
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
To accurately depict the given ball-stick model, the dash-wedge notations in the given line structure are to be added.
Concept introduction:
The dash-wedge notations are used to represent the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms or groups of molecules in plane of paper. There are three types of lines used for such arrangements, straight line, dash line, and wedge line. The straight line represents the bond is in the plane of the paper. The dash line represents the bond pointing away from the observer, that is, below the plane of paper. The wedge line represents the bond pointing towards the observer that is above the plane of paper.
Answer to Problem 2.36P
The dash-wedge notations in the given line structure is:
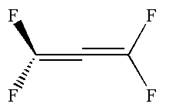
Explanation of Solution
The given ball-stick model and the line structure are:
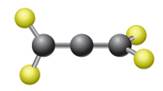
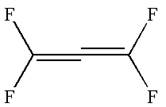
In the given ball-stick model, the yellow balls represent fluorine atoms and black balls are carbon atoms. The fluorine atoms on the left side appear in the plane of the paper. Thus, these fluorine atoms will be represented by straight lines. The two fluorine atoms on the right side are arranged such that, one fluorine atom is above the plane of paper and other is below. The one which is above the plane will be represented by a wedge bond while the one which is below the plane of the paper will be represented by a dash line.
Hence dash-wedge notation for the given molecules is shown below:
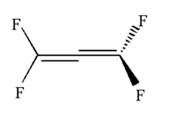
The dash-wedge notation in the given line structure is added on the basis of three dimensional arrangement given in ball-stick model.
(b)
Interpretation:
To accurately depict the given ball-stick model, the dash-wedge notations in the given line structure are to be added.
Concept introduction:
The dash-wedge notations are used while representing the three dimensional arrangement of atoms or groups of molecules on the plane of paper. There are three types of lines used for such arrangements, straight line, dash line, and wedge line. The straight line represents the bond that is in the plane of the paper. The dash line represents the bond pointing away from the observer that is below the plane of paper. The wedge line represents the bond pointing towards the observer that is above the plane of paper.
Answer to Problem 2.36P
The dash-wedge notations in the given line structure is:
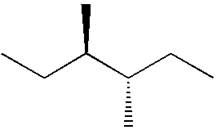
Explanation of Solution
The given ball-stick model and its line structure are:
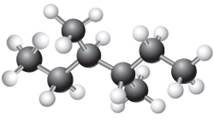
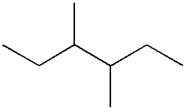
In the given ball-stick model, the white balls represent hydrogen atoms while black balls are carbon atoms. The longest continuous chain is of six carbon atoms having two methyl substituents at
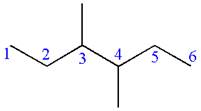
If the chain is numbered from left to right, the methyl group at
Hence, the dash-wedge notation for the given molecules is shown below:
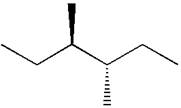
The dash-wedge notation in the given line structure is added on the basis of three dimensional arrangement given in ball-stick model.
(c)
Interpretation:
To accurately depict the given ball-stick model, the dash-wedge notations in the given line structure are to be added.
Concept introduction:
The dash-wedge notations are used while representing the three dimensional arrangement of atoms or groups of molecules on the plane of paper. There are three types of lines used for such arrangements, straight line, dash line, and wedge line. The straight line represents the bond is in the plane of paper. The dash line represents the bond pointing away from the observer that is below the plane of paper. The wedge line represents the bond pointing towards the observer that is above the plane of paper.
Answer to Problem 2.36P
The dash-wedge notations in the given line structure is:
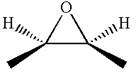
Explanation of Solution
The given ball-stick model and its line structure are:
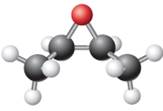
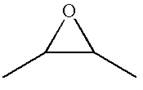
In the given ball-stick model the white balls represent hydrogen atoms, black balls represents carbon atoms and the red ball is an oxygen atom. The two carbon atoms that are directly bonded to the oxygen atom are in the plane of paper. Each of these carbon atoms has one methyl substituent and one hydrogen atom attached. Two methyl substituents points towards the observer, while the hydrogen atoms are pointing away from the observer. The bond towards the observer is considered as above the plane of the paper and is represented by wedge bond. The bond away from the observer is considered as below the plane of the paper and is represented by dash bond.
Hence dash-wedge notation for the given molecules is shown below:
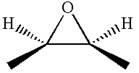
The dash-wedge notation in the given line structure is added on the basis of three dimensional arrangement given in ball-stick model.
(d)
Interpretation:
To accurately depict the given ball-stick model, the dash-wedge notations in the given line structure are to be added.
Concept introduction:
The dash-wedge notations are used while representing the three dimensional arrangement of atoms or groups of molecules on the plane of paper. There are three types of lines used for such arrangements, straight line, dash line, and wedge line. The straight line represents the bond is in the plane of the paper. The dash line represents the bond pointing away from the observer that is below the plane of paper. The wedge line represents the bond pointing towards the observer that is above the plane of paper.
Answer to Problem 2.36P
The dash-wedge notations in the given line structure is:
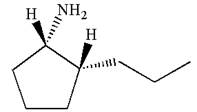
Explanation of Solution
The given ball-stick model and its line structure are:
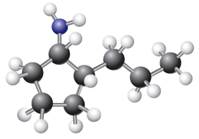
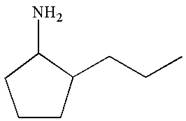
In the given ball-stick model the white balls represent hydrogen atoms, black balls are carbon atoms, and the blue ball is a nitrogen atom. The cyclopentane ring is on the plane of paper having two substituents. The
The
The second substituent is propyl group which points away from the observer and the hydrogen atoms bonded to the same carbon having propyl group is pointed towards observer.
The bond towards the observer is considered as above the plane of the paper and is represented by a wedge line. The bond away from the observer is considered as below the plane of the paper and is represented by dash line
Hence dash-wedge notation for the given molecules is shown below:
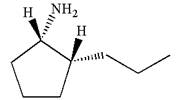
The dash-wedge notation in the given line structure is added on the basis of three dimensional arrangement given in ball-stick model.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY PRINCIPLES & MECHANISM
- Draw product A, indicating what type of reaction occurs. NH2 F3C CF3 NH OMe NH2-NH2, ACOH Aarrow_forwardPhotochemical smog is formed in part by the action of light on nitrogen dioxide. The wavelength of radiation absorbed by NO2 in this reaction is 197 nm.(a) Draw the Lewis structure of NO2 and sketch its π molecular orbitals.(b) When 1.56 mJ of energy is absorbed by 3.0 L of air at 20 °C and 0.91 atm, all the NO2 molecules in this sample dissociate by the reaction shown. Assume that each absorbed photon leads to the dissociation (into NO and O) of one NO2 molecule. What is the proportion, in parts per million, of NO2 molecules in this sample? Assume that the sample behaves ideally.arrow_forwardCorrect each molecule in the drawing area below so that it has the skeletal ("line") structure it would have if it were dissolved in a 0.1 M aqueous solution of HCI. If there are no changes to be made, check the No changes box under the drawing area. No changes. HO Explanation Check NH, 2 W O :□ G ©2025 M unter Accessibilityarrow_forward
- An expression for the root mean square velocity, vrms, of a gas was derived. Using Maxwell’s velocity distribution, one can also calculate the mean velocity and the most probable velocity (mp) of a collection of molecules. The equations used for these two quantities are vmean=(8RT/πM)1/2 and vmp=(2RT/M)1/2 These values have a fixed relationship to each other.(a) Arrange these three quantities in order of increasing magnitude.(b) Show that the relative magnitudes are independent of the molar mass of the gas.(c) Use the smallest velocity as a reference for establishing the order of magnitude and determine the relationship between the larger and smaller values.arrow_forwardThe reaction of solid dimethylhydrazine, (CH3)2N2H2, and liquefied dinitrogen tetroxide, N2O4, has been investigated for use as rocket fuel. The reaction produces the gases carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen (N2), and water vapor (H2O), which are ejected in the exhaust gases. In a controlled experiment, solid dimethylhydrazine was reacted with excess dinitrogen tetroxide, and the gases were collected in a closed balloon until a pressure of 2.50 atm and a temperature of 400.0 K were reached.(a) What are the partial pressures of CO2, N2, and H2O?(b) When the CO2 is removed by chemical reaction, what are the partial pressures of the remaining gases?arrow_forwardOne liter of chlorine gas at 1 atm and 298 K reacts completely with 1.00 L of nitrogen gas and 2.00 L of oxygen gas at the same temperature and pressure. A single gaseous product is formed, which fills a 2.00 L flask at 1.00 atm and 298 K. Use this information to determine the following characteristics of the product:(a) its empirical formula;(b) its molecular formula;(c) the most favorable Lewis formula based on formal charge arguments (the central atom is N);(d) the shape of the molecule.arrow_forward
- How does the square root mean square velocity of gas molecules vary with temperature? Illustrate this relationship by plotting the square root mean square velocity of N2 molecules as a function of temperature from T=100 K to T=300 K.arrow_forwardDraw product B, indicating what type of reaction occurs. F3C CF3 NH2 Me O .N. + B OMearrow_forwardBenzimidazole E. State its formula. sState the differences in the formula with other benzimidazoles.arrow_forward
- Draw product A, indicating what type of reaction occurs. F3C CN CF3 K2CO3, DMSO, H₂O2 Aarrow_forward19) Which metal is most commonly used in galvanization to protect steel structures from oxidation? Lead a. b. Tin C. Nickel d. Zinc 20) The following molecule is an example of a: R₁ R2- -N-R3 a. Secondary amine b. Secondary amide c. Tertiary amine d. Tertiary amidearrow_forwardpls helparrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning

