. Do not use this example for your project.) Use the following steps…arrow_forward
- Can you guys help me with this? Thank you! The project is Terminal 1 at JFK International Airport Here's what need to do: Time Content: What was the estimated time of the project; what was the final time (or the estimated date) of the project; what are the major contributing factors for the disparity? (Please make sure all the information here can be present around 2 minutes) Risk management content: Discuss a major risk management event that affected the project. while researching if any team member finds an interesting risk management event *Include sources that you have the information when go over these 2 parts above.arrow_forwardI only need help with part C. Please and thank you :) ANSWERED: Gracie recorded the following times assembling a watch. Performance rating given is 95%. A) Average time of Gracie for the Operation? (round to three decimal places) ANSWER=0.107 B) normal time for this operation? (round to three decimal places) ANSWER=0.102 C) HELP PLEASE. "For a given personal allowance of 8% the standard time for the operation is how many minutes?" (round your answer to three decimal places)arrow_forwardGracie recorded the following times assembling a watch. Performance rating given is 95%. Average time of Gracie for the Operation? (round to three decimal places) normal time for this operation? (round to three decimal places)arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Management, Loose-Leaf VersionManagementISBN:9781305969308Author:Richard L. DaftPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Management, Loose-Leaf VersionManagementISBN:9781305969308Author:Richard L. DaftPublisher:South-Western College Pub Understanding Management (MindTap Course List)ManagementISBN:9781305502215Author:Richard L. Daft, Dorothy MarcicPublisher:Cengage Learning
Understanding Management (MindTap Course List)ManagementISBN:9781305502215Author:Richard L. Daft, Dorothy MarcicPublisher:Cengage Learning Foundations of Business (MindTap Course List)MarketingISBN:9781337386920Author:William M. Pride, Robert J. Hughes, Jack R. KapoorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Foundations of Business (MindTap Course List)MarketingISBN:9781337386920Author:William M. Pride, Robert J. Hughes, Jack R. KapoorPublisher:Cengage Learning




