
Concept explainers
(a)
The sketch of speed – time graph.
(a)
Answer to Problem 54P
The sketch of speed – time graph of air plane is drawn.
Explanation of Solution
The below figure shows the speed time graph of the airplane.
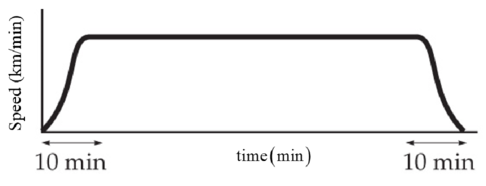
Airplane was initially at rest on the ground, accelerates quickly and gains its top speed in first 10 minutes and then it travels with constant speed and then while it lands off it decelerates quickly to the ground similar to the acceleration while taking off.
Conclusion:
The sketch of speed – time graph of air plane is drawn.
(b)
The average speed of the trip.
(b)
Answer to Problem 54P
The average speed of the trip is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression to calculate the average speed.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the average speed of the trip is
(c)
The top speed in the trip
(c)
Answer to Problem 54P
The top speed in the trip is
Explanation of Solution
For the first 10 min and last 10 min that is for a total of 20 min the average speed of the airplane was half the top speed. For the remaining time
Here,
Write the expression to calculate the total distance travelled by the airplane.
Here
Use
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the a top speed of the trip is
(d)
The average acceleration during first 10 min.
(d)
Answer to Problem 54P
The average acceleration during first 10 min is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for average acceleration during first 10 min.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the average acceleration during first 10 min is
(e)
The average acceleration during the central hours of the trip.
(e)
Answer to Problem 54P
The average acceleration during the central hours of the trip is
Explanation of Solution
During the central hours of the trip, the airplane travelled with top speed. Top speed is constant and hence during the central hours of the trip the acceleration was zero.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the average acceleration during the central hours of the trip is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Bundle: College Physics: Reasoning And Relationships, 2nd + Webassign Printed Access Card For Giordano's College Physics, Volume 1, 2nd Edition, Multi-term
- The position of a 0.300 kg object attached to a spring is described by x=0.271 m ⋅ cos(0.512π⋅rad/s ⋅t) (Assume t is in seconds.) Find the amplitude of the motion. Find the spring constant. Find the position of the object at t = 0.324 s. Find the object's velocity at t = 0.324 s.arrow_forwardMin Min is hanging from her spring-arms off the edge of the level. Due to the spring like nature of her arms she is bouncing up and down in simple harmonic motion with a maximum displacement from equilibrium of 0.118 m. The spring constant of Min-Min’s arms is 9560. N/m and she has a mass of 87.5 kg. What is the period at which she oscillates? Find her maximum speed. Find her speed when she is located 5.00 cm from her equilibrium position.arrow_forward(a) What magnification in multiples is produced by a 0.150 cm focal length microscope objective that is 0.160 cm from the object being viewed? 15.9 (b) What is the overall magnification in multiples if an eyepiece that produces a magnification of 7.90x is used? 126 × ×arrow_forward
- Gravitational Potential Energyarrow_forwardE = кедо Xo A continuous line of charge lies along the x axis, extending from x = +x to positive infinity. The line carries positive charge with a uniform linear charge density 10. (a) What is the magnitude of the electric field at the origin? (Use the following as necessary: 10, Xo, and ke.) (b) What is the direction of the electric field at the origin? O O O O O O G -y +z ○ -z +x -x +yarrow_forwardInclude free body diagramarrow_forward
- 2 Spring 2025 -03 PITT Calculate the acceleration of a skier heading down a 10.0° slope, assuming the coefficient of cold coast at a constant velocity. You can neglect air resistance in both parts. friction for waxed wood on wet snow fly 0.1 (b) Find the angle of the slope down which this skier Given: 9 = ? 8=10° 4=0.1arrow_forwarddry 5. (a) When rebuilding her car's engine, a physics major must exert 300 N of force to insert a c piston into a steel cylinder. What is the normal force between the piston and cyli=030 What force would she have to exert if the steel parts were oiled? k F = 306N 2 =0.03 (arrow_forwardInclude free body diagramarrow_forward
- Include free body diagramarrow_forwardTest 2 МК 02 5. (a) When rebuilding her car's engine, a physics major must exert 300 N of force to insert a dry = 0.03 (15 pts) piston into a steel cylinder. What is the normal force between the piston and cylinder? What force would she have to exert if the steel parts were oiled? Mk Giren F = 306N MK-0.3 UK = 0.03 NF = ?arrow_forward2. A powerful motorcycle can produce an acceleration of 3.50 m/s² while traveling at 90.0 km/h. At that speed the forces resisting motion, including friction and air resistance, total 400 N. (Air resistance is analogous to air friction. It always opposes the motion of an object.) What force does the motorcycle exert backward on the ground to produce its acceleration if the mass of the motorcycle with rider is 245 ke? a = 350 m/s 2arrow_forward
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





