
Concept explainers
Propranolol is an antihypertensive agent—that is, it lowers blood pressure. (a)
Which proton in propranolol is most acidic? (b) What products are formed when propranolol is treated with
(a)
Interpretation: The most acidic proton in propranolol is to be identified.
Concept introduction: An acid is a substance that is capable to donate
Answer to Problem 36P
The most acidic proton is
Explanation of Solution
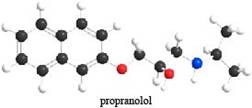
The given ball-and-stick model of propranolol is,
Figure 1
In ball-and-stick model, each colored ball represents a specific atom and each stick represents a bond. In this model, each black ball represents
Thus, the given compound is drawn as,
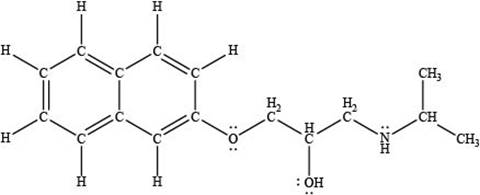
Figure 2
The acidity of an acid is directly proportional to the resonance stabilization of its conjugate base. In propranolol, when the
Figure 3
Thus, the most acidic proton is
The most acidic proton is
(b)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of propranolol with
Concept introduction: Sodium hydride
Answer to Problem 36P
The product formed by the treatment of propranolol with
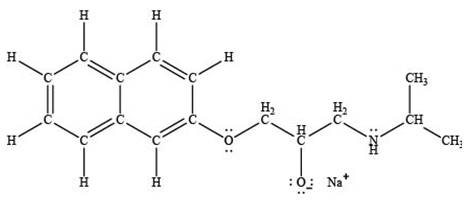
Explanation of Solution
Sodium hydride
The products formed by the treatment of propranolol with
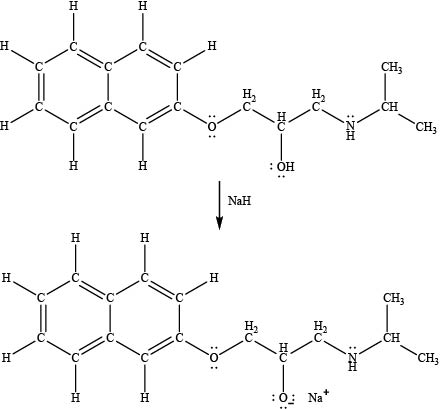
Figure 4
The product formed by the treatment of propranolol with
(c)
Interpretation: The most basic atom in propranolol is to be identified.
Concept introduction: A base is a substance that is capable to accept a
Answer to Problem 36P
The most basic atom is
Explanation of Solution
A base is a substance that is capable to accept
Thus, the most basic atom is
The most basic atom is N of
(d)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of propranolol with
Concept introduction: Hydrogen chloride
Answer to Problem 36P
The product formed by the treatment of propranolol with
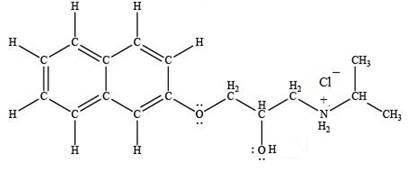
Explanation of Solution
Hydrogen chloride
The product formed by the treatment of propranolol with
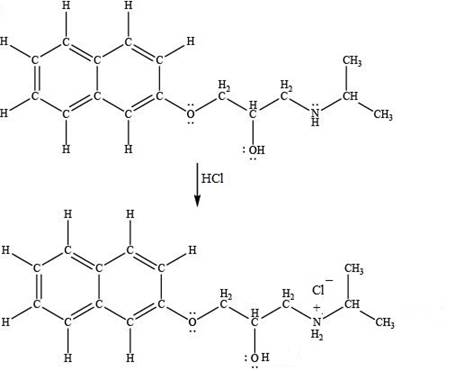
Figure 5
The product formed by the treatment of propranolol with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY W/BIOLOGICAL TOPICS
- Name the following molecules with IUpacarrow_forwardWhat is the molecular orbital for cyclopropenyl anion and is it aromatic, antiaromatic or nonaromatic?arrow_forwardUsing the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid and its impact on the protein.arrow_forward
- How to get the predicted product of this reaction belowarrow_forwardPlease help me fill out the chart then using the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Then using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid.arrow_forwardWrite the Esterification reaction mechanism for acetic acid, and one propanol to make propanol ethanoate (molecule that gives peas its odor in flavor)arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





