
a.
To determine: The
a.
Answer to Problem 28PS
The present value at the end of each year is $12.50 billion.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the present value at the end of each year
Therefore the present value at the end of each year is $12.50 billion.
b.
To determine: The present value at the end of first year if the growth rate is 4%.
b.
Answer to Problem 28PS
The present value at the end of first year if the growth rate is 4% is $25 billion.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the present value at the end of first year if the growth rate is 4%
Therefore the present value at the end of first year if the growth rate is 4% is $25 billion.
c.
To determine: The present value at the end of 20 years.
c.
Answer to Problem 28PS
The present value at the end of 20 years is $9.82 billion.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the present value at the end of 20 years
Excel Spreadsheet:
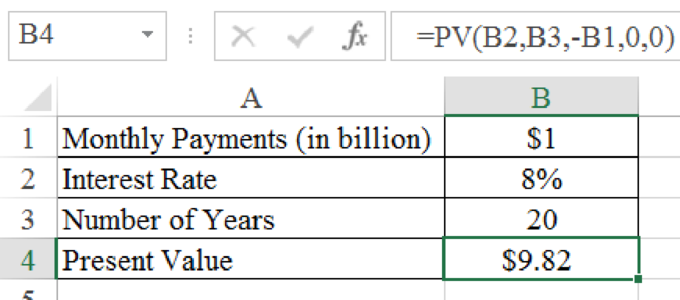
Therefore the present value at the end of 20 years is $9.82 billion.
d.
To determine: The present value if spread evenly for 20 years.
d.
Answer to Problem 28PS
The present value if spread evenly for 20 years is $10.20 billion.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the continuous compounded rate
Therefore the continuous compounded rate is 7.70%.
Determine the present value if spread evenly for 20 years
Therefore the present value if spread evenly for 20 years is $10.20 billion.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
PRIN.OF CORPORATE FINANCE
- Ends Apr 27 Explain why we start with Sales forecasts when we do our financial forecasting. What are the limitations of the Percent of Sales Forecasting method?arrow_forwardDescribe in detail what exactly is the Cash Conversion Cycle, how is it computed and what is the purpose of this calculation (how is it used).arrow_forwardExplain what Interest Rate Parity is, how it is calculated, and why it is important to a company operating internationally.arrow_forward
- Compare and contrast the three core means of adding shareholder wealth; Cash Dividends, Stock Dividends and Stock Splits, and Stock Repurchases. Include the various advantages and disadvantages of each one.arrow_forwardHow to calculate the future value?arrow_forwardhow to caculate the future value?arrow_forward
- what are some of the question can i asek my prinsiple of finance teache?arrow_forwardA critical discussion of the hockey stick model of start-up financing should be presented, supported by recent in-text citations. Provide a detailed explanation of the model. Describe each of the three stages of the hockey stick model of start-up financing, including a detailed characterisation of each stage. The characterisation of each stage should detail the growth, risk, and funding expectations. Present a critical evaluation and an insightful conclu sion.arrow_forwardQuestion Workspace Check My Work New-Project Analysis The president of your company, MorChuck Enterprises, has asked you to evaluate the proposed acquisition of a new chromatograph for the firm's R&D department. The equipment's basic price is $64,000, and it would cost another $18,000 to modify it for special use by your firm. The chromatograph, which falls into the MACRS 3-year class, would be sold after 3 years for $28,400. The MACRS rates for the first three years are 0.3333, 0.4445 and 0.1481. (Ignore the half-year convention for the straight-line method.) Use of the equipment would require an increase in net working capital (spare parts inventory) of $3,000. The machine would have no effect on revenues, but it is expected to save the firm $24,760 per year in before-tax operating costs, mainly labor. The firm's marginal federal-plus-state tax rate is 25%. Cash outflows and negative NPV value, if any, should be indicated by a minus sign. Do not round intermediate…arrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT



