
Interpretation:
All carbon atoms, hydrogen atoms and lone pairs can be drawn for the given bond-line structured compounds.
Concept introduction:
The representation of each atom with their symbol in a bond-line structure of a compound is called as the structural formula of that compound. In bond-line structure each corner represent the carbon atom which in bonded with hydrogen atoms. The number of hydrogen depends upon the number of atoms attached to that particular carbon, because the covalence of carbon should be four. The lone-pairs of the compound are the non-bonding valence electrons of hetero atoms occupied in the compound. It can be calculated by the formula,
Then the lone pairs are represented as dots on its heteroatoms in structural formula.
To draw: the all carbon atoms, hydrogen atoms and lone pairs for given compounds can be do with looking upon the corners of bond-line structure and attached heteroatoms.
Answer to Problem 34PP
The structural formula of the following given compounds are
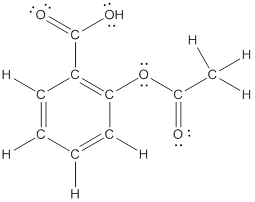
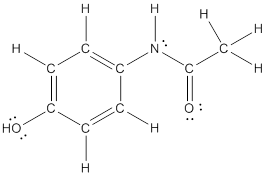
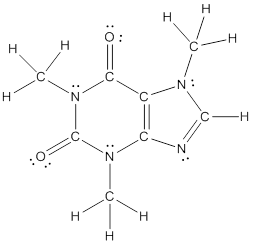
Explanation of Solution
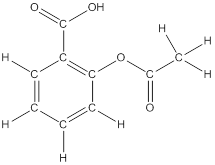
To draw all carbon atoms for given bond-line structures of compounds.
Put a carbon atom ‘C’ to each corner in bond-line structure.
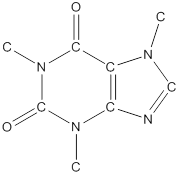
In bond-line structure, every corner represents the carbon atoms. Hence, all corners are replaced with the carbon symbol ‘C’.
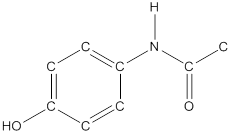
To draw hydrogen atoms for given bond-line structure of compounds.
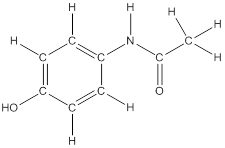
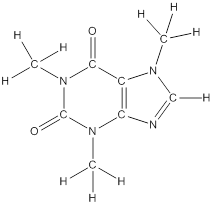
Count the adjacent atoms of carbon whether it is carbon or heteroatoms and if it is less than four we have to add hydrogen atoms in that carbon to make four as covalence.
To draw lone pairs for compound structures.

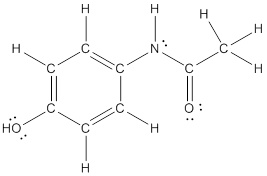

In all given compounds the lone pairs of electron are carried by heteroatoms attached to the carbon. Hence, identify the heteroatoms presented in the compound and count its bond pairs of electrons. Because Lone pairs of electron are the non-bonding pairs of electrons. The numbers of lone pairs of electron are calculated by the formula,
These lone pairs are represented by dots on the atoms in structural formula.
The structural formula of given bond-line structured compounds are drawn by representing the all atoms presented in that compound and the number of lone pairs of electron are calculated by above equation.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-STD.WILEY PLUS CARD
- 7.5 1.93 2.05 C B A 4 3 5 The Joh. 9 7 8 1 2 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 ppm 9 7 8 0.86 OH 10 4 3 5 1 2 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 ppm 9 7 8 CI 4 3 5 1 2 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 2.21 4.00 1.5 2.00 2.07 1.0 ppm 2.76arrow_forwardAssign the functional group bands on the IR spectra.arrow_forwardFind the pH of a 0.120 M solution of HNO2. Find the pH ignoring activity effects (i.e., the normal way). Find the pH in a solution of 0.050 M NaCl, including activityarrow_forward
- Please help me answer these three questions. Required info should be in data table.arrow_forwardDraw the major organic substitution product or products for (2R,3S)-2-bromo-3-methylpentane reacting with the given nucleophile. Clearly drawn the stereochemistry, including a wedged bond, a dashed bond and two in-plane bonds at each stereogenic center. Omit any byproducts. Bri CH3CH2O- (conc.) Draw the major organic product or products.arrow_forwardTartaric acid (C4H6O6) is a diprotic weak acid. A sample of 875 mg tartaric acid are dissolved in 100 mL water and titrated with 0.994 M NaOH. How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the first equivalence point? How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the second equivalence point?arrow_forward
- Including activity, calculate the solubility of Pb(IO3)2 in a matrix of 0.020 M Mg(NO3)2.arrow_forwardIncluding activity coefficients, find [Hg22+] in saturated Hg2Br2 in 0.00100 M KBr.arrow_forwardIncluding activity, calculate the pH of a 0.010 M HCl solution with an ionic strength of 0.10 M.arrow_forward
- Can I please get the graph 1: Concentration vs. Density?arrow_forwardOrder the following series of compounds from highest to lowest reactivity to electrophilic aromatic substitution, explaining your answer: 2-nitrophenol, p-Toluidine, N-(4-methylphenyl)acetamide, 4-methylbenzonitrile, 4-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile.arrow_forwardOrdene la siguiente serie de compuestos de mayor a menor reactividad a la sustitución aromática electrofílica, explicando su respuesta: ácido bencenosulfónico, fluorobenceno, etilbenceno, clorobenceno, terc-butilbenceno, acetofenona.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





