
Concept explainers
Vocabulary Reinforcement
Complete each statement with the correct term from the column on the right. Some of the choices may be used more than once, and some may not be used at all.
* x-intercept
* y-intercept
* at least one
* exactly one
* slope-intercept
* point-slope
* slope
* function
* relation
* parallel
* perpendicular
* vertical
* horizontal
* domain
* range
The graph of
To fill: The blank space provided in the statement, “The graph of
Answer to Problem 1VR
Solution:
The graph of
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The provided options are,
1.
2.
3. at least one
4. exactly one
5. slope-intercept
6. point slope
7. slope
8. function
9. relation
10. parallel
11. perpendicular
12. vertical
13. horizontal
14. domain
15. range
Here, the equation of line is
Now, the equation of line
Now, while calculating the slope of the equation of line
Thus, the slope is not defined and the graph will be a vertical line passing through
For example:
Consider an equation of line,
Now, the graph of line
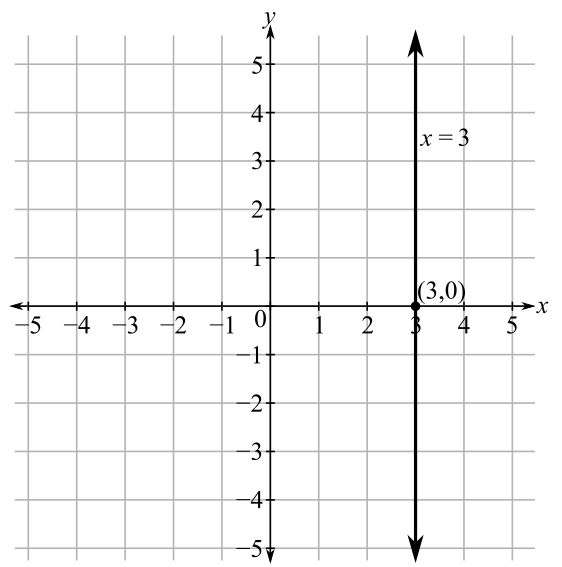
From the graph, it is clear that the line of equation
Hence, the graph of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA
- A person is tossing a fair, two-sided coin three times and recording the results (either a Heads, H, or a Tails, T). Let E be the event that exactly two heads are tossed. Which of the following sets represent the event E? Group of answer choices {HHT, HTH, THH} {HHT, THH} {HHH, HHT, HTH, THH, TTT, TTH, THT, HTT} {HH}arrow_forwardTake Quiz 54m Exit Let the universal set be whole numbers 1 through 20 inclusive. That is, U = {1, 2, 3, 4, . . ., 19, 20}. Let A, B, and C be subsets of U. Let A be the set of all prime numbers: A = {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19} Let B be the set of all odd numbers: B = {1,3,5,7, • • , 17, 19} Let C be the set of all square numbers: C = {1,4,9,16} ☐ Question 2 3 pts Which of the following statement(s) is true? Select all that apply. (1) АСВ (2) A and C are disjoint (mutually exclusive) sets. (3) |B| = n(B) = 10 (4) All of the elements in AC are even numbers. ☐ Statement 1 is true. Statement 2 is true. Statement 3 is true. Statement 4 is true.arrow_forward☐ Question 1 2 pts Let G be the set that represents all whole numbers between 5 and 12 exclusive. Which of the following is set G in standard set notation. (Roster Method)? O G = [5, 12] G = {5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12} O G = (5, 12) OG = {6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11}arrow_forward
- Solve thisarrow_forwardint/PlayerHomework.aspx?homeworkId=689099898&questionId=1&flushed=false&cid=8120746¢erw BP Physical Geograph... HW Score: 0%, 0 of 13 points ○ Points: 0 of 1 Determine if the values of the variables listed are solutions of the system of equations. 2x - y = 4 3x+5y= - 6 x=1, y = 2; (1,-2) Is (1, 2) a solution of the system of equations? L No Yes iew an example Get more help - Aarrow_forward12:01 PM Tue May 13 < AA ✓ Educatic S s3.amazona... A Assess Your... 目 accelerate-iu15-bssd.vschool.com S s3.amazona... Trigonometric Identities Module Exam Dashboard ... Dashboard ... Algebra 2 Pa... Algebra 2 Part 4 [Honors] (Acc. Ed.) (Zimmerman) 24-25 / Module 11: Trigonometric Identities i + 38% ✰ Start Page Alexis Forsythe All changes saved 10. A sound wave's amplitude can be modeled by the function y = −7 sin ((x-1) + 4). Within the interval 0 < x < 12, when does the function have an amplitude of 4? (Select all that apply.) 9.522 seconds 4.199 seconds 0.522 seconds 1.199 seconds Previous 10 of 20 Nextarrow_forward
- Jamal wants to save $48,000 for a down payment on a home. How much will he need to invest in an account with 11.8% APR, compounding daily, in order to reach his goal in 10 years? Round to the nearest dollar.arrow_forwardr nt Use the compound interest formula, A (t) = P(1 + 1)". An account is opened with an intial deposit of $7,500 and earns 3.8% interest compounded semi- annually. Round all answers to the nearest dollar. a. What will the account be worth in 10 years? $ b. What if the interest were compounding monthly? $ c. What if the interest were compounded daily (assume 365 days in a year)? $arrow_forwardKyoko has $10,000 that she wants to invest. Her bank has several accounts to choose from. Her goal is to have $15,000 by the time she finishes graduate school in 7 years. To the nearest hundredth of a percent, what should her minimum annual interest rate be in order to reach her goal assuming they compound daily? (Hint: solve the compound interest formula for the intrerest rate. Also, assume there are 365 days in a year) %arrow_forward
- 3:56 wust.instructure.com Page 0 Chapter 5 Test Form A of 2 - ZOOM + | Find any real numbers for which each expression is undefined. 2x 4 1. x Name: Date: 1. 3.x-5 2. 2. x²+x-12 4x-24 3. Evaluate when x=-3. 3. x Simplify each rational expression. x²-3x 4. 2x-6 5. x²+3x-18 x²-9 6. Write an equivalent rational expression with the given denominator. 2x-3 x²+2x+1(x+1)(x+2) Perform the indicated operation and simplify if possible. x²-16 x-3 7. 3x-9 x²+2x-8 x²+9x+20 5x+25 8. 4.x 2x² 9. x-5 x-5 3 5 10. 4x-3 8x-6 2 3 11. x-4 x+4 x 12. x-2x-8 x²-4 ← -> Copyright ©2020 Pearson Education, Inc. + 5 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. T-97arrow_forwardProblem #5 Suppose you flip a two sided fair coin ("heads" or "tails") 8 total times. a). How many ways result in 6 tails and 2 heads? b). How many ways result in 2 tails and 6 heads? c). Compare your answers to part (a) and (b) and explain in a few sentences why the comparison makes sense.arrow_forwardA local company has a 6 person management team and 20 employees. The company needs to select 3 people from the management team and 7 employees to attend a regional meeting. How many different possibilities are there for the group that can be sent to the regional meeting?arrow_forward
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell Intermediate AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781285195728Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781285195728Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9780998625713Author:Lynn Marecek, MaryAnne Anthony-SmithPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
Elementary AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9780998625713Author:Lynn Marecek, MaryAnne Anthony-SmithPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University





