
Concept explainers
Journal entries and
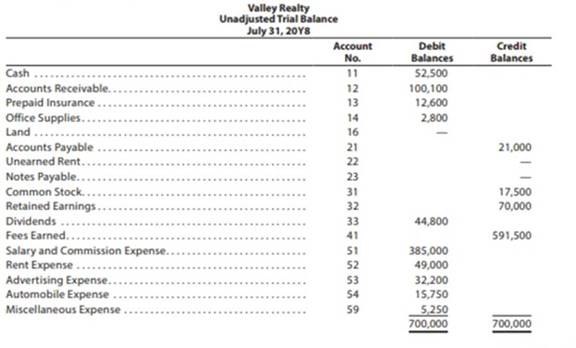
Valley Realty acts as an agent in buying, selling, renting, and managing real estate. The unadjusted trial balance on July 31, 20Y8, follows:
The following I hi sine vs transactions were completed by Valley Realty during August 20Y8:
Aug. 1. Purchased office supplies on account, $3,150.
2. Paid rent on office for month, $7,200.
3. Received cash from clients on account, $83,900.
5. Paid insurance premiums, $ 12.000.
9. Returned a portion of the office supplies purchased on August 1, receiving full credit for their cost, $400.
17. Paid advertising expense, $8,000.
23. Paid creditors on account, $ 13,750.
Enter the following transactions on Page 19 of the two-column journal:
29. Paid miscellaneous expenses, $ 1,700.
30. Paid automobile expense (including rental charges for an automobile), $2,500.
31. Discovered an error in computing a commission during Ally; received cash from the salesperson for the overpayment, $2,000.
31. Paid salaries and commissions for the month, $53,000.
31. Recorded revenue earned and billed to clients during the month, $183,500.
31. Purchased land for a future building site for $75,000, paying $7,500 in cash and giving a note payable for the remainder.
31. Paid dividends, $1,000.
31. Rented land purchased on August 31 to a local university for use as a parking lot during football season (September. October, and November); received advance payment of $5,000.
Instructions
1. Record the August 1 balance of each account in the appropriate balance column of a four-column account, write Balance in item section, and place a check mark (»O in the Posting Reference column.
2. Journalize the transactions for August in a two-column journal beginning on Page 18.
3. Post to the ledger, extending the account balance to the appropriate balance column after each posting.
4. Prepare an unadjusted trial balance of the ledger as of August 31. 20Y8.
5. Assume that the August 31 transaction for dividends should have been $10,000. (a) Why did the unadjusted trial balance in (4) balance? (b) Journalize the correcting entry, (c) Is this error a transposition or slide?
(2) and (3)
To journalize: The transactions of August in a two column journal beginning on page 18.
Explanation of Solution
Journal:
Journal is the book of original entry. Journal consists of the day today financial transactions in a chronological order. The journal has two aspects; they are debit aspect and the credit aspect.
Rules of debit and credit:
“An increase in an asset account, an increase in an expense account, a decrease in liability account, and a decrease in a revenue account should be debited.
Similarly, an increase in liability account, an increase in a revenue account and a decrease in an asset account, a decrease in an expenses account should be credited”.
Journalize the transactions of August in a two column journal beginning on page 18.
| Journal Page 18 | |||||
| Date | Description | Post. Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 20Y8 | Office supplies | 14 | 3,150 | ||
| August | 1 | Accounts payable | 21 | 3,150 | |
| (To record the purchase of supplies of account) | |||||
| 2. | Rent expense | 52 | 7,200 | ||
| Cash | 11 | 7,200 | |||
| (To record the payment of rent) | |||||
| 3 | Cash | 11 | 83,900 | ||
| Accounts receivable | 12 | 83,900 | |||
| (To record the receipt of cash from clients) | |||||
| 5 | Prepaid insurance | 13 | 12,000 | ||
| Cash | 11 | 12,000 | |||
| (To record the payment of insurance premium) | |||||
| 9 | Accounts payable | 21 | 400 | ||
| Office supplies | 14 | 400 | |||
| (To record the payment made to creditors on account) | |||||
| 17 | Advertising expense | 53 | 8,000 | ||
| Cash | 11 | 8,000 | |||
| (To record the payment of advertising expense) | |||||
| 23 | Accounts payable | 21 | 13,750 | ||
| Cash | 11 | 13,750 | |||
| (To record the payment made to creditors on account) | |||||
Table (1)
| Journal Page 19 | |||||
| Date | Description | Post. Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 20Y8 | 29 | Miscellaneous expense | 59 | 1,700 | |
| August | Cash | 11 | 1,700 | ||
| (To record the payment made for Miscellaneous expense) | |||||
| 30 | Automobile expense | 54 | 2,500 | ||
| Cash | 11 | 2,500 | |||
| (To record the payment made for automobile expense) | |||||
| 31 | Cash | 11 | 2,000 | ||
| Salary and commission expense | 51 | 2,000 | |||
| (To record the receipt of cash) | |||||
| 31 | Salary and commission expense | 51 | 53,000 | ||
| Cash | 11 | 53,000 | |||
| (To record the payment made for salary and commission expense) | |||||
| 31 | Accounts receivable | 12 | 183,500 | ||
| Fees earned | 41 | 183,500 | |||
| (To record the revenue earned and billed) | |||||
| 31 | Land | 16 | 75,000 | ||
| Cash | 11 | 7,500 | |||
| Notes payable | 23 | 67,500 | |||
| (To record the purchase of land party for cash and party on signing a note) | |||||
| 31 | Dividends | 33 | 1,000 | ||
| Cash | 11 | 1,000 | |||
| (To record the drawing made for personal use) | |||||
| 31 | Cash | 11 | 5,000 | ||
| Unearned rent | 22 | 5,000 | |||
| (To record the cash received for the service yet to be provide) | |||||
Table (2)
(1) and (3)
To record: The beginning balances of each accounts in the appropriate balance column of a four-column account, and post them to the ledger extending the account balance to the appropriate balance column after each posting.
Explanation of Solution
T-account:
An account is referred to as a T-account, because the alignment of the components of the account resembles the capital letter ‘T’. An account consists of the three main components which are as follows:
- The title of the account
- The left or debit side
- The right or credit side
| Account: Cash Account no. 11 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20Y8 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 52,500 | |||
| 2 | 18 | 7,200 | 45,300 | ||||
| 3 | 18 | 83,900 | 129,200 | ||||
| 5 | 18 | 12,000 | 117,200 | ||||
| 17 | 18 | 8,000 | 109,200 | ||||
| 23 | 18 | 13,750 | 95,450 | ||||
| 29 | 19 | 1,700 | 93,750 | ||||
| 30 | 19 | 2,500 | 91,250 | ||||
| 31 | 19 | 2,000 | 93,250 | ||||
| 31 | 19 | 53,000 | 40,250 | ||||
| 31 | 19 | 7,500 | 32,750 | ||||
| 31 | 19 | 1,000 | 31,750 | ||||
| 31 | 19 | 5,000 | 36,750 | ||||
Table (3)
| Account: Accounts Receivable Account no. 12 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20Y8 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 100,100 | |||
| 3 | 18 | 83,900 | 16,200 | ||||
| 31 | 19 | 183,500 | 199,700 | ||||
Table (4)
| Account: Prepaid Insurance Account no. 13 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20Y8 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 12,600 | |||
| 5 | 18 | 12,000 | 24,600 | ||||
Table (5)
| Account: Office Supplies Account no. 14 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20Y8 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 2,800 | |||
| 1 | 18 | 3,150 | 5,950 | ||||
| 9 | 18 | 400 | 5,550 | ||||
Table (6)
| Account: Land Account no. 16 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20Y8 | |||||||
| August | 31 | 19 | 75,000 | 75,000 | |||
Table (7)
| Account: Accounts Payable Account no. 21 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20Y8 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 21,000 | |||
| 1 | 18 | 3,150 | 24,150 | ||||
| 9 | 18 | 400 | 23,750 | ||||
| 23 | 18 | 13,750 | 10,000 | ||||
Table (8)
| Account: Unearned Rent Account no. 22 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20Y8 | |||||||
| August | 31 | 19 | 5,000 | 5,000 | |||
Table (9)
| Account: Notes Payable Account no. 23 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20Y8 | |||||||
| August | 31 | 19 | 67,500 | 67,500 | |||
Table (11)
| Account: Common stock Account no. 31 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20Y8 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 17,500 | |||
Table (12)
| Account: Retained earnings Account no. 32 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20Y8 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 70,000 | |||
Table (13)
| Account: Dividends Account no. 33 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20Y8 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 44,800 | |||
| 31 | 19 | 1,000 | 45,800 | ||||
Table (13)
| Account: Fees earned Account no. 41 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20Y8 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 591,500 | |||
| 31 | 19 | 183,500 | 775,000 | ||||
Table (14)
| Account: Salary and commission expense Account no. 51 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20Y8 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 385,000 | |||
| 31 | 19 | 2,000 | 383,000 | ||||
| 31 | 19 | 53,000 | 436,000 | ||||
Table (15)
| Account: Rent expense Account no. 52 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20Y8 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 49,000 | |||
| 2 | 18 | 7,200 | 56,200 | ||||
Table (16)
| Account: Advertising expense Account no. 53 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20Y8 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 32,200 | |||
| 17 | 18 | 8,000 | 40,200 | ||||
Table (17)
| Account: Automobile expense Account no. 54 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20Y8 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 15,750 | |||
| 30 | 19 | 2,500 | 18,250 | ||||
Table (19)
| Account: Miscellaneous expense Account no. 59 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20Y8 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 5,250 | |||
| 29 | 19 | 1,700 | 6,950 | ||||
Table (20)
(4)
To prepare: An unadjusted trial balance of Company V at August 31, 20Y8.
Explanation of Solution
Unadjusted trial balance:
The unadjusted trial balance is the summary of all the ledger accounts that appears on the ledger accounts before making adjusting journal entries.
Prepare an unadjusted trial balance of Company V at August 31, 20Y8 as follows:
|
Company V Unadjusted Trial Balance August 31, 20Y8 | |||
| Particulars | Account No. |
Debit $ | Credit $ |
| Cash | 11 | 36,750 | |
| Accounts receivable | 12 | 199,700 | |
| Prepaid insurance | 13 | 24,600 | |
| Office supplies | 14 | 5,550 | |
| Land | 16 | 75,000 | |
| Accounts payable | 21 | 10,000 | |
| Unearned rent | 22 | 5,000 | |
| Notes payable | 23 | 67,500 | |
| Common stock | 31 | 17,500 | |
| Retained earnings | 32 | 70,000 | |
| Dividends | 33 | 45,800 | |
| Fees earned | 41 | 775,000 | |
| Salaries and commission expense | 51 | 436,000 | |
| Rent expense | 52 | 56,200 | |
| Advertising expense | 53 | 40,200 | |
| Automobile expense | 54 | 18,250 | |
| Miscellaneous expense | 59 | 6,950 | |
| Total | 945,000 | 945,000 | |
Table (20)
(5) a.
To explain: Whether the unadjusted trial balance in (4) balance
Explanation of Solution
The unadjusted trial balance in (4) would still balance, since the debit equalized the credit in the original journal entry.
b.
To journalize: The correcting entry
Explanation of Solution
The Correcting entry is as follows:
| Journal Page 19 | |||||
| Date | Description | Post. Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 20Y8 | Dividends | 33 | 9,000 | ||
| August | 31 | Cash | 11 | 9,000 | |
| (To record the correcting entry) | |||||
Table (21)
Working notes:
c.
To identify: Whether the error made is a slide or transposition.
Explanation of Solution
Slide error:
A slide error occurs, when the decimal point of an amount has been misplaced.
The drawings account balance recorded as $10,000 instead of $1,000 is a slide error. Since, the decimal point of the amount has been misplaced.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Cengagenowv2, 1 Term Printed Access Card For Warren/jones’ Corporate Financial Accounting, 15th
- I am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the correct explanation.arrow_forwardThe balanced scorecard approach includes _.arrow_forwardMichiko Industries uses flexible budgets. At a normal capacity of 25,000 units, the budgeted manufacturing overhead is $75,000 variable and $300,000 fixed. If Michiko Industries had actual overhead costs of $385,500 for 27,000 units produced, what is the difference between actual and budgeted costs?arrow_forward
- Please provide the correct answer to this general accounting problem using valid calculations.arrow_forwardPlease provide the accurate answer to this general accounting problem using valid techniques.arrow_forwardNaiya Enterprises reported the following results from last year's operations: Sales $2,250,000 Variable expenses $900,000 Contribution margin $1,350,000 Fixed expenses $850,000 Net operating income $500,000 Average operating assets $1,600,000 This year, the company has a $320,000 investment opportunity with the following cost and revenue characteristics: Sales $480.000 Contribution margin ratio 55% of sales Fixed expenses $160,000 The company's minimum required rate of return is 11%. What is the margin % related to this year's investment opportunity?arrow_forward
- The company's statement of cash flows for 2022 reported $860,000 of cash received from customers.arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting problem with appropriate steps and explanations?arrow_forwardI need guidance with this general accounting problem using the right accounting principles.arrow_forward
- Can you solve this general accounting problem using accurate calculation methods?arrow_forwardI need help with this financial accounting problem using proper accounting guidelines.arrow_forwardPlease provide the correct answer to this general accounting problem using accurate calculations.arrow_forward
- Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:CengagePrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning





