
Financial Statements:
Financial statements are the accounting reports of any organization that are prepared with a purpose to disclose its past performance and also the assets and liabilities of the company along with the finances. These statements are prepared either on an annual basis or on a quarterly basis.
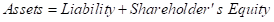
Cash Flow Statement − The cash flow statement represents the amount of cash that flows in and out of a business for a particular time period. It is mostly prepared on the accrual basis of accounting. The cash flow statement considers the fact that the net profit which a company earns in a year is not necessarily in the form of cash. It can be in the form of other assets as well like the receivables, inventory and so on. Therefore, the cash flow statement represents the total amount of cash that moves into a business organization.
Changes In The Shareholder’s Equity − The changes in the shareholder’s equity represents the changes in the amount of the
To Identify:
The financial statements of the Starbucks Corporation (SBUX) from different sources.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
Fundamentals of Corporate Finance, Student Value Edition
- Solve quicarrow_forwardNeed soln for thisarrow_forwardMuskoka Tourism has announced a rights offer to raise $30 million for a new magazine, titled ‘Discover Muskoka’. The magazine will review potential articles after the author pays a nonrefundable reviewing fee of $5,000 per page. The stock currently sells for $52 per share and there are 3.9 million shares outstanding. Required What is the maximum possible subscription price? What is the minimum? If the subscription price is set at $46 per share, how many shares must be sold? How many rights will it take to buy one share? What is the ex-rights price? What is the value of a right?arrow_forward
- Northern Escapes Inc. has 225,000 shares of stock outstanding. Each share is worth $73, so the company’s market value of equity is $16,425,000. Suppose the firm issues 30,000 new shares at the following prices: $73, $69, and $60. What will the effect be of each of these alternative offering prices on the existing price per share?arrow_forwardNeed answer correctly.arrow_forwardMuskoka Tourism has announced a rights offer to raise $30 million for a new magazine, titled ‘Discover Muskoka’. The magazine will review potential articles after the author pays a nonrefundable reviewing fee of $5,000 per page. The stock currently sells for $52 per share and there are 3.9 million shares outstanding.arrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





