
The expression for force versus piston travel d up to d = 10 mm.
Answer to Problem 2.82P
The expression for Force F versus piston travel d is
And the value of force F at d =10 mm is 127996.71 N
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
A cylindrical is surrounded by a compressible matrix. Cylindrical slug is compressed vertically by a force F which is to be determined. When the force F is acted then there will be the generation of stress inside the cylindrical slug and pressure is also generated inside the compressible matrix. The force acted will be equal to the force generated inside the cylindrical slug plus the force generated inside the matrix.
Calculation:
Drawing the free body diagram of the given system,
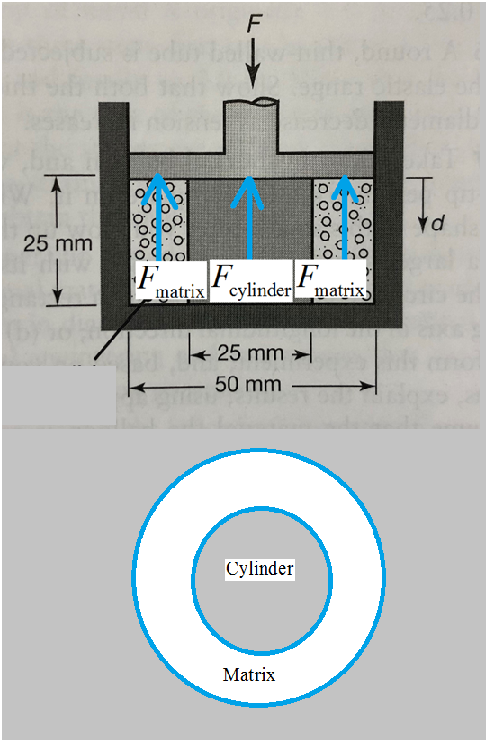
From the free body diagram, it can be written as,
Area of the matrix and cylinder can be given as −
Calculating the force exerted by the matrix:-
The strain developed inside the cylinder for deformation of height d is −
True strain inside the cylinder would be −
Writing true stress-true strain relation,
The force will be given as,
From equation (1), (2) and (3),
The above is the required expression for force versus d .
Putting d = 10 mm we get,
Hence, the expression for Force F versus piston travel d is
And the value of force F at d =10 mm is 127996.71 N
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Pearson eText for Manufacturing Processes for Engineering Materials -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
- Thermodynamics: Mass and Energy Analysis Of Control Volumes An insulated piston-cylinder device contains 4 L of saturated liquid water at a constant pressure of 200 kPa.Water is stirred by a paddle wheel while a current of 8 A flows for 50 min through a resistor placed in thewater. If one-half of the liquid is evaporated during this constant-pressure process and the paddle-wheelwork amounts to 300 kJ, determine the voltage of the source. Also, show the process on a P–v diagram withrespect to the saturation lines.arrow_forwardThermodynamics: Mass and Energy Analysis Of Control Volumes The state of liquid water is changed from 55 psia and 45◦F to 2000 psia and 120◦F. Determine the change inthe internal energy and enthalpy of water on the basis of the (a) compressed liquid tables, (b) incompressiblesubstance approximation and property tables, and (c) specific-heat model.arrow_forwardThermodynamics: Mass and Energy Analysis Of Control Volumes What is the change in enthalpy, in kJ/kg, of oxygen as its temperature changes from 150 to 250◦C? Is thereany difference if the temperature change were from −50 to 100◦C? Does the pressure at the beginning andend of this process have any effect on the enthalpy change?arrow_forward
- Thermodynamics: Mass and Energy Analysis Of Control Volumes A 50-L electrical radiator containing heating oil is placed in a 50-m3 room. Both the room and the oil in theradiator are initially at 5◦C. The radiator with a rating of 3 kW is now turned on. At the same time, heatis lost from the room at an average rate of 0.3 kJ/s. After some time, the average temperature is measuredto be 20◦C for the air in the room, and 60◦C for the oil in the radiator. Taking the density and the specificheat of the oil to be 950 kg/m3 and 2.2 kJ/(kg◦C), respectively, determine how long the heater is kept on.Assume the room is well-sealed so that there are no air leaks.arrow_forwardProblem 3 For the beam and loading shown, consider section n-n and determine (a) the largest shearing stress in that section, (b) the shearing stress at point a. 1ft 15 kips 20 kips 15 kips AITT in 1 0.6 in. -10 in. 1 in. 0.375 in.- 2 ft 2ft 2 ft 2ft 10 in. 1 0.6 in.arrow_forwardpractice problems want detailed break downarrow_forward
- 6.105. Determine force P on the cable if the spring is compressed 0.025 m when the mechanism is in the position shown. The spring has a stiffness of k = 6 kN/m. E P 150 mm D T 30° 200 mm 200 mm 200 mm B 800 mmarrow_forward6.71. Determine the reactions at the supports A, C, and E of the compound beam. 3 kN/m 12 kN A B CD E -3 m 4 m 6 m 3 m 2 marrow_forwardA countershaft carrying two V-belt pullets is shown in the figure. Pulley A receives power from a motor through a belt with the belt tensions shown. The power is transmitted through the shaft and delivered to the belt on pulley B. Assume the belt tension on the loose side (T1) at B is 30% of the tension on the tight side (T2). (a) Determine the tension (i.e., T₂ and T₁) in the belt on pulley B, assuming the shaft is running at a constant speed. (b) Find the magnitudes of the bearing reaction forces, assuming the bearings act as simple supports. (c) Draw shear-force and bending moment diagrams for the shaft (in XZ and XY plane if needed). (d) Calculate the maximum moments at points A and B respectively and find the point of maximum bending moment (A or B). (e) Find maximum stresses (tensile, compressive, and shear stresses) at the identified point of maximum moment (hint: principal and max shear stresses) 8 dia. 9 400lbf 50lbf 45° 1.5 dia. T₂ B Units in inches T₁ 10 dia.arrow_forward
- The cantilevered bar in the figure is made from a ductile material and is statically loaded with F,, = 200 lbf and Fx = F₂ = 0. Analyze the stress situation in rod AB by obtaining the following information. Note that the stress concentration factors are neglected in the following questions (Kt and Kts=1). (a) Determine the precise location of the critical stress element. (b) Sketch the critical stress element and determine magnitudes and direction for all stresses acting on it. (Transverse shear may only be neglected if you can justify this decision.) (c) For the critical stress element, determine the principal stresses and maximum shear stress. 6 in 1-in dia. B +1- in in 2 in 5 inarrow_forwardA laminated thick-walled hydraulic cylinder was fabricated by shrink-fitting jacket having an outside diameter of 300mm onto a SS 304 steel tube having an inside diameter of 100mm and an outside diameter of 200mm as shown in the figure. The interference (8) was 0.15mm. When the Young's modulus for both SS304 and 1020 steel is the same as 200GPa, and the Poisson's ratio is also the same as 0.3 for both materials, find the followings. Initially 100 mm Initially 200 mm Initially 300 mm SS 304 1020 steel (a) P; (interfacial contact stress) (b) The maximum stresses (σ, and σ+) in the laminated steel cylinder resulting from the shrink fit.arrow_forwardAuto Controls Design a proportional derivitivecontroller for a plant orsystemthat satisfies the following specifications : 1. is steady-state error is less than 2 % for a ramp input. 2.) Damping ratio (zeta) is greater than 0.7have determined the 3. Once youvalue of kp and kd, then plotthe response of the compensated(with controller) and uncompensated( without the controller, only the plantsystem using MATLAB.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





