
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Volume 2
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781337553582
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 40AP
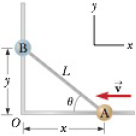
Two objects, A and B, are connected by hinges to a rigid rod that has a length L. The objects slide along perpendicular guide rails as shown in Figure P2.40. Assume object A slides to the left with a constant speed v. (a) Find the velocity vB of object B as a function of the angle θ. (b) Describe vB relative to v. Is vB always smaller than v, larger than v, or the same as v, or does it have some other relationship?
Figure P2.40
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
You are standing a distance x = 1.75 m away from this mirror. The object you are looking at is y = 0.29 m from the mirror. The angle of incidence is θ = 30°. What is the exact distance from you to the image?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Volume 2
Ch. 2.1 - Which of the following choices best describes what...Ch. 2.2 - Are officers in the highway patrol more interested...Ch. 2.5 - Make a velocitytime graph for the car in Figure...Ch. 2.5 - If a car is traveling eastward and slowing down,...Ch. 2.6 - Which one of the following statements is true? (a)...Ch. 2.7 - In Figure 2.12, match each vxt graph on the top...Ch. 2.8 - Consider the following choices: (a) increases, (b)...Ch. 2 - The speed of a nerve impulse in the human body is...Ch. 2 - A particle moves according to the equation x =...Ch. 2 - The position of a pinewood derby car was observed...
Ch. 2 - An athlete leaves one end of a pool of length L at...Ch. 2 - A positiontime graph for a particle moving along...Ch. 2 - A car travels along a straight line at a constant...Ch. 2 - A person takes a trip, driving with a constant...Ch. 2 - A child rolls a marble on a bent track that is 100...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.9 shows a graph of vx versus t for the...Ch. 2 - (a) Use the data in Problem 3 to construct a...Ch. 2 - A particle starts from rest and accelerates as...Ch. 2 - Draw motion diagrams for (a) an object moving to...Ch. 2 - Each of the strobe photographs (a), (b), and (c)...Ch. 2 - An electron in a cathode-ray tube accelerates...Ch. 2 - A parcel of air moving in a straight tube with a...Ch. 2 - In Example 2.7, we investigated a jet landing on...Ch. 2 - An object moving with uniform acceleration has a...Ch. 2 - Solve Example 2.8 by a graphical method. On the...Ch. 2 - A glider of length moves through a stationary...Ch. 2 - Why is the following situation impossible?...Ch. 2 - A glider of length 12.4 cm moves on an air track...Ch. 2 - In the particle under constant acceleration model,...Ch. 2 - At t = 0, one toy car is set rolling on a straight...Ch. 2 - You are observing the poles along the side of the...Ch. 2 - Why is the following situation impossible? Emily...Ch. 2 - An attacker at the base of a castle wall 3.65 m...Ch. 2 - The height of a helicopter above the ground is...Ch. 2 - A ball is thrown upward from the ground with an...Ch. 2 - A student throws a set of keys vertically upward...Ch. 2 - At time t = 0, a student throws a set of keys...Ch. 2 - You have been hired by the prosecuting attorney as...Ch. 2 - A student drives a moped along a straight road as...Ch. 2 - Automotive engineers refer to the time rate of...Ch. 2 - In Figure 2.11b, the area under the velocitytime...Ch. 2 - The froghopper Philaenus spumarius is supposedly...Ch. 2 - A woman is reported to have fallen 144 ft from the...Ch. 2 - At t = 0, one athlete in a race running on a long,...Ch. 2 - Why is the following situation impossible? A...Ch. 2 - Hannah tests her new sports car by racing with...Ch. 2 - Two objects, A and B, are connected by hinges to a...Ch. 2 - Lisa rushes down onto a subway platform to find...Ch. 2 - Two thin rods are fastened to the inside of a...Ch. 2 - In a womens 100-m race, accelerating uniformly,...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
1. Rub your hands together vigorously. What happens? Discuss the energy transfers and transformations that take...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
The active ingredient in Tylenol and a host of other over-the-counter pain relievers is acetaminophen (C8H9NO2)...
Chemistry: Atoms First
Sea turtles have disappeared from many regions, and one way of trying to save them is to reintroduce them to ar...
MARINE BIOLOGY
Separate the list P,F,V,,T,a,m,L,t, and V into intensive properties, extensive properties, and nonproperties.
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Why are mutants used as test organisms in the Ames test?
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For each of the actions depicted below, a magnet and/or metal loop moves with velocity v→ (v→ is constant and has the same magnitude in all parts). Determine whether a current is induced in the metal loop. If so, indicate the direction of the current in the loop, either clockwise or counterclockwise when seen from the right of the loop. The axis of the magnet is lined up with the center of the loop. For the action depicted in (Figure 5), indicate the direction of the induced current in the loop (clockwise, counterclockwise or zero, when seen from the right of the loop). I know that the current is clockwise, I just dont understand why. Please fully explain why it's clockwise, Thank youarrow_forwardA planar double pendulum consists of two point masses \[m_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}, \qquad m_2 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}\]connected by massless, rigid rods of lengths \[L_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{m}, \qquad L_2 = 1.20~\mathrm{m}.\]The upper rod is hinged to a fixed pivot; gravity acts vertically downward with\[g = 9.81~\mathrm{m\,s^{-2}}.\]Define the generalized coordinates \(\theta_1,\theta_2\) as the angles each rod makes with thedownward vertical (positive anticlockwise, measured in radians unless stated otherwise).At \(t=0\) the system is released from rest with \[\theta_1(0)=120^{\circ}, \qquad\theta_2(0)=-10^{\circ}, \qquad\dot{\theta}_1(0)=\dot{\theta}_2(0)=0 .\]Using the exact nonlinear equations of motion (no small-angle or planar-pendulumapproximations) and assuming the rods never stretch or slip, determine the angle\(\theta_2\) at the instant\[t = 10.0~\mathrm{s}.\]Give the result in degrees, in the interval \((-180^{\circ},180^{\circ}]\).arrow_forwardWhat are the expected readings of the ammeter and voltmeter for the circuit in the figure below? (R = 5.60 Ω, ΔV = 6.30 V) ammeter I =arrow_forward
- simple diagram to illustrate the setup for each law- coulombs law and biot savart lawarrow_forwardA circular coil with 100 turns and a radius of 0.05 m is placed in a magnetic field that changes at auniform rate from 0.2 T to 0.8 T in 0.1 seconds. The plane of the coil is perpendicular to the field.• Calculate the induced electric field in the coil.• Calculate the current density in the coil given its conductivity σ.arrow_forwardAn L-C circuit has an inductance of 0.410 H and a capacitance of 0.250 nF . During the current oscillations, the maximum current in the inductor is 1.80 A . What is the maximum energy Emax stored in the capacitor at any time during the current oscillations? How many times per second does the capacitor contain the amount of energy found in part A? Please show all steps.arrow_forward
- A long, straight wire carries a current of 10 A along what we’ll define to the be x-axis. A square loopin the x-y plane with side length 0.1 m is placed near the wire such that its closest side is parallel tothe wire and 0.05 m away.• Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop using Ampere’s law.arrow_forwardDescribe the motion of a charged particle entering a uniform magnetic field at an angle to the fieldlines. Include a diagram showing the velocity vector, magnetic field lines, and the path of the particle.arrow_forwardDiscuss the differences between the Biot-Savart law and Coulomb’s law in terms of their applicationsand the physical quantities they describe.arrow_forward
- Explain why Ampere’s law can be used to find the magnetic field inside a solenoid but not outside.arrow_forward3. An Atwood machine consists of two masses, mA and m B, which are connected by an inelastic cord of negligible mass that passes over a pulley. If the pulley has radius RO and moment of inertia I about its axle, determine the acceleration of the masses mA and m B, and compare to the situation where the moment of inertia of the pulley is ignored. Ignore friction at the axle O. Use angular momentum and torque in this solutionarrow_forwardA 0.850-m-long metal bar is pulled to the right at a steady 5.0 m/s perpendicular to a uniform, 0.650-T magnetic field. The bar rides on parallel metal rails connected through a 25-Ω, resistor (Figure 1), so the apparatus makes a complete circuit. Ignore the resistance of the bar and the rails. Please explain how to find the direction of the induced current.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Kinematics Part 3: Projectile Motion; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aY8z2qO44WA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY