
EBK PRINCIPLES OF GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEER
9th Edition
ISBN: 8220103611718
Author: SOBHAN
Publisher: CENGAGE L
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 2.12P
Repeat Problem 2.11 with the following data.
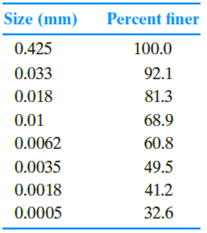
2.11 The grain-size characteristics of a soil are given in the following table.
a. Draw the grain-size distribution curve.
b. Determine the percentages of gravel, sand, silt, and clay according to the MIT system.
c. Repeat Part b using the USDA system.
d. Repeat Part b using the AASHTO system.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
steel design
steel design
SITUATION 1: A W250 x 131 is used as a column with an unbraced length of 8 m with respect to the x-x axis
and 4 m with respect to the y-y axis. Assume an A36 steel member, pin-connected at the top and fixed at the
bottom. Assume that the column is pin connected at mid-height. Use NSCP 2001 NSCP. Fy = 250 MPa.
Properties of W250 x 131:
A = 16,774 mm²
d=274 mm
bf=262 mm
tf=25 mm
tw = 16 mm
Ix=222.268 x 10 mm
ly = 74.505 x 10° mm*
Effective Length Factors:
Pinned at both ends, K = 1.0
Pinned at one end and fixed at the other, K = 0.8
1. What is the value of the slenderness ratio to be used for the column?
2. What is the nominal axial stress?
3. What is the design axial load?
1. 60.019
2. 206.543 MPa
3. 3118.091 kN
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK PRINCIPLES OF GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEER
Ch. 2 - For a gravel with D60 = 0.48 mm, D30 = 0.25 mm,...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.2PCh. 2 - Prob. 2.3PCh. 2 - The following are the results of a sieve analysis....Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 2.4 with the following data. 2.4...Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 2.4 with the following data. 2.4...Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 2.4 with the following data. 2.4...Ch. 2 - The following are the results of a sieve and...Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 2.8 using the following data. 2.8...Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 2.8 using the following data. 2.8...
Ch. 2 - The grain-size characteristics of a soil are given...Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 2.11 with the following data. 2.11...Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 2.11 with the following data. 2.11...Ch. 2 - A hydrometer test has the following result: Gs =...Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 2.14 with the following values: Gs...Ch. 2 - Three groups of students from the Geotechnical...Ch. 2 - Refer to Problem 2.C.1. Results of the sieve...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- SITUATION 2: An 8-meter simply supported beam is to be loaded, in addition to its self-weight, a triangular distributed load that linearly increases from zero at the left support to 20 kN/m (dead) + 35 kN/m (live) at the right support. It is braced laterally at the end supports and at midspan. The details for the beam cross-section are given below. Use the LRFD provisions of NSCP 2015. W 540 mm x 150 kg/m: Area, A 19,225 mm² Depth, D = 540 mm Clear Distance between Flanges, h = 455 mm Flange width, bf=310 mm Flange thickness, tf = 20 mm Web thickness, tw 12.5 mm Elastic Section Modulus, Sx = 3.72 x 106 mm³ Plastic Section Modulus, Zx = 4.14 x 10 mm³ Torsional Constant, J = 2.04 x 10% mm* Distance between flange centroids, ho = 520 mm Radius of gyration along y-axis, ry = 72 mm Cb = 1.196 Effective radius of gyration, rts = 85 mm Yield Strength of Steel, Fy = 345 MPa Modulus of Elasticity, E=200 GPa 1. What is the ultimate moment capacity of the beam, in kN-m? 1. 1285.470 kN-marrow_forwardSITUATION 4: A steel column W 300 x 203 kg/m is subjected to an axial load of 2670 kN. Unbraced length of column is 3m, and assume that the column is pinned at both ends, side sway prevented. Show your complete solution and box only the final answer. Properties of Column: Area, A = 25,740 mm² Depth, d=340 mm Flange thickness, tf = 32 mm Flange Width, bf=315 mm Web thickness, tw = 20 mm Ix = 5.16 x 10 mm² ly = 1.65 x 10° mm* Fy = 345.6 MPa 1. Determine the design strength (kN) of the column. 2. Determine the allowable strength (kN) of the column. 3. What is the value of the slenderness ratio to be used for the column? 1. 7223.401 kN 2. 4805.988 kN 3. 37.470arrow_forwardGive me a steel member design problems under combined axial and bending forces, using interaction equations, with complete solution and final answerarrow_forward
- Give me compression member problems in steel design, including calculation of slenderness ratio and critical stress using Euler formula, with complete solution and answer.arrow_forwardGive me flexural design problems of steel beams, including lateral-torsional buckling, and solve for nominal moment capacity, with step-by-step solution and answer.arrow_forwardGive me a sample tension member problems with staggered bolt holes where I calculate net area using the staggered hole formula, with complete solution and answer.arrow_forward
- Give me a block shear failure problem involving a bolted steel plate, and solve for nominal strength, with detailed solution and answer.arrow_forwardGive me a sample problems computing effective net area of a tension member with staggered holes, with full solution and answer. plsssarrow_forwardCan u pls give me sample problems on steel tension member design involving gross and net area, with complete solution and final answer. Note: I just needed to reviewarrow_forward
- (a) Determine the Nataf model for the joint PDF fxx, (xx) of the basic (physical) random variables X₁ and X, with marginal PDF's fx(x)=e, 0≤x (Exponential distribution) fx₁ (x2)=x2e-0.5x, 0≤x (Rayleigh distribution) and correlation coefficient Pxx=0.50 Note: Use Table 6 of paper by Liu and Der Kiureghian, 1986. (b) Generate a 3D surface plot and contour plot of the joint PDF fxx, (x,x) using Matlab or any other software of your choice. (c) What is the standard deviation of X2? (d) Construct a transformation from the physical X space (defined by random variables X, and X,) to the standard normal U space (defined by the statistically independent standard normal random variables (U, and U₂), i.e., U=T(X). Also describe the inverse transform X=T(U) and the Jacobian matrices J = ди θα and Ju Ox ди (e) According to the inverse transformation X = T¹ (U) and using Matlab, generate 1,000 samples from the Nataf joint PDF fxx, (x1,x2) derived in part (a). Start by generating samples of U using a…arrow_forwardBased on the results obtained, comment on the relative importance of the body and the tails of thedistributions of R and S on the probability of failure with increasing central safety factor CSF .arrow_forward1. The beam is supported by a roller constraint at B, which allows vertical displacement but resists axial load and moment. If the bar is subjected to the loading shown and constant El (L = 12 ft, E = 3100 ksi, I = 1728 in (rectangular section 12"x12"), w = 1 klf). Caution: pay attention to unit conversion between ft and in) x W B a. Sketch the deflected shape. L b. Determine the equations of the slope and the elastic curve using the coordinate x. First, solve this problem parametrically, and then substitute the numerical values for L, E, I, w at the end. There will be a significant penalty for solutions that do not calculate the slope and deflection as parametric functions. c. Specify the slope (in radians) at point A (parametrically and numerically). d. Specify the vertical displacement at point B (parametrically and numerically).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning
Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305970939
Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305635180
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305086272
Author:William P. Spence, Eva Kultermann
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305081550
Author:Braja M. Das
Publisher:Cengage Learning
How Are Highways Designed?; Author: Practical Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9XIjqdk69O4;License: Standard Youtube License