
Concept explainers
Requirement – 1
To analyze: The given transaction, and explain their effect on the
Requirement – 1
Explanation of Solution
Accounting equation is an accounting tool expressed in the form of equation, by creating a relationship between the resources or assets of a company, and claims on the resources by the creditors and the owners. Accounting equation is expressed as shown below:
Accounting equation for each transaction is as follows:
 Figure (1)
Figure (1)
Therefore, the total assets are equal to the liabilities and stockholder’s equity.
Requirement – 2
To record: The
Requirement – 2
Explanation of Solution
Journal:
Journal is the method of recording monetary business transactions in chronological order. It records the debit and credit aspects of each transaction to abide by the double-entry system.
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
- Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and stockholders’ equities.
- Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, expenses.
Journal entries of Company B are as follows:
a. Issuance of common stock:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash (+A) | 600,000 | |||
| Common stock (+SE) | 600,000 | |||
| (To record the issuance of common stock) |
Table (1)
- Cash is an assets account and it increased the value of asset by $600,000. Hence, debit the cash account for $600,000.
- Common stock is a component of stockholder’s equity and it increased the value of stockholder’s equity by $600,000, Hence, credit the common stock for $600,000.
b. Cash borrowed from bank (long term)
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash (+A) | 60,000 | |||
| Notes payable (+L) | 60,000 | |||
| (To record cash borrowed from bank) |
Table (2)
- Cash is an assets account and it increased the value of asset by $60,000. Hence, debit the cash account for $60,000.
- Notes payable is a liability account, and it increased the value of liabilities by $60,000. Hence, credit the notes payable for $60,000.
c. Building purchased on account and in cash:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Building (+A) | 166,000 | |||
| Cash (-A) | 66,000 | |||
| Notes payable (+L) | 100,000 | |||
| (To record purchase of building on account and in cash) |
Table (3)
- Building is an assets account and it increased the value of asset by $166,000. Hence, debit the building account for $166,000.
- Cash is an assets account and it decreased the value of asset by $66,000. Hence, credit the cash account for $66,000.
- Notes payable is a liability account, and it increased the value of liabilities by $100,000. Hence, credit the notes payable for $100,000.
d. Equipment purchased:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Equipment (+A) | 90,000 | |||
| Cash (-A) | 90,000 | |||
| (To record purchase of equipment in cash) |
Table (4)
- Equipment is an assets account and it increased the value of asset by $90,000. Hence, debit the equipment account for $90,000.
- Cash is an assets account and it decreased the value of asset by $90,000. Hence, credit the cash account for $90,000.
e. Purchase of supplies on account:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Supplies (+A) | 90,000 | |||
| Accounts payable (+L) | 90,000 | |||
| (To record purchase of supplies on account) |
Table (5)
- Supplies are an assets account and it increased the value of asset by $90,000. Hence, debit the supplies account for $90,000.
- Accounts payable is a liability account and it increased the value of liability by $90,000. Hence, credit the liability account by $90,000.
Requirement – 3
To prepare: T-account for each account listed in the requirement 2.
Requirement – 3
Explanation of Solution
T-account:
T-account refers to an individual account, where the increasesor decreases in the value of specific asset, liability, stockholder’s equity, revenue, and expenditure items are recorded.
This account is referred to as the T-account, because the alignment of the components of the account resembles the capital letter ‘T’.’ An account consists of the three main components which are as follows:
- (a) The title of the account
- (b) The left or debit side
- (c) The right or credit side
T-accounts of Company B are as follows:
| Cash (A) | |||
| Beg. | 90,000 | ||
| (a) | 600,000 | 66,000 | (c) |
| (b) | 60,000 | 90,000 | (d) |
| End. | 594,000 | ||
| Supplies (A) | |||
| Beg. | 9,000 | ||
| (e) | 90,000 | ||
| End. | 99,000 | ||
| Equipment (A) | |||
| Beg. | 148,000 | ||
| (d) | 90,000 | ||
| End. | 238,000 | ||
| Buildings (A) | |||
| Beg. | 500,000 | ||
| (c) | 166,000 | ||
| End. | 666,000 | ||
| Land (A) | |||
| Beg. | 444,000 | ||
| End. | 444,000 | ||
| Accounts payable (L) | |||
| 50,000 | Beg. | ||
| 90,000 | (e) | ||
| 140,000 | End. | ||
| Note payable (L) | ||||
| 5,000 | Beg. | |||
| 60,000 | (b) | |||
| 100,000 | (c) | |||
| 165,000 | End. | |||
| Common stock (SE) | |||
| 170,000 | Beg. | ||
| 600,000 | (a) | ||
| 770,000 | End. | ||
| 966,000 | Beg. | ||
| 966,000 | End. | ||
Requirement – 4
To prepare: The
Requirement – 4
Explanation of Solution
Trial balance:
Trial balance is the summary of accounts, and their debit and credit balances at a given time. It is usually prepared at end of the accounting period. Debit balances are listed in left column and credit balances are listed in right column. The totals of debit and credit column should be equal. Trial balance is useful in the preparation of the financial statements.
Trial balance of Company B is as follows:
| Company B | ||
| Adjusted Trial Balance | ||
| At July, 31 | ||
| Accounts | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 594,000 | |
| Supplies | 99,000 | |
| Equipment | 238,000 | |
| Building | 666,000 | |
| Land | 444,000 | |
| Accounts payable | 140,000 | |
| Notes payable | 165,000 | |
| Common stock | 770,000 | |
| Retained earnings | 966,000 | |
| Totals | $2,041,000 | $2,041,000 |
Table (6)
Therefore, the total of debit, and credit columns of trial balance is $2,041,000 and agree.
Requirement – 5
To prepare: The classified
Requirement – 5
Explanation of Solution
Classified balance sheet:
This is the financial statement of a company which shows the grouping of similar assets and liabilities under subheadings.
Classified balance sheet of Company B is as follows:
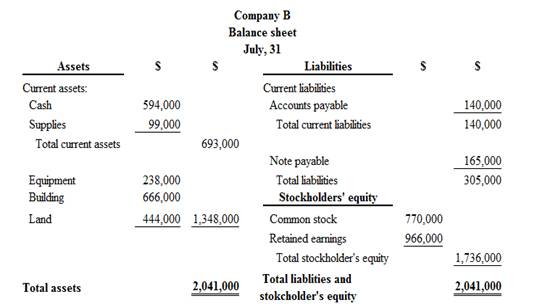
Figure (2)
Therefore, the total assets of Company B are$2,041,000, and the total liabilities and stockholders’ equity are $2,041,000.
Requirement – 6
Whether the assets amount of Company B is primarily come from liabilities or stockholders’ equity.
Requirement – 6
Explanation of Solution
The invested amount of assets are primarily come from stockholder’s’ equity of Company B, because the stockholder’s equity (common stock) financed $1,736,000 of the Company B’s total assets, and liabilities financed $305,000.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING LL
- Can you solve this general accounting problem with appropriate steps and explanations?arrow_forward(1) prepare the december 31 entry for bramble corporation to record amortization of intangibles. the trademark has an estimated useful life of 4 years with a residual value of $3,520 [it is not $3,460]arrow_forwardPlease provide the solution to this general accounting question with accurate financial calculations.arrow_forward
- Please provide the solution to this general accounting question using proper accounting principles.arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting question with the appropriate accounting analysis techniques?arrow_forwardJournal entry for July 1 to record the purchase of Steve Young by Bramble Corporation: A B C D 1 01-07-2025 Cash $51,800 2 Accounts receivable $91,200 3 Inventory $125,700 4 Land $64,600 5 Buildings (net) $75,400 6 Equipment (net) $69,700 7 Trademarks $17,360 8 Goodwill $65,340 9 Accounts payable $202,500 10 Cash $256,600 11 Notes payable $102,000 12 (To record the purchase of Young Company) 13 01-07-2025 Investment in Young compan $358,600 14 Cash $256,600 15 Notes payable $102,000 16 (To record investment in Young Company) (a) prepare the december 31 entry for bramble corporation to record amortization of intangibles. the trademark has an estimated…arrow_forward
- Journal entry for July 1 to record the purchase of Steve Young by Bramble Corporation: A B C D 1 01-07-2025 Cash $51,800 2 Accounts receivable $91,200 3 Inventory $125,700 4 Land $64,600 5 Buildings (net) $75,400 6 Equipment (net) $69,700 7 Trademarks $17,360 8 Goodwill $65,340 9 Accounts payable $202,500 10 Cash $256,600 11 Notes payable $102,000 12 (To record the purchase of Young Company) 13 01-07-2025 Investment in Young compan $358,600 14 Cash $256,600 15 Notes payable $102,000 16 (To record investment in Young Company) (a)arrow_forwardI am searching for the correct answer to this general accounting problem with proper accounting rules.arrow_forwardPlease explain the solution to this general accounting problem with accurate explanations.arrow_forward
- Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:CengagePrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,




