
Fill in the blanks in this concept map to help you tie together the key concepts concerning elements, atoms, and molecules.
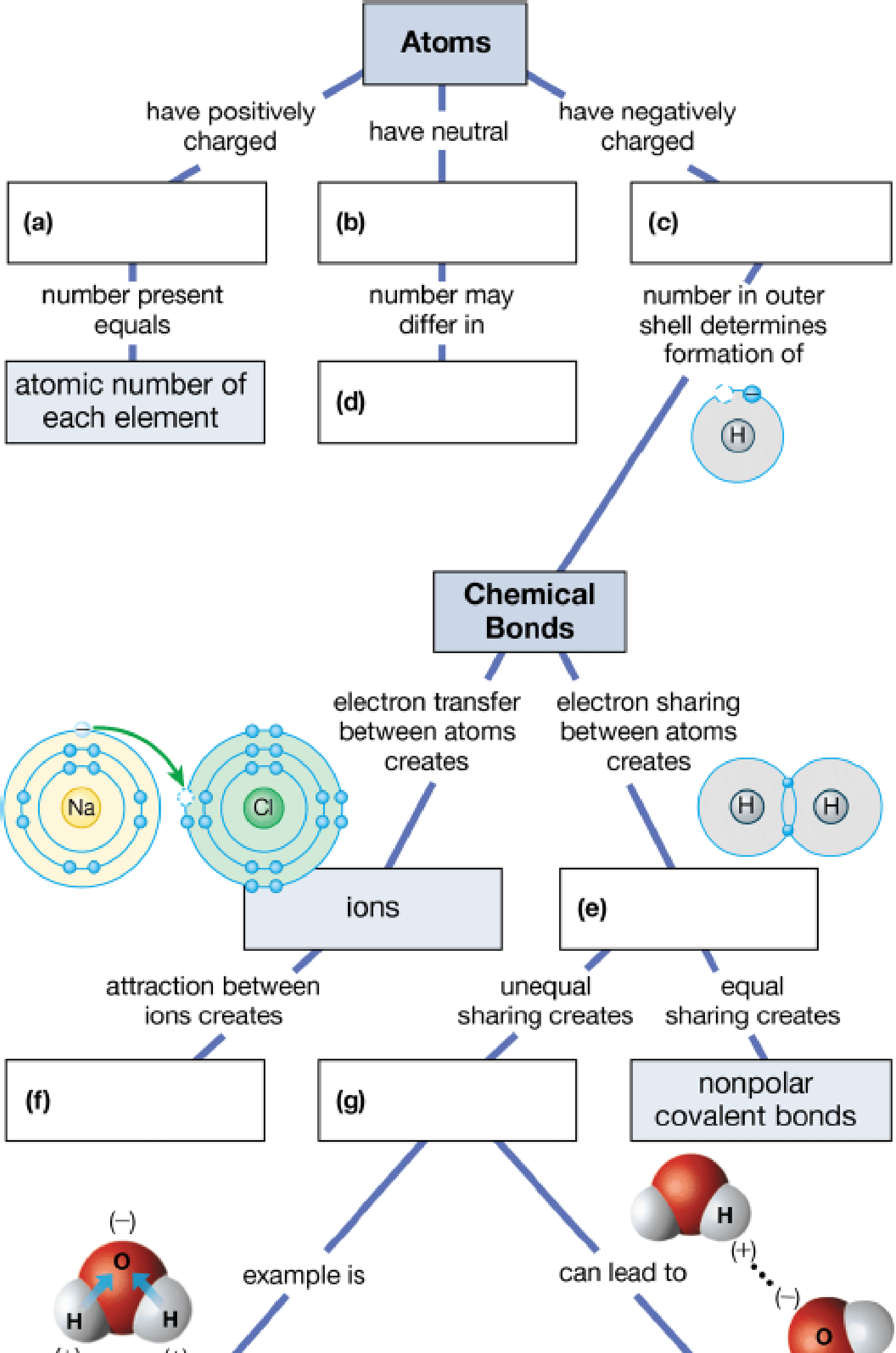

To complete: The concept map to help tie together the key concepts concerned with elements, atoms, and molecules.
Introduction:
A substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by ordinary chemical process is known as element. Every element has the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element. This smallest unit is called atom. An atom consists of electrons (e), protons (p) and neutrons (n). Different atoms have specific numbers of electrons, protons and neutrons. Nucleus of an atom contains protons and neutrons that constitute the mass of an atom. Electrons revolve around the nucleus in their orbit. The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of its atoms.
Answer to Problem 1CC
Pictorial representation: The Fig. 1 shows a concept map for hierarchy from atoms to bonding between molecules.
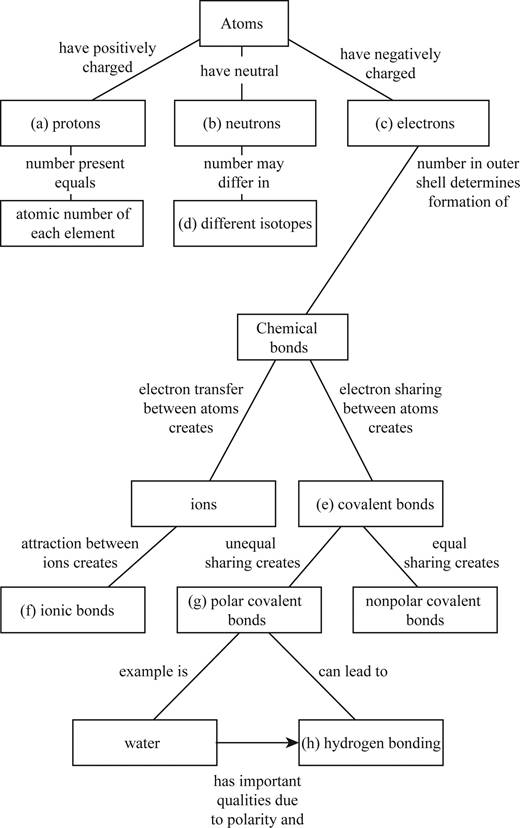
Fig.1:Concepts map of elements, atoms and molecules.
Explanation of Solution
(a)
Correct answer: Protons
Explanation: Proton is present in the nucleus of the atom and has positive charge. Hence the correct answer is proton.
(b)
Correct answer: Neutrons
Explanation: Neutron is present in the nucleus of the atom and is neutral due to no charge.
Hence, the correct answer is neutrons.
(c)
Correct answer: Electrons
Explanation: Electron revolves around the nucleus and has negative charge.
Hence, the correct answer is electrons.
(d)
Correct answer: Different isotopes
Explanation:
An isotope of an atom differs from neutron numbers and therefore by mass. Hence, the correct answer is different isotopes.
(e)
Correct answer: Covalent bond
Explanation: Electrons revolve around the nucleus in different electronic shells. The electrons present in the outermost shell are called valence electrons. The valence electron takes part in chemical bond formation by electron sharing known as covalent bond.
Hence, the correct answer is covalent bond.
(f)
Correct answer: Ionic bonds
Explanation: The transfer of electrons between two atoms creates ions and its attraction creates ionic bond. Hence, the correct answer is ionic bonds.
(g)
Correct answer: Polar covalent bonds
Explanation: Electron sharing between atoms creates covalent bond. The more electronegative atom attracts the bonded electrons towards itself. This results in unequal sharing of electrons and formation of polar covalent bond.
Hence, the correct answer is polar covalent bonds.
(h)
Correct answer: Hydrogen bonding
Explanation: Unequal sharing of electrons of covalent bond results in polar covalent bond. For example: Water molecule (H2O) consists of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Oxygen atom shares one electron to each of the hydrogen atom and forms two covalent bonds. The oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen. It attracts the bonded electron towards itself. This induces partial positive charge on hydrogen atoms and partial negative charge on oxygen atom. So, water molecule attains polarity. Oxygen atom of water molecule form a weak bond called hydrogen bond with hydrogen atom of another water molecule. This makes water molecule to have unique qualities.
Hence, the correct answer is hydrogen bonding.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
CAMPBELL BIO: CONCEPTS&CONNECTIONS (LL)
- Noggin mutation: The mouse, one of the phenotypic consequences of Noggin mutationis mispatterning of the spinal cord, in the posterior region of the mouse embryo, suchthat in the hindlimb region the more ventral fates are lost, and the dorsal Pax3 domain isexpanded. (this experiment is not in the lectures).a. Hypothesis for why: What would be your hypothesis for why the ventral fatesare lost and dorsal fates expanded? Include in your answer the words notochord,BMP, SHH and either (or both of) surface ectoderm or lateral plate mesodermarrow_forwardNot part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forwardNot part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forward
- please helparrow_forwardWhat does the heavy dark line along collecting duct tell us about water reabsorption in this individual at this time? What does the heavy dark line along collecting duct tell us about ADH secretion in this individual at this time?arrow_forwardBiology grade 10 study guidearrow_forward

 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning





