
Plate tectonics works today in the same way as in the past. Can you project the future positions of the continents by looking at a map of their present positions and the positions of the mid-ocean ridges (see Fig. 2.5)? Which oceans are growing and which are shrinking? Where will new oceans form?
FIGURE 2.5 The major features of the sea floor. Compare this map with Figure 2.6.
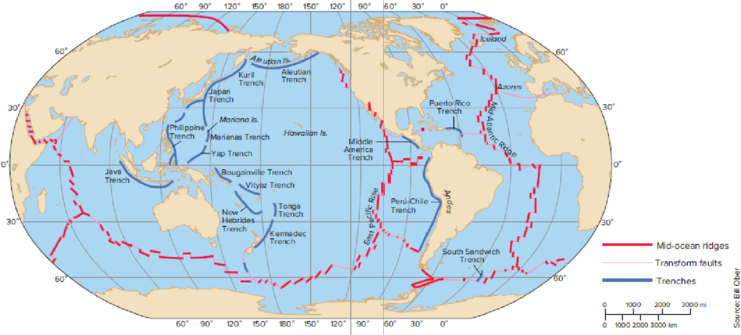
To predict: The future positions of the continents by looking at the map of their present positions and the positions of the mid-ocean ridges.
Introduction: The continents in the earth’s crust or plates that float on the mantle portion of the Earth are called plate tectonics. The movement of plate causes formation of the mountain and continents over a millions of years that result in the geographical changes of the Earth.
Explanation of Solution
Plate tectonics are the lithospheric plates composed of continental and oceanic lithosphere. Refer to Fig. 2.5, “The major features of the sea floor”, in the text book. The future positions of the continents are given in Table 1.
Tabular representation: The following table shows the future positions of the continents.
Table 1: The future positions of the continents
| Continents | Future positions |
| North and South America | Farther west toward the Pacific Ocean |
| Europe and Asia | Farther southeast |
| Australia | Farther northeast |
| Africa | Farther east |
To determine: The oceans that are growing and shrinking.
Introduction: The continents in the earth’s crust or plates that float on the mantle portion of the Earth are called plate tectonics. The movement of plate causes formation of the mountain and continents over a millions of years, which result in the geographical changes of the Earth.
Explanation of Solution
Plate tectonics are the lithospheric plates composed of continental and oceanic lithosphere. Refer to Fig. 2.5, “The major features of the sea floor”, in the text book. The shrinking ocean is Pacific Ocean (expected to be narrower) and the growing ocean is Atlantic Ocean (expected to be wider).
To determine: Where will the new oceans form.
Introduction: The continents in the earth’s crust or plates that float on the mantle portion of the Earth are called Plate tectonics. The movement of plate causes formation of the mountain and continents over a millions of years, which result in the geographical changes of the Earth.
Explanation of Solution
Refer to Fig. 2.5, “The major features of the sea floor”, in the text book. The edges of several plates are formed by the mid-ocean ridges. At this point, the lithospheric plates move apart to form the new oceanic lithosphere (new sea floor). If the plate contains a block of continental crust, the plate moves away from the ridge, and the continent is carried along with the plate.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Connect with LearnSmart for Castro: Marine Biology
- Ch.21 What causes patients infected with the yellow fever virus to turn yellow (jaundice)? A. low blood pressure and anemia B. excess leukocytes C. alteration of skin pigments D. liver damage in final stage of disease — What is the advantage for malarial parasites to grow and replicate in red blood cells? A. able to spread quickly B. able to avoid immune detection C. low oxygen environment for growth D. cooler area of the body for growth — Which microbe does not live part of its lifecycle outside humans? A. Toxoplasma gondii B. Cytomegalovirus C. Francisella tularensis D. Plasmodium falciparum — explain your answer thoroughlyarrow_forwardCh.22 Streptococcus pneumoniae has a capsule to protect it from killing by alveolar macrophages, which kill bacteria by… A. cytokines B. antibodies C. complement D. phagocytosis — What fact about the influenza virus allows the dramatic antigenic shift that generates novel strains? A. very large size B. enveloped C. segmented genome D. over 100 genes — explain your answer thoroughlyarrow_forwardWhat is this?arrow_forward
- Molecular Biology A-C components of the question are corresponding to attached image labeled 1. D component of the question is corresponding to attached image labeled 2. For a eukaryotic mRNA, the sequences is as follows where AUGrepresents the start codon, the yellow is the Kozak sequence and (XXX) just represents any codonfor an amino acid (no stop codons here). G-cap and polyA tail are not shown A. How long is the peptide produced?B. What is the function (a sentence) of the UAA highlighted in blue?C. If the sequence highlighted in blue were changed from UAA to UAG, how would that affecttranslation? D. (1) The sequence highlighted in yellow above is moved to a new position indicated below. Howwould that affect translation? (2) How long would be the protein produced from this new mRNA? Thank youarrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question Explain why the cell doesn’t need 61 tRNAs (one for each codon). Please help. Thank youarrow_forwardMolecular Biology You discover a disease causing mutation (indicated by the arrow) that alters splicing of its mRNA. This mutation (a base substitution in the splicing sequence) eliminates a 3’ splice site resulting in the inclusion of the second intron (I2) in the final mRNA. We are going to pretend that this intron is short having only 15 nucleotides (most introns are much longer so this is just to make things simple) with the following sequence shown below in bold. The ( ) indicate the reading frames in the exons; the included intron 2 sequences are in bold. A. Would you expected this change to be harmful? ExplainB. If you were to do gene therapy to fix this problem, briefly explain what type of gene therapy youwould use to correct this. Please help. Thank youarrow_forward
- Molecular Biology Question Please help. Thank you Explain what is meant by the term “defective virus.” Explain how a defective virus is able to replicate.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Explain why changing the codon GGG to GGA should not be harmful. Please help . Thank youarrow_forwardStage Percent Time in Hours Interphase .60 14.4 Prophase .20 4.8 Metaphase .10 2.4 Anaphase .06 1.44 Telophase .03 .72 Cytukinesis .01 .24 Can you summarize the results in the chart and explain which phases are faster and why the slower ones are slow?arrow_forward
- Can you circle a cell in the different stages of mitosis? 1.prophase 2.metaphase 3.anaphase 4.telophase 5.cytokinesisarrow_forwardWhich microbe does not live part of its lifecycle outside humans? A. Toxoplasma gondii B. Cytomegalovirus C. Francisella tularensis D. Plasmodium falciparum explain your answer thoroughly.arrow_forwardSelect all of the following that the ablation (knockout) or ectopoic expression (gain of function) of Hox can contribute to. Another set of wings in the fruit fly, duplication of fingernails, ectopic ears in mice, excess feathers in duck/quail chimeras, and homeosis of segment 2 to jaw in Hox2a mutantsarrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning





