
Determining Financial Statement Effects of Various Transactions
Adamson Incorporated is a small manufacturing company that makes model trains to sell to toy stores. It has a small service department that repairs customers’ trains for a fee. The company has been in business for Five years. At the end of the company’s prior fiscal year ending on December 31, the accounting records reflected total assets of $500,000 (cash, $120,000; equipment, $70,000: buildings, $310,000), total liabilities of $200,000 (short-term notes payable, $140,000; long-term notes payable, $60,000), and total stockholders’ equity of $300,000 (common stock [par value $1.00 per share], $20,000; additional paid-in capital. $200,000;
- a. Borrowed $110,000 cash from the bank and signed a 10-year note.
- b. Purchased equipment for $30,000, paying $3,000 in cash and signing a note due in six months for the balance.
- c. Issued an additional 10,000 shares of capital stock for $100,000 cash.
- d. Purchased a delivery truck (equipment) for $10,000; paid $5,000 cash and signed a short-term note payable for the remainder.
- e. Lent $2,000 cash to the company president, Clark Adamson, who signed a note with terms showing the principal plus interest due in one year.
- f. Built an addition on the factory for $200,000 and paid cash to the contractor.
- g. Purchased $85,000 in long-term investments.
- h. Returned a $3,000 piece of equipment purchased in (b) because it proved to be defective; received a reduction of its short-term note payable.
- i. A stockholder sold $5,000 of his capital stock in Adamson Incorporated to his neighbor.
Required:
1. Was Adamson Incorporated organized as a sole proprietorship, a
2. During the current year, the records of the company were inadequate. You were asked to prepare the summary of transactions shown above. To develop a quick assessment of their economic effects on Adamson Incorporated, you have decided to complete the tabulation that follows and to use plus (+) for increases and minus (−) for decreases for each account. The first transaction is used as an example.
| ASSETS | = | LIABILITIES | + | STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | |||||||||||||
| Cash | Notes Long-Term Receivable | Long-Term Investments | Equipment | Buildings | Short-Term Notes Payable | Long-Term Notes Payable | Common Stock | Additional Paid-in Capital | Retained Earnings | ||||||||
| Beg. (a) | 120,000+110000 | 70,000 | 310,000 | =_ | 140000 | 60,000 +110,000 | 20,000 | 200,000 | 80,000 | ||||||||
3. Did you include event (i) in the tabulation? Why?
4. Based on beginning balances plus the completed tabulation, provide the following amounts (show computations):
- a. Total assets at the end of the year.
- b. Total liabilities at the end of the year.
- c. Total stockholders’ equity at the end of the year.
- d. Cash balance at the end of the year.
- e. Total current assets at the end of the year.
5. Compute the
1.
Ascertain whether Company A is a corporation, a partnership or a sole proprietorship.
Explanation of Solution
Corporation:
A business concern where there is a separate legal entity and are owned by stockholders are classified as corporation. Transfer of ownership and raising funds are easy in this form of organization. No personal legal liability exists among the stockholders.
Company A is a corporation, because it issued common stock to investors for raising fund.
2.
Ascertain the effect of accounting equation, and calculate the ending balance of each account.
Explanation of Solution
Accounting equation:
Accounting equation is an accounting tool expressed in the form of equation, by creating a relationship between the resources or assets of a company, and claims on the resources by the creditors and the owners. Accounting equation is expressed as shown below:
The effect of accounting equation is as follows:
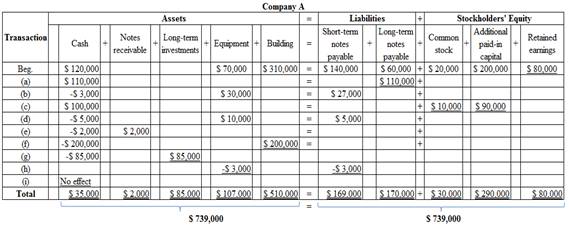
Figure (1)
3.
Discuss whether the transaction between the two stockholders (event- i) is included in the spreadsheet or not and also explains the reason.
Explanation of Solution
Separate entity assumption:
Business is considered as an individual entity, as per the separate entity assumption, hence it indicates the business and personal record keeping should be maintained separately.
The transaction between the two stockholders is not included in the table, because it is not a business transaction under separate entity assumption.
4.
Calculate the amount of given items based on the completed table.
Answer to Problem 2.2AP
(a) Total assets at the end of the month = $739,000 (1)
(b) Total liabilities = $339,000 (2)
(c) Total stockholder’s equity = $400,000 (3)
(d) Cash balance at the end of the year = $35,000
(e) Total current assets = $37,000
Explanation of Solution
Total assets:
The sum of all current and non-current assets that are owned in a company is called as total assets. The total assets are reported in the balance sheet.
Liabilities:
Liabilities are an obligation of the business to pay to the creditors in future for the goods and services purchased on account or any for other financial benefit received.
Stockholders’ equity
Stockholders’ equity refers to the rights of the stockholders on the assets of the company. It is increased by issuance of stock and retained earnings of the company and decreased by the payment of dividends and repurchase of treasury stock.
Working note:
Calculate the total assets value
Calculate the total liabilities:
Calculate the total stockholders’ equity:
5.
Calculate the current ratio of Company A and evaluate the ratio.
Explanation of Solution
Current Ratio:
A part of liquidity ratios, current ratio reflects the ability to oblige the short term debts of a company. It is calculated based on the current assets and current liabilities; a company has in an accounting period. A current ratio is a useful tool for analysis of financials of a company.
Calculate the current ratio of Company A as follows:
Here,
Current assets = $37,000 (4)
Current liabilities= $169,000 (short-term notes payable)
Therefore, the current ration of Company A is 0.22
In this case, Company A has more current assets than current liabilities. Therefore, Company A has better position to repay the current liabilities.
Working note:
Calculate the value of current assets
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Connect Access Card for Financial Accounting
- Journal entry for July 1 to record the purchase of Steve Young by Bramble Corporation: A B C D 1 01-07-2025 Cash $51,800 2 Accounts receivable $91,200 3 Inventory $125,700 4 Land $64,600 5 Buildings (net) $75,400 6 Equipment (net) $69,700 7 Trademarks $17,360 8 Goodwill $65,340 9 Accounts payable $202,500 10 Cash $256,600 11 Notes payable $102,000 12 (To record the purchase of Young Company) 13 01-07-2025 Investment in Young compan $358,600 14 Cash $256,600 15 Notes payable $102,000 16 (To record investment in Young Company) (a) prepare the december 31 entry for bramble corporation to record amortization of intangibles. the trademark has an estimated…arrow_forwardJournal entry for July 1 to record the purchase of Steve Young by Bramble Corporation: A B C D 1 01-07-2025 Cash $51,800 2 Accounts receivable $91,200 3 Inventory $125,700 4 Land $64,600 5 Buildings (net) $75,400 6 Equipment (net) $69,700 7 Trademarks $17,360 8 Goodwill $65,340 9 Accounts payable $202,500 10 Cash $256,600 11 Notes payable $102,000 12 (To record the purchase of Young Company) 13 01-07-2025 Investment in Young compan $358,600 14 Cash $256,600 15 Notes payable $102,000 16 (To record investment in Young Company) (a)arrow_forwardI am searching for the correct answer to this general accounting problem with proper accounting rules.arrow_forward
- Please explain the solution to this general accounting problem with accurate explanations.arrow_forwardI am searching for the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the right approach.arrow_forwardPlease provide the correct answer to this general accounting problem using accurate calculations.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





