
Variable Cost: The variable cost is a cost that changes when the volume of production changes, in the same direction and in the same proportion.
Fixed Cost: Fixed cost is a cost that remains constant irrespective of the changes in the production volume.
Income Statement: Income statement is a financial statement that shows the net income or loss for a particular period. It is the summary of expenses and income of a particular period.
Traditional Income Statement: In the traditional income statement, costs are organized or reported by functions such as production, administration, selling and marketing. Fixed and variable costs are merged within the respective function cost.
Contribution approach Income Statement: Income statement under contribution approach is prepared based on the variable and fixed costs. First, the variable expenses are deducted to obtain the contribution margin, and then the fixed expenses are deducted to obtain the net operating income.
- An income statement using the traditional format.
- An income statement using the contribution format.
- Comments on why it is misleading to show the fixed costs on a per unit basis in the income statement prepared in (2) above.
Answer to Problem 19P
Solution:
- Income Statement using the traditional format for the data given is prepared.
- Income Statement using the contribution format for the data given is prepared.
- Comments given on why it is misleading to show the fixed costs on a per unit basis in the income statement under the contribution format.
Explanation of Solution
-
Income Statement using the traditional format.
Marwick's Pianos, Inc Traditional Income Statement For the month ended August 31 No of pianos sold 40 Sales $125,000 Less : Cost of goods sold $98,000 Gross Profit $27,000 Less: Selling expenses Advertising $700 Salaries and commissions $10,950 Delivery of Pianos to customers $1,200 Utilities $350 Depreciation of sales facilities$800 $14,000 Less: Administrative expenses Executive salaries $2,500 Insurance $400 Clerical $1,800 Depreciation of office equipment $300 $5,000 Net Income $8,000 - Income statement using the contribution format.
- Fixed costs remain constant irrespective of the change in the unit of pianos sold. As the sales level increases, for example, the fixed costs will decrease on a per unit basis or vice versa. Showing fixed costs on a per unit basis on the income statement might be misleading as it may seem that the fixed costs behave in the same way as the variable costs. That is, anyone using the data might be misled into thinking that per unit fixed cost would be the same regardless of how many pianos were sold during the month. For this reason, fixed costs are generally are shown only in totals on a contribution format income statement.
| Marwick's Pianos, Inc | ||
| Contribution format Income Statement | ||
| For the month ended August 31 | ||
| Total | Per Piano | |
| Sales (A) | $125,000 | $3,125 |
| Variable expenses | ||
| Cost of goods sold | $98,000 | $2,450 |
| Salaries and commissions | $10,000 | $250 |
| Delivery of Pianos to customers | $1,200 | $30 |
| Clerical | $800 | $20 |
| Total variable expenses (B) | $110,000 | $2,525 |
| Contribution margin (A-B) (C) | $15,000 | |
| Fixed expenses | ||
| Advertising | $700 | |
| Salaries and commissions | $950 | |
| Utilities | $350 | |
| Depreciation of sales facilities | $800 | |
| Executive salaries | $2,500 | |
| Insurance | $400 | |
| Clerical | $1,000 | |
| Depreciation of office equipment | $300 | |
| Total fixed expenses (D) | $7,000 | |
| Net Operating Income (C-D) | $8,000 | |
Calculation: Calculations and working are explained using the traditional income statement.
| Marwick's Pianos, Inc | Calculations | |
| Sales | $125,000 | 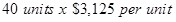 |
| Cost of goods sold | $98,000 | 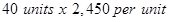 |
| Salaries and commissions | $10,950 | 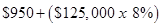 |
| Delivery of Pianos to customers | $1,200 | 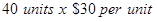 |
| Clerical | $1,800 | 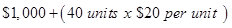 |
Thus, for the for Marwick’s Pianos, Inc. the income statement under both traditional and contribution formats are prepared and the calculations are explained.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
ACC 202 Principles of Accounting 2 Ball State University
- Financial accounting problemarrow_forwardA firm has a market value equal to ns book value Currently, the firm has excess cash of s800, other assets of $5.200, and equity of $6.000 The firm has 600 shares of stock outstanding and a net income of $500. The firm has decided to spend half of its excess cash on a share repurchase program How many shares of stock we be outstanding after the stock repurchase is completed?arrow_forwardHaven Manufacturing applies manufacturing overhead to jobs based on machine hours used. Overhead costs are expected to total $350,000 for the year, and machine usage is estimated at 140,000 hours. For the year, $365,000 of overhead costs are incurred, and 150,000 hours are used. Compute the manufacturing overhead rate for the year.arrow_forward
- Please explain this financial accounting problem with accurate financial standards.arrow_forwardHindenburger, Inc., began operations on January 1. It made 5,000 burgers and sold 4,000 of them. Hindenburger incurred the following costs: Raw materials $1,000 Wagos of production workers 7,000 Rent for corporate headquarters 5,000 Depreciation on manufacturing equipment 2,000 Commissions paid to sales people 4,000 Calculate the total product cost for the year ended December 31.arrow_forwardHorizon Innovations incurred $120,000 in research and development costs and $60,000 in legal fees to acquire a patent. The patent has a legal life of 20 years and a useful life of 8 years. What amount should Horizon record as Patent Amortization Expense in the first year? a. $7,500 b. $15.000 c. $22,500 d. $0arrow_forward
- Solomon Manufacturing Company began operations on January 1. During the year, it started and completed 1,790 units of product. The financial statements are prepared in accordance with GAAP. The company incurred the following costs: 1 Raw materials purchased and used 2 Wages of production workers $ 3,060 $ 3,590 3 Salaries of administrative and sales personnel $ 1,915 $ 6,417 $1,760 4 Depreciation on manufacturing equipment 5 Depreciation on administrative equipment Solomon sold 1,030 units of product. Required: a. Determine the total product cost for the year. b. Determine the total cost of the ending inventory. c. Determine the total cost of goods sold.arrow_forwardA company sells a machinery asset which originally costarrow_forwardSolve this issuearrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





