
a.
To determine: The
a.
Answer to Problem 25PS
The present value at the end of each year is $12.50 billion.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the present value at the end of each year
Therefore the present value at the end of each year is $12.50 billion.
b.
To determine: The present value at the end of first year if the growth rate is 4%.
b.
Answer to Problem 25PS
The present value at the end of first year if the growth rate is 4% is $25 billion.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the present value at the end of first year if the growth rate is 4%
Therefore the present value at the end of first year if the growth rate is 4% is $25 billion.
c.
To determine: The present value at the end of 20 years.
c.
Answer to Problem 25PS
The present value at the end of 20 years is $9.82 billion.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the present value at the end of 20 years
Excel Spreadsheet:
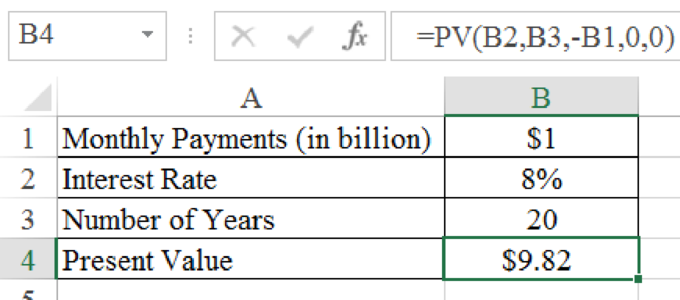
Therefore the present value at the end of 20 years is $9.82 billion.
d.
To determine: The present value if spread evenly for 20 years.
d.
Answer to Problem 25PS
The present value if spread evenly for 20 years is $10.20 billion.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the continuous compounded rate
Therefore the continuous compounded rate is 7.70%.
Determine the present value if spread evenly for 20 years
Therefore the present value if spread evenly for 20 years is $10.20 billion.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Principles of Corporate Finance (Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series in Finance, Insurance, and Real Estate)
- What corporate finance?? can you explain this? fully no aiarrow_forwardWhat is corporate finance? how this is usefull?arrow_forwardPam and Jim are saving money for their two children who they plan to send to university.The eldest child will enter university in 5 years while the younger will enter in 7 years. Each child is expected spend four years at university. University fees are currently R20 000 per year and are expected to grow at 5% per year. These fees are paid at the beginning of each year.Pam and Jim currently have R40 000 in their savings and their plan is to save a fixed amount each year for the next 5 years. The first deposit taking place at the end of the current year and the last deposit at the date the first university fees are paid.Pam and Jim expect to earn 10% per year on their investments.What amount should they invest each year to meet the cost of their children’s university fees?arrow_forward
- Pam and Jim are saving money for their two children who they plan to send to university.The eldest child will enter university in 5 years while the younger will enter in 7 years. Each child is expected spend four years at university. University fees are currently R20 000 per year and are expected to grow at 5% per year. These fees are paid at the beginning of each year.Pam and Jim currently have R40 000 in their savings and their plan is to save a fixed amount each year for the next 5 years. The first deposit taking place at the end of the current year and the last deposit at the date the first university fees are paid.Pam and Jim expect to earn 10% per year on their investments.What amount should they invest each year to meet the cost of their children’s university fees?arrow_forwardYou make a loan of R100 000, with annual payments being made at the end of each year for the next 5 years at a 10% interest rate. How much interest is paid in the second year?arrow_forwardDr Z. Mthembu is the owner of Mr Granite, a business in the Western Cape. After more than 28 years of operation, the business is thinking about taking on a new project that would provide a profitable new clientele. With only R1.5 million in resources, the company is now working on two competing projects. The starting costs for Project X and Project Y are R625,000 and R600000, respectively. These projected are estimated for the next 7 years timeframe. According to SARS, the tax rate is 28%, and a discount rate of 11.25% is applied.Projects X Project YProject X Project Y129000 145000154000 145000312000 145000168000 14500098250 14500088750 14500016050 145000arrow_forward
- Dr Z. Mthembu is the owner of Mr Granite, a business in the Western Cape. After more than 28 years of operation, the business is thinking about taking on a new project that would provide a profitable new clientele. With only R1.5 million in resources, the company is now working on two competing projects. The starting costs for Project X and Project Y are R625,000 and R600000, respectively. These projected are estimated for the next 7 years timeframe. According to SARS, the tax rate is 28%, and a discount rate of 11.25% is applied.Projects X Project YProject X Project Y129000 145000154000 145000312000 145000168000 14500098250 14500088750 14500016050 145000arrow_forwardDr Z. Mthembu is the owner of Mr Granite, a business in the Western Cape. After more than 28 years of operation, the business is thinking about taking on a new project that would provide a profitable new clientele. With only R1.5 million in resources, the company is now working on two competing projects. The starting costs for Project X and Project Y are R625,000 and R600000, respectively. These projected are estimated for the next 7 years timeframe. According to SARS, the tax rate is 28%, and a discount rate of 11.25% is applied.Projects X Project YProject X Project Y129000 145000154000 145000312000 145000168000 14500098250 14500088750 14500016050 145000arrow_forwardDr Z. Mthembu is the owner of Mr Granite, a business in the Western Cape. After more than 28 years of operation, the business is thinking about taking on a new project that would provide a profitable new clientele. With only R1.5 million in resources, the company is now working on two competing projects. The starting costs for Project X and Project Y are R625,000 and R600000, respectively. These projected are estimated for the next 7 years timeframe. According to SARS, the tax rate is 28%, and a discount rate of 11.25% is applied.Projects X Project YProject X Project Y129000 145000154000 145000312000 145000168000 14500098250 14500088750 14500016050 145000arrow_forward
- An investor buys 100 shares of a $40 stock that pays an annual cash dividend of $2 a share (a 5 percent dividend yield) and signs up for the DRIP. a. If neither the dividend nor the price changes, how many shares will the investor have at the end of 10 years? How much will the position in the stock be worth? Answer: 5.000 shares purchased in year 1 5.250 shares purchased in year 2 6.078 shares purchased in year 5 62.889 total shares purchased b. If the price of the stock rises by 6 percent annually but the dividend remains at $2 a share, how many shares are purchased each year for the next 10 years? How much is the total position worth at the end of 10 years? Answer: 4.717 shares purchased in year 1 4.592 shares in year 3 3.898 shares in year 10 Value of position: $10,280 c. If the price of the stock rises by 6 percent annually but the dividend rises by only 3 percent annually, how many shares are purchased each year for the next 10 years? How much is the total position worth at the…arrow_forwardDr Z. Mthembu is the owner of Mr Granite, a business in the Western Cape. After more than 28 years of operation, the business is thinking about taking on a new project that would provide a profitable new clientele. With only R1.5 million in resources, the company is now working on two competing projects. The starting costs for Project X and Project Y are R625,000 and R600000, respectively. These projected are estimated for the next 7 years timeframe. According to SARS, the tax rate is 28%, and a discount rate of 11.25% is applied.Projects X Project YProject X Project Y129000 145000154000 145000312000 145000168000 14500098250 14500088750 14500016050 145000 Calculate the IRR for the two proposed Projectsarrow_forwardYour sibling want to go on a holiday in 7 years. The cost of a similar holiday today is R70,000 and the cost of the holiday increases by 5% per annum.If he/she can earn 11% per annum on a savings account, how much must he/she save per month as from today to have the money ready in 7 years time? Note: savings will be at the beginning of each month.arrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT



