
- Total hotel stays produced if fishermen employed by the hotel
- Total metric tons of fish produced if hotel employees become fishermen
- A
production possibility frontier for Bermuda
Opportunity Cost is the loss of benefit incurred by a person by choosing an alternative course of action.
(a) Total hotel stays produced if fishermen employed by the hotel, (b) total metric tons of fish produced if hotel employees become fishermen and (c) a production possibility frontier for Bermuda.
Explanation of Solution
(a) A total number of hotel stays produced if fishermen employed by the hotel.
- The opportunity cost of one metric ton fish is 2,000 hotel stays.
- Production of 306 fishermen is 387 metric ton fish.
- Thus, the total number of hotel stays produced by 306 fishermen will be 774,000.
- The total number of hotel stays produced by Bermuda will be 1,328,400.
Working Notes:
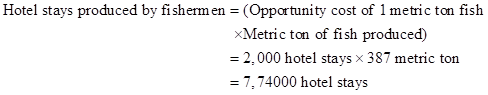
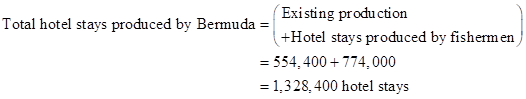
Conclusion:
Thus, the total hotel stays are 1,328,400.
(b) A total metric ton of fish produced by Bermuda if hotel employees become fishermen.
- The opportunity cost of one metric ton fish is 2,000 hotel stays.
- Total hotel stays produced by the 2,719 employees of the hotel are 554,400.
- Thus, the production of fish by hotel employees will be 277.2 metric ton.
- The total fish produced by Bermuda will be 664.2 metric ton.
Working Notes:
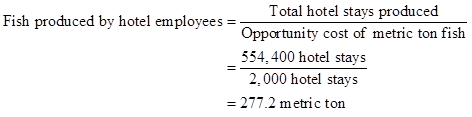
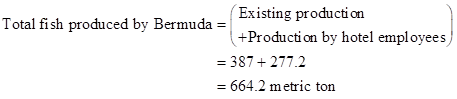
Conclusion:
Thus, the total fish produced are 664.2 metric ton.
(c) Draw a production possibility frontier for Bermuda.
PPF for Bermuda for the year 2009
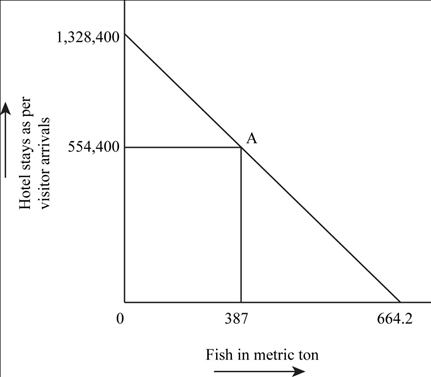
- The PPF is a straight line for Bermuda because the opportunity cost for two industries is constant.
- If all the resources are concentrated on the tourism industry, then the total hotel stays shall be 1,328,400 as shown on the vertical axis.
- If all the resources are concentrated on the fishing industry, then the total fish production shall be 664.2 metric ton as shown on the horizontal axis.
- The current production of Bermuda is shown by point A that shows the production of 554,400 hotel stays and 387 metric ton fish.
Conclusion:
Thus, the PPF for Bermuda is a straight line due to constant opportunity cost.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Essentials of Economics
- Critically analyse the five (5) characteristics of Ubuntu and provide examples of how they apply to the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forwardCritically analyse the five (5) characteristics of Ubuntu and provide examples of how they apply to the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forwardOutline the nine (9) consumer rights as specified in the Consumer Rights Act in South Africa.arrow_forward
- In what ways could you show the attractiveness of Philippines in the form of videos/campaigns to foreign investors? Cite 10 examples.arrow_forwardExplain the following terms and provide an example for each term: • Corruption • Fraud • Briberyarrow_forwardIn what ways could you show the attractiveness of a country in the form of videos/campaigns?arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





